将字符串转换为 Int 的Java程序
在Java中,在对字符串进行操作时,有时我们需要将表示为字符串的数字转换为整数类型。我们通常这样做是因为我们可以对字符串进行广泛灵活的操作。 Java中一般用于将String转换为Integer的方法是String类的parseInt ()。
parseInt() 方法的变体
此方法有两种变体:
- parseInt(String s):此函数将字符串参数解析为有符号十进制整数。
- parseInt(String s, int radix):此函数将字符串参数解析为第二个参数指定的基数中的有符号整数。
句法:
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatExceptionpublic static int parseInt(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException参数:
- 需要转换为整数的字符串。它还可以将第一个字符作为减号'-'('\u002D')或加号'+'('\u002B')来表示数字的符号。
- 在解析字符串时使用基数。
Note: This parameter is only specific to the second variant of the method.
返回类型:两种方法都将字符串转换为其等效的整数。唯一的区别是参数基数。第一种方法可以被认为与基数 = 10(十进制)的第二种方法等效。
Note: If your String has leading zeroes, the parseInt() method will ignore them.
抛出异常:如果出现以下任何一种情况,此方法将抛出 NumberFormatException。
记住与这两种变体相关的某些关键点:
- 字符串为空或长度为零
- 字符串表示的值不是int类型的值
- 专门针对函数的 parseInt(String s, int radix) 变体:
- 第二个参数 radix 小于字符.MIN_RADIX 或大于字符 .MAX_RADIX
- 字符串的任何字符都不是指定基数的数字,除非第一个字符可以是减号'-'('\u002D')或加号'+'('\u002B'),前提是字符串是长于长度 1
让我们使用一个随机代码片段来更好地理解这些插图。
String str=”0111”;
int t=Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(t); 输出:
111对于上面的代码,片段输出是 111。因此,在前导零很重要的情况下(在二进制表示中)避免使用 parseInt() 方法。
插图:
parseInt("20") returns 20
parseInt("+20") returns 20
parseInt("-20") returns -20parseInt("20", 16) returns 16, (2)*16^1 + (0)*16^0 = 32
parseInt("2147483648", 10) throws a NumberFormatExceptionparseInt("99", 8) throws a NumberFormatException
as 9 is not an accepted digit of octal number systemparseInt("geeks", 28) throws a NumberFormatExceptionparseInt("geeks", 29) returns 11670324,
Number system with base 29 can have digits 0-9
followed by characters a,b,c... upto sparseInt("geeksforgeeks", 29) throws a NumberFormatException as the
result is not an integer.如何使用 parseInt() 方法?
让我们直接举一个例子,以便使用 parseint() 方法的工作并实现上述内容,如下所示:
示例 1:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate working parseInt()
// Where No NumberFormatException is Thrown
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Custom wide-varied inputs to illustrate
// usage of valueOf() method
int decimalExample = Integer.parseInt("20");
int signedPositiveExample = Integer.parseInt("+20");
int signedNegativeExample = Integer.parseInt("-20");
int radixExample = Integer.parseInt("20", 16);
int stringExample = Integer.parseInt("geeks", 29);
// Print commands on console
System.out.println(decimalExample);
System.out.println(signedPositiveExample);
System.out.println(signedNegativeExample);
System.out.println(radixExample);
System.out.println(stringExample);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of parseInt() Method
// Where NumberFormatException is Thrown
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Custom wide-varied inputs to illustrate
// usage of valueOf() method
int decimalExample = Integer.parseInt("20");
int signedPositiveExample = Integer.parseInt("+20");
int signedNegativeExample = Integer.parseInt("-20");
int radixExample = Integer.parseInt("20", 16);
int stringExample = Integer.parseInt("geeks", 29);
// It will raise NumberFormatException
String invalidArguments = "";
int emptyString
= Integer.parseInt(invalidArguments);
int outOfRangeOfInteger
= Integer.parseInt("geeksforgeeks", 29);
int domainOfNumberSystem
= Integer.parseInt("geeks", 28);
// Print commands on console
System.out.println(decimalExample);
System.out.println(signedPositiveExample);
System.out.println(signedNegativeExample);
System.out.println(radixExample);
System.out.println(stringExample);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of valueOf() Method
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Custom wide-varied inputs to illustrate
// usage of valueOf() method
int decimalExample = Integer.valueOf("20");
int signedPositiveExample = Integer.valueOf("+20");
int signedNegativeExample = Integer.valueOf("-20");
int radixExample = Integer.valueOf("20", 16);
int stringExample = Integer.valueOf("geeks", 29);
// Print statements
System.out.println(decimalExample);
System.out.println(signedPositiveExample);
System.out.println(signedNegativeExample);
System.out.println(radixExample);
System.out.println(stringExample);
}
}输出
20
20
-20
32
11670324示例 2:
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of parseInt() Method
// Where NumberFormatException is Thrown
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Custom wide-varied inputs to illustrate
// usage of valueOf() method
int decimalExample = Integer.parseInt("20");
int signedPositiveExample = Integer.parseInt("+20");
int signedNegativeExample = Integer.parseInt("-20");
int radixExample = Integer.parseInt("20", 16);
int stringExample = Integer.parseInt("geeks", 29);
// It will raise NumberFormatException
String invalidArguments = "";
int emptyString
= Integer.parseInt(invalidArguments);
int outOfRangeOfInteger
= Integer.parseInt("geeksforgeeks", 29);
int domainOfNumberSystem
= Integer.parseInt("geeks", 28);
// Print commands on console
System.out.println(decimalExample);
System.out.println(signedPositiveExample);
System.out.println(signedNegativeExample);
System.out.println(radixExample);
System.out.println(stringExample);
}
}
输出:
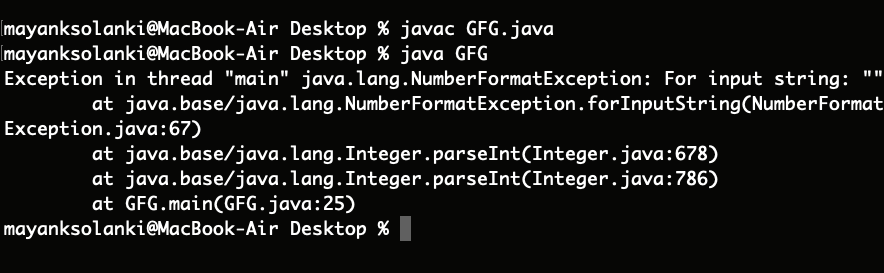
同样,我们可以将字符串转换为任何其他原始数据类型:
- parseLong():将字符串解析为 Long
- parseDouble():将字符串解析为 Double
如果我们想在不使用 parseInt()的情况下将字符串转换为整数,我们可以使用valueOf()方法。它还有两个类似于 parseInt() 的变体 - parseInt() 和 valueOf() 的区别: parseInt() 解析字符串并返回原始整数类型。但是, valueOf() 返回一个 Integer 对象。
Note: valueOf() uses parseInt() internally to convert to integer.
示例 3:
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of valueOf() Method
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Custom wide-varied inputs to illustrate
// usage of valueOf() method
int decimalExample = Integer.valueOf("20");
int signedPositiveExample = Integer.valueOf("+20");
int signedNegativeExample = Integer.valueOf("-20");
int radixExample = Integer.valueOf("20", 16);
int stringExample = Integer.valueOf("geeks", 29);
// Print statements
System.out.println(decimalExample);
System.out.println(signedPositiveExample);
System.out.println(signedNegativeExample);
System.out.println(radixExample);
System.out.println(stringExample);
}
}
输出
20
20
-20
32
11670324