先决条件:相关系数
给定两个数组X []和Y []。查找Spearman的等级相关性。在Spearman等级相关中,而不是处理数据值本身(如“相关系数”中所述),它使用这些值的等级。首先对观察结果进行排名,然后将这些排名关联使用。该相关的算法如下
Rank each observation in X and store it in Rank_X
Rank each observation in Y and store it in Rank_Y
Obtain Pearson Correlation Coefficient for Rank_X and Rank_Y
用于计算集合X和Y的皮尔逊相关系数(r或rho)的公式如下: ![由QuickLaTeX.com渲染 {{\displaystyle r=\frac {n(\sum xy)-\left ( \sum x \right )\left ( \sum y \right )}{\sqrt{[n\sum x^2-(\sum x)^2 ][n\sum y^2 - (\sum y)^2]}}}](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Program%20for%20Spearman%E2%80%99s%20Rank%20Correlation_0.jpg)
计算集合X和Y的Pearson系数的算法
function correlationCoefficient(X, Y)
n = X.size
sigma_x = sigma_y = sigma_xy = 0
sigma_xsq = sigma_ysq = 0
for i in 0...N-1
sigma_x = sigma_x + X[i]
sigma_y = sigma_y + Y[i]
sigma_xy = sigma_xy + X[i] * Y[i]
sigma_xsq = sigma_xsq + X[i] * X[i]
sigma_ysq = sigma_ysq + Y[i] * Y[i]
num =( n * sigma_xy - sigma_x * sigma_y)
den = sqrt( [n*sigma_xsq - (sigma_x)^ 2]*[ n*sigma_ysq - (sigma_y) ^ 2] )
return num/den
在分配等级时,它可能会遇到联系,即具有相同等级的两个或多个观察值。要解决平局,将使用分数排名方案。在此方案中,如果n个观测值具有相同的等级,则每个观测值将得到由以下公式得出的分数等级:
fractional_rank = (rank) + (n-1)/2
下一个要分配的等级是等级+ n,而不是等级+1。例如,如果这3个项目具有相同的等级r,则每个项目都将如上所述获得fractional_rank。可以给另一个观察值的下一个等级是r +3。请注意,分数等级不必是分数。它们是n个连续等级ex r,r + 1,r + 2…r + n-1的算术平均值。
(r + r+1 + r+2 + ... + r+n-1) / n = r + (n-1)/2
一些例子 :
Input : X = [15 18 19 20 21]
Y = [25 26 28 27 29]
Solution : Rank_X = [1 2 3 4 5]
Rank_Y = [1 2 4 3 5 ]
sigma_x = 1+2+3+4+5 = 15
sigma_y = 1+2+4+3+5 = 15
sigma_xy = 1*2+2*2+3*4+4*3+5*5 = 54
sigma_xsq = 1*1+2*2+3*3+4*4+5*5 = 55
sigma_ysq = 1*1+2*2+3*3+4*4+5*5 = 55
Substitute values in formula
Coefficient = Pearson(Rank_X, Rank_Y) = 0.9
Input: X = [15 18 21 15 21 ]
Y = [25 25 27 27 27 ]
Solution: Rank_X = [1.5 3 4.5 1.5 4.5]
Rank_Y = [1.5 1.5 4 4 4]
Calculate and substitute values of sigma_x, sigma_y,
sigma_xy, sigma_xsq, sigma_ysq.
Coefficient = Pearson(Rank_X, Rank_Y) = 0.456435
分数排名方案的算法如下
function rankify(X)
N = X.size()
// Vector to store ranks
Rank_X(N)
for i = 0 ... N-1
r = 1 and s = 1
// Count no of smaller elements in 0...i-1
for j = 0...i-1
if X[j] < X[i]
r = r+1
if X[j] == X[i]
s = s+1
// Count no of smaller elements in i+1...N-1
for j = i+1...N-1
if X[j] < X[i]
r = r+1
if X[j] == X[i]
s = s+1
//Assign Fractional Rank
Rank_X[i] = r + (s-1) * 0.5
return Rank_X
笔记:
有一个直接公式可以计算出Spearman系数: 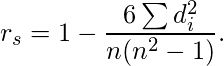 但是,我们需要输入一个校正项来解决每条领带,因此尚未讨论此公式。从等级相关系数计算Spearman系数是最通用的方法。
但是,我们需要输入一个校正项来解决每条领带,因此尚未讨论此公式。从等级相关系数计算Spearman系数是最通用的方法。
下面给出了评估Spearman系数的CPP程序
C++
// Program to find correlation
// coefficient
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef vector Vector;
// Utility Function to print
// a Vector
void printVector(const Vector &X)
{
for (auto i: X)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Function returns the rank vector
// of the set of observations
Vector rankify(Vector & X) {
int N = X.size();
// Rank Vector
Vector Rank_X(N);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int r = 1, s = 1;
// Count no of smaller elements
// in 0 to i-1
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (X[j] < X[i] ) r++;
if (X[j] == X[i] ) s++;
}
// Count no of smaller elements
// in i+1 to N-1
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++) {
if (X[j] < X[i] ) r++;
if (X[j] == X[i] ) s++;
}
// Use Fractional Rank formula
// fractional_rank = r + (n-1)/2
Rank_X[i] = r + (s-1) * 0.5;
}
// Return Rank Vector
return Rank_X;
}
// function that returns
// Pearson correlation coefficient.
float correlationCoefficient
(Vector &X, Vector &Y)
{
int n = X.size();
float sum_X = 0, sum_Y = 0,
sum_XY = 0;
float squareSum_X = 0,
squareSum_Y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// sum of elements of array X.
sum_X = sum_X + X[i];
// sum of elements of array Y.
sum_Y = sum_Y + Y[i];
// sum of X[i] * Y[i].
sum_XY = sum_XY + X[i] * Y[i];
// sum of square of array elements.
squareSum_X = squareSum_X +
X[i] * X[i];
squareSum_Y = squareSum_Y +
Y[i] * Y[i];
}
// use formula for calculating
// correlation coefficient.
float corr = (float)(n * sum_XY -
sum_X * sum_Y) /
sqrt((n * squareSum_X -
sum_X * sum_X) *
(n * squareSum_Y -
sum_Y * sum_Y));
return corr;
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
Vector X = {15,18,21, 15, 21};
Vector Y= {25,25,27,27,27};
// Get ranks of vector X
Vector rank_x = rankify(X);
// Get ranks of vector y
Vector rank_y = rankify(Y);
cout << "Vector X" << endl;
printVector(X);
// Print rank vector of X
cout << "Rankings of X" << endl;
printVector(rank_x);
// Print Vector Y
cout << "Vector Y" << endl;
printVector(Y);
// Print rank vector of Y
cout << "Rankings of Y" << endl;
printVector(rank_y);
// Print Spearmans coefficient
cout << "Spearman's Rank correlation: "
<< endl;
cout< 输出:
Vector X
15 18 21 15 21
Rankings of X
1.5 3 4.5 1.5 4.5
Vector Y
25 25 27 27 27
Rankings of Y
1.5 1.5 4 4 4
Spearman's Rank correlation:
0.456435
用于计算Spearman等级相关性的Python代码:
# Import pandas and scipy.stats
import pandas as pd
import scipy.stats
# Two lists x and y
x = [15,18,21, 15, 21]
y = [25,25,27,27,27]
# Create a function that takes in x's and y's
def spearmans_rank_correlation(x, y):
# Calculate the rank of x's
xranks = pd.Series(x).rank()
print("Rankings of X:")
print(xranks)
# Caclulate the ranking of the y's
yranks = pd.Series(y).rank()
print("Rankings of Y:")
print(yranks)
# Calculate Pearson's correlation coefficient on the ranked versions of the data
print("Spearman's Rank correlation:",scipy.stats.pearsonr(xranks, yranks)[0])
# Call the function
spearmans_rank_correlation(x, y)
# This code is contributed by Manish KC
# profile: mkumarchaudhary06
输出:
Rankings of X:
0 1.5
1 3.0
2 4.5
3 1.5
4 4.5
dtype: float64
Rankings of Y:
0 1.5
1 1.5
2 4.0
3 4.0
4 4.0
dtype: float64
Spearman's Rank correlation: 0.456435464588
使用Scipy计算Spearman的相关性的Python代码
有一种简单的方法可以使用scipy直接获取spearman的相关值。
# Import scipy.stats
import scipy.stats
# Two lists x and y
x = [15,18,21, 15, 21]
y = [25,25,27,27,27]
print(scipy.stats.spearmanr(x, y)[0])
# This code is contributed by Manish KC
# Profile: mkumarchaudhary06
输出:
0.45643546458763845参考
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spearman%27s_rank_correlation_coefficient