Java.lang.Thread Java中的类
线程化程序中的一行执行。每个程序可以有多个关联的线程。每个线程都有一个优先级,线程调度程序使用该优先级来确定哪个线程必须首先运行。 Java提供了一个线程类,它具有各种方法调用,以便通过提供构造函数和方法来对线程执行操作来管理线程的行为。
创建线程的方法
- 创建自己的类,该类扩展到父线程类
- 实现 Runnable 接口。
以下是可以参考的伪代码,以便更好地了解线程(此后称为 Thread 类)。
插图 1:
Java
// Way 1
// Creating thread By Extending To Thread class
class MyThread extends Thread {
// Method 1
// Run() method for our thread
public void run()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Thread is running created by extending to parent Thread class");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of our thread class inside main()
// method
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
// Starting the thread
myThread.start();
}
}Java
// Way 2
// Creating thread using Runnable interface
class ThreadUsingInterface implements Runnable {
// Method 1
// run() method for the thread
public void run()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("Thread is created using Runnable interface");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of our thread class inside main()
// method
ThreadUsingInterface obj = new ThreadUsingInterface();
// Passing the object to thread in main()
Thread myThread = new Thread(obj);
// Starting the thread
myThread.start();
}
}Java
// Java program Demonstrating Methods of Thread class
// Importing package
package generic;
// Class 1
// Helper class implementing Runnable interface
class Helper implements Runnable {
//
public void run() {
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Print statement
System.out.println("thread2 going to sleep for 5000");
// Making thread sleep for 0.5 seconds
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Thread2 interrupted");
}
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending Runnable interface
public class Test implements Runnable {
// Method 1
// run() method of this class
public void run() {
// Thread run() method
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Making objects of class 1 and 2 in main() method
Test obj = new Test();
Helper obj2 = new Helper();
// Creating 2 threads in main() method
Thread thread1 = new Thread(obj);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(obj2);
// Moving thread to runnable states
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
// Loading thread 1 in class 1
ClassLoader loader = thread1.getContextClassLoader();
// Creating 3rd thread in main() method
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Helper());
// Getting number of active threads
System.out.println(Thread.activeCount());
thread1.checkAccess();
// Fetching an instance of this thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Print and display commands
System.out.println(t.getName());
System.out.println("Thread1 name: " + thread1.getName());
System.out.println("Thread1 ID: " + thread1.getId());
// Fetching the priority and state of thread1
System.out.println("Priority of thread1 = " + thread1.getPriority());
// Getting the state of thread 1 using getState() method
// and printing the same
System.out.println(thread1.getState());
thread2 = new Thread(obj2);
thread2.start();
thread2.interrupt();
System.out.println("Is thread2 interrupted? " + thread2.interrupted() );
System.out.println("Is thread2 alive? " + thread2.isAlive());
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
thread1.setDaemon(true);
System.out.println("Is thread1 a daemon thread? " + thread1.isDaemon());
System.out.println("Is thread1 interrupted? " + thread1.isInterrupted());
// Waiting for thread2 to complete its execution
System.out.println("thread1 waiting for thread2 to join");
try {
thread2.join();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Display the exception along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Now setting the name of thread1
thread1.setName("child thread xyz");
// Print and display command
System.out.println("New name set for thread 1" + thread1.getName());
// Setting the priority of thread1
thread1.setPriority(5);
thread2.yield();
// Fetching the string representation of thread1
System.out.println(thread1.toString());
// Getting list of active thread in current thread's group
Thread[] tarray = new Thread[3];
Thread.enumerate(tarray);
// Display commands
System.out.println("List of active threads:");
System.out.printf("[");
// Looking out using for each loop
for (Thread thread : tarray) {
System.out.println(thread);
}
// Display commands
System.out.printf("]\n");
System.out.println(Thread.getAllStackTraces());
ClassLoader classLoader = thread1.getContextClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader.toString());
System.out.println(thread1.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread2.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(thread1.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread1.setContextClassLoader(thread2.getContextClassLoader());
thread1.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(thread2.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
StackTraceElement[] trace = thread1.getStackTrace();
System.out.println("Printing stack trace elements for thread1:");
for (StackTraceElement e : trace) {
System.out.println(e);
}
ThreadGroup grp = thread1.getThreadGroup();
System.out.println("ThreadGroup to which thread1 belongs " + grp.toString());
System.out.println(thread1.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
System.out.println("Does thread1 holds Lock? " + thread1.holdsLock(obj2));
Thread.dumpStack();
}
}Thread is running created by extending to parent Thread class插图 2:
Java
// Way 2
// Creating thread using Runnable interface
class ThreadUsingInterface implements Runnable {
// Method 1
// run() method for the thread
public void run()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("Thread is created using Runnable interface");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of our thread class inside main()
// method
ThreadUsingInterface obj = new ThreadUsingInterface();
// Passing the object to thread in main()
Thread myThread = new Thread(obj);
// Starting the thread
myThread.start();
}
}
Thread is created using Runnable interfaceJava中的线程类
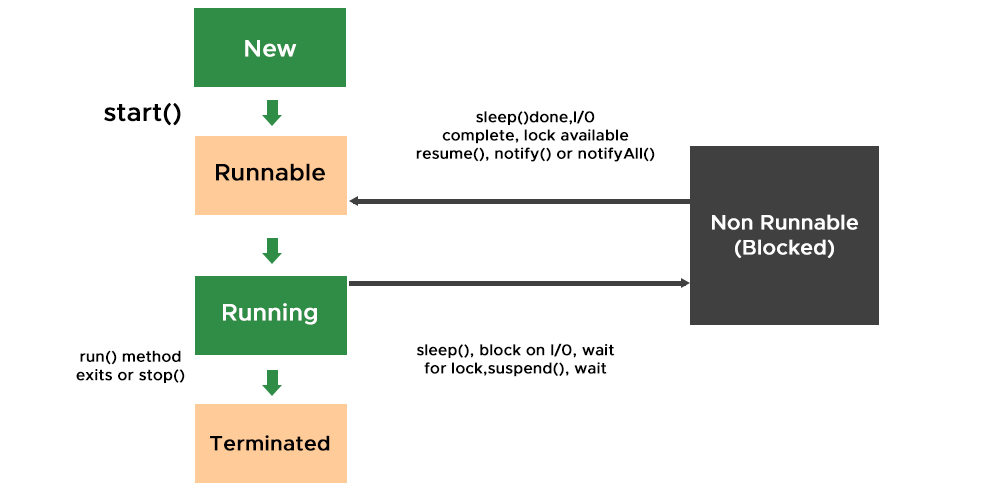
线程是一个以此类中经常使用的 method() 开始的程序,仅称为 start() 方法。此方法查找也是此类的方法的 run() 方法并开始执行 run() 方法的主体。这里密切关注将在下面讨论的 sleep() 方法。
Note: Every class that is used as thread must implement Runnable interface and over ride it’s run method.
句法:
public class Thread extends Object implements Runnable该类的构造函数如下:
| Constructor | Action Performed |
|---|---|
| Thread() | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(Runnable target) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(Runnable target, String name) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(String name) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) | Allocates a new Thread object so that it has targeted as its run object, has the specified name as its name, and belongs to the thread group referred to by a group. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) | Allocates a new Thread object so that it has targeted as its run object, has the specified name as its name, and belongs to the thread group referred to by group, and has the specified stack size. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
Thread类的方法:
现在让我们来讨论一下这个类的所有方法,说明如下:Methods Action Performed activeCount() Returns an estimate of the number of active threads in the current thread’s thread group and its subgroups checkAccess() Determines if the currently running thread has permission to modify this thread clone() Throws CloneNotSupportedException as a Thread can not be meaningfully cloned currentThread() Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object dumpStack() Prints a stack trace of the current thread to the standard error stream enumerate(Thread[] tarray) Copies into the specified array every active thread in the current thread’s thread group and its subgroups getAllStackTraces() Returns a map of stack traces for all live threads getContextClassLoader() Returns the context ClassLoader for this Thread getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler() Returns the default handler invoked when a thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception getId() Returns the identifier of this Thread getName() Returns this thread’s name getPriority() Returns this thread’s priority getStackTrace() Returns an array of stack trace elements representing the stack dump of this thread getState() Returns the state of this thread getThreadGroup() Returns the thread group to which this thread belongs getUncaughtExceptionHandler() Returns the handler invoked when this thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception holdsLock(Object obj) Returns true if and only if the current thread holds the monitor lock on the specified object interrupt() Interrupts this thread interrupted() Tests whether the current thread has been interrupted isAlive() Tests if this thread is alive isDaemon() Tests if this thread is a daemon thread isInterrupted() Tests whether this thread has been interrupted join() Waits for this thread to die join(long millis) Waits at most millis milliseconds for this thread to die run() If this thread was constructed using a separate Runnable run object, then that Runnable object’s run method is called; otherwise, this method does nothing and returns setContextClassLoader(ClassLoader cl) Sets the context ClassLoader for this Thread setDaemon(boolean on) Marks this thread as either a daemon thread or a user thread setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler( Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) Set the default handler invoked when a thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception, and no other handler has been defined for that thread setName(String name) Changes the name of this thread to be equal to the argument name. setUncaughtExceptionHandler( Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) Set the handler invoked when this thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception setPriority(int newPriority) Changes the priority of this thread sleep(long millis) Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease execution) for the specified number of milliseconds, subject to the precision and accuracy of system timers and schedulers start() Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine calls the run method of this thread toString() Returns a string representation of this thread, including the thread’s name, priority, and thread group yield() A hint to the scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield its current use of a processor
还要记住有些方法是从类Java继承的。 lang.Object 如下:
- equals() 方法
- finalize() 方法
- getClass() 方法
- hashCode() 方法
- notify() 方法
- notifyAll() 方法
- toString() 方法
- 等待()方法
示例:演示 Thread 类用法的Java程序
Java
// Java program Demonstrating Methods of Thread class
// Importing package
package generic;
// Class 1
// Helper class implementing Runnable interface
class Helper implements Runnable {
//
public void run() {
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Print statement
System.out.println("thread2 going to sleep for 5000");
// Making thread sleep for 0.5 seconds
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Thread2 interrupted");
}
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending Runnable interface
public class Test implements Runnable {
// Method 1
// run() method of this class
public void run() {
// Thread run() method
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Making objects of class 1 and 2 in main() method
Test obj = new Test();
Helper obj2 = new Helper();
// Creating 2 threads in main() method
Thread thread1 = new Thread(obj);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(obj2);
// Moving thread to runnable states
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
// Loading thread 1 in class 1
ClassLoader loader = thread1.getContextClassLoader();
// Creating 3rd thread in main() method
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Helper());
// Getting number of active threads
System.out.println(Thread.activeCount());
thread1.checkAccess();
// Fetching an instance of this thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Print and display commands
System.out.println(t.getName());
System.out.println("Thread1 name: " + thread1.getName());
System.out.println("Thread1 ID: " + thread1.getId());
// Fetching the priority and state of thread1
System.out.println("Priority of thread1 = " + thread1.getPriority());
// Getting the state of thread 1 using getState() method
// and printing the same
System.out.println(thread1.getState());
thread2 = new Thread(obj2);
thread2.start();
thread2.interrupt();
System.out.println("Is thread2 interrupted? " + thread2.interrupted() );
System.out.println("Is thread2 alive? " + thread2.isAlive());
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
thread1.setDaemon(true);
System.out.println("Is thread1 a daemon thread? " + thread1.isDaemon());
System.out.println("Is thread1 interrupted? " + thread1.isInterrupted());
// Waiting for thread2 to complete its execution
System.out.println("thread1 waiting for thread2 to join");
try {
thread2.join();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Display the exception along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Now setting the name of thread1
thread1.setName("child thread xyz");
// Print and display command
System.out.println("New name set for thread 1" + thread1.getName());
// Setting the priority of thread1
thread1.setPriority(5);
thread2.yield();
// Fetching the string representation of thread1
System.out.println(thread1.toString());
// Getting list of active thread in current thread's group
Thread[] tarray = new Thread[3];
Thread.enumerate(tarray);
// Display commands
System.out.println("List of active threads:");
System.out.printf("[");
// Looking out using for each loop
for (Thread thread : tarray) {
System.out.println(thread);
}
// Display commands
System.out.printf("]\n");
System.out.println(Thread.getAllStackTraces());
ClassLoader classLoader = thread1.getContextClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader.toString());
System.out.println(thread1.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread2.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(thread1.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread1.setContextClassLoader(thread2.getContextClassLoader());
thread1.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(thread2.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
StackTraceElement[] trace = thread1.getStackTrace();
System.out.println("Printing stack trace elements for thread1:");
for (StackTraceElement e : trace) {
System.out.println(e);
}
ThreadGroup grp = thread1.getThreadGroup();
System.out.println("ThreadGroup to which thread1 belongs " + grp.toString());
System.out.println(thread1.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
System.out.println("Does thread1 holds Lock? " + thread1.holdsLock(obj2));
Thread.dumpStack();
}
}
输出:
3
main
Thread1 name: Thread-0
Thread1 ID: 10
Priority of thread1 = 5
RUNNABLE
Is thread2 interrupted? false
Is thread2 alive? true
Is thread1 a daemon thread? true
Is thread1 interrupted? false
thread1 waiting for thread2 to join
thread2 going to sleep for 5000 ms
thread2 going to sleep for 5000 ms
Thread2 interrupted
New name set for thread 1child thread xyz
Thread[child thread xyz, 5, main]
List of active threads:
[Thread[main, 5, main]
Thread[Thread-1, 5, main]
null
]
{Thread[Signal Dispatcher, 9, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@33909752,
Thread[Thread-1, 5, main]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@55f96302,
Thread[main, 5, main]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@3d4eac69,
Thread[Attach Listener, 5, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@42a57993,
Thread[Finalizer, 8, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@75b84c92,
Thread[Reference Handler, 10, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@6bc7c054}
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@73d16e93
null
Printing stack trace elements for thread1:
ThreadGroup to which thread1 belongs java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main, maxpri=10]
java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main, maxpri=10]
Does thread1 holds Lock? false
java.lang.Exception: Stack trace
at java.lang.Thread.dumpStack(Unknown Source)
at generic.Test.main(Test.java:111)