给定两个数组start []和end [],它们分别由正整数组成,分别表示一个分段的起点和终点,任务是找到至少存在于给定分段之一中的最小整数数,并且每个分段都包含,其中至少之一。
例子:
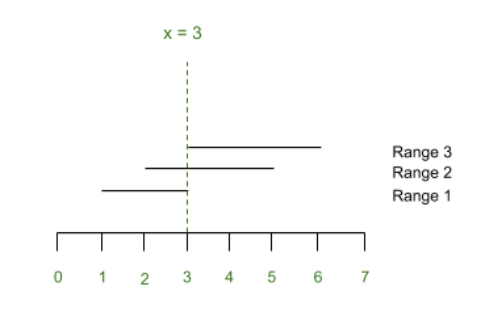
Input: start[] = {1, 2, 3}, end[] = { 3, 5, 6}
Output: 3
Explanation:
All three ranges ([1, 3], [2, 5], [3, 6]) contains the integer 3.
Input: start[] = {4, 1, 2, 5}, end[] = {7, 3, 5, 6}
Output: 3 6
Explanation:
Segments {1, 3} and {2, 5} are contains the integer 3.
Segments {4, 7} and {5, 6} contains the integer 6.
数学公式:
描述问题的数学方法是将每个给定的整数范围视为由一条线上的两个整数坐标[a i ,b i ]定义的线段。然后,覆盖每个给定范围所需的最小整数数是最小点数,以使每个段至少包含一个点。
示例1的表示如下所示:
天真的方法:
解决该问题的最简单方法是找到所有段的所有起点的最小值和所有终点的所有终点的最大值。在此范围内进行迭代,并针对此范围内的每个点,跟踪使用该点可以覆盖的段数。使用数组将段数存储为:
arr [point] =可以使用此点覆盖的段数
- 在数组arr []中找到最大值。
- 如果该最大值等于N,则对应于该值的索引是覆盖所有段的点。
- 如果该最大值小于N ,则对应于该值的索引是一个覆盖某些段的点。
- 对数组arr []重复步骤1至3(不包括此最大值),直到找到的所有最大值的总和等于N。
时间复杂度: O((A-B + 1)* N),其中A是分段终点的最大值,B是分段起点的最小值。
辅助空间: O(1)
高效方法:
通过使用贪婪技术可以有效地解决该问题。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 按分段的终点对它们进行排序。
- 选择与所有线段的最小终点相对应的点(或坐标)。
- 现在,该起点可以覆盖所有起点小于该选定点且终点大于该选定点的线段。
- 然后打印最小点数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// function to sort the 2D vector
// on basis of second element.
bool sortcol(const pair p1,
const pair p2)
{
return p1.second < p2.second;
}
// Function to compute minimum number
// of points which cover all segments
void minPoints(pair points[], int n)
{
// Sort the list of tuples by
// their second element.
sort(points, points + n, sortcol);
// To store the solution
vector cordinates;
int i = 0;
// Iterate over all the segments
while (i < n)
{
int seg = points[i].second;
cordinates.push_back(seg);
int p = i + 1;
if (p >= n)
break;
// Get the start point of next segment
int arrived = points[p].first;
// Loop over all those segements whose
// start point is less than the end
// point of current segment
while (seg >= arrived)
{
p += 1;
if (p >= n)
break;
arrived = points[p].first;
}
i = p;
}
// Print the possibles values of M
for(auto point : cordinates)
cout << point << " ";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
// Starting points of segments
int start[] = { 4, 1, 2, 5 };
// Ending points of segments
int end[] = { 7, 3, 5, 6 };
pair points[n];
// Insert ranges in points[]
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
points[i] = { start[i], end[i] };
}
// Function call
minPoints(points, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to compute minimum number
// of points which cover all segments
static void minPoints(int[][] points, int n)
{
// Sort the list of tuples by
// their second element.
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
// To store the solution
ArrayList cordinates = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
// Iterate over all the segments
while (i < n)
{
int seg = points[i][1];
cordinates.add(seg);
int p = i + 1;
if (p >= n)
break;
// Get the start point of next segment
int arrived = points[p][0];
// Loop over all those segements whose
// start point is less than the end
// point of current segment
while (seg >= arrived)
{
p += 1;
if (p >= n)
break;
arrived = points[p][0];
}
i = p;
}
// Print the possibles values of M
for(Integer point : cordinates)
System.out.print(point + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
// Starting points of segments
int[] start = { 4, 1, 2, 5 };
// Ending points of segments
int[] end = { 7, 3, 5, 6 };
int[][] points = new int[n][2];
// Insert ranges in points[]
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
points[i][0] = start[i];
points[i][1] = end[i];
}
// Function call
minPoints(points, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to compute minimum number
# of points which cover all segments
def minPoints(points):
# Sort the list of tuples by
# their second element.
points.sort(key = lambda x: x[1])
# To store the solution
cordinates = []
i = 0
# Iterate over all the segments
while i < n:
seg = points[i][1]
cordinates.append(seg)
p = i + 1
if p >= n:
break
# Get the start point of next segment
arrived = points[p][0]
# Loop over all those segements whose
# start point is less than the end
# point of current segment
while seg >= arrived:
p += 1
if p >= n:
break
arrived = points[p][0]
i = p
# Print the possibles values of M
for point in cordinates:
print(point, end =" ")
# Driver Code
n = 4
# Starting points of segments
start = [4, 1, 2, 5]
# Ending points of segments
end = [7, 3, 5, 6]
points = []
# Insert ranges in points[]
for i in range(n):
tu = (start[i], end[i])
points.append(tu)
# Function Call
minPoints(points)3 6时间复杂度: O(N * log N)
辅助空间: O(N)