使用Python检测突变
先决条件: Python中的随机数
以下文章描述了如何使用Python检测突变的 DNA 链。
使用的功能
- generateDNASequence():此方法使用 DNA 碱基 A、C、G、T 列表生成长度为 40 个字符的随机 DNA 链。此方法返回生成的 DNA 链。
- applyGammaRadiation():该方法将上述方法生成的DNA链作为输入参数,然后仅在随机生成的突变概率大于50%时才在随机位置改变链。所选位置的 DNA 碱基必须与替换它的 DNA 碱基不同。此方法返回更改后的 DNA 链。
- detectMutation():该方法将原始和改变的 DNA 链作为输入,并检查两个字符串是否被改变。如果字符串被改变,它会返回改变的 DNA 碱基的位置
入门
遵循以下步骤以实现我们所需的功能:
- 导入随机库
- generateDNASequence()函数用于生成 DNA 链。 DNA 链是通过从可用选项列表中随机选择字符来生成的。当字符串长度变为 40 时,循环完成并返回 DNA 链。
- applyGammaRadiation()函数改变 DNA 链。突变的可能性是随机产生的。如果随机产生突变的可能性大于 50,则发生突变,否则不发生突变。如果发生突变,则随机选择突变的位置。
- 接下来,将 DNA 链中的字符转换为列表。
- 获取突变位置的字符。由于提取的字符应该与替换它的字符不同,因此我们从可用选项列表中删除提取的字符,以便在其位置选择另一个字符。从列表中选择新的字符或 DNA 碱基。
- 原始 DNA 链字符再次附加到新列表中。新的 base/字符设置在 mutated 位置。
- 使用 join() 将 cl 列表中的字符再次转换为字符串。这是新的变异DNA字符串。
- 如果没有发生突变,原始 dna 与突变的 DNA 相同。
- 最后返回突变/未突变的 DNA。
- 然后用detectMutation()函数检测突变。在这个函数中,x 和 y 取 dna 和 cdna字符的每个字符进行逐字符比较。如果相同索引处的字符匹配,则增加计数。如果不匹配,则循环被破坏。
- 计数值指向突变位置之前的索引。如果 count=40 表示 2 条链的所有字符都匹配,因此没有突变 如果 count 小于 40,则表示发生了突变。
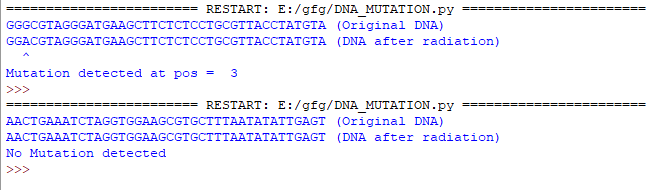
下面是实现。
Python3
# import random library
import random
# function to generate dna strands
def generateDNASequence():
# list of available DNA bases
l = ['C', 'A', 'G', 'T']
res = ""
for i in range(0, 40):
# creating the DNA strand by appending
# random characters from the list
res = res + random.choice(l)
return res
# function to alter dna strands
def applyGammaRadiation(dna):
# possibility of mutation is generated randomly
pos = random.randint(1, 100)
cdna = ''
# list of available DNA bases
l = ['C', 'A', 'G', 'T']
# if the possibility of mutation generated randomly
# is >50 then mutation happens
if(pos > 50):
# the position where mutation will take place
# is chosen randomly
changepos = random.randint(0, 39)
dl = []
# the characters in DNA strand is converted to list
dl[:0] = dna
# the character at the determined mutation position
# is fetched.
ch = "" + dl[changepos]
# since the fetched character should be different from
# the one replacing it we remove the fetched character
# from the list of available choices for choosing another
# character in its place
l.remove(ch)
# the new character or DNA base is chosen from the list
ms = random.choice(l)
cl = []
# DNA strand characters are again appended to a new list
cl[:0] = dna
# the new base in the mutated position is set
cl[changepos] = ms
# the characters in the cl list is converted to string again
# this is the new mutated DNA string
cdna = ''.join([str(e) for e in cl])
# if possibility of mutation is less than 50% then no
# mutation happens
else:
# if no mutation occurs original dna is same as mutated dna
cdna = dna
return cdna
# function to detect mutation
def detectMutation(dna, cdna):
count = 0
# x and y take each character in dna and cdna
# for character by character comparison
for x, y in zip(dna, cdna):
# if the character at the same index match
# then the count is increased
if x == y:
count = count + 1
# incase of mismatch the loop is broken
else:
break
# the count value points to the index before the
# position of mutation
return count
dna = generateDNASequence()
print(dna+" (Original DNA)")
cdna = applyGammaRadiation(dna)
print(cdna+" (DNA after radiation)")
count = detectMutation(dna, cdna)
# if count=40 it means all the characters of the 2 strands match
# hence no mutation
if count == 40:
print("No Mutation detected")
# if count is less than 40
# it means mutation has occurred
else:
# ^ denotes the position of mutation
pos = "^"
print(pos.rjust(count+1))
print("Mutation detected at pos = ", (count+1))输出