Spring – 带有示例的 init() 和 destroy() 方法
在 Spring 应用程序开发过程中,有时在创建 spring bean 时,开发人员需要在 bean 销毁之前执行初始化操作和清理操作。在spring框架中,我们可以在bean配置中使用init-method和destroy-method标签。
init() 方法
在实际应用程序中, init()方法是随处可见的方法。 init-method 是 spring
这里的myPostConstruct()方法是 Student 类中的 bean 初始化方法。此初始化方法在初始化 bean 属性后调用。我们可以使用这样的初始化方法来验证 bean 属性的值或初始化任何任务。 spring 中的 InitializingBean 接口执行相同的任务,但它与 spring 高度耦合,因此我们应该更喜欢 init 方法。
为什么是 init()?
- 您可以在 bean 初始化期间添加自定义代码/逻辑
- 它可用于设置数据库/套接字/文件等资源。
destroy()方法
在从容器中删除 bean 之前,将调用 destroy() 方法。 destroy-method 是 bean 属性,我们可以使用它分配一个自定义 bean 方法,该方法将在 bean 被销毁之前调用。要使用 destroy-method 属性,我们执行以下操作。
这里myPreDestroy()方法将在 Student 类中定义。 Spring 将在销毁 bean 之前调用此方法。 destroy-method 用于释放资源或执行一些销毁任务。 Spring 中的 DisposableBean 接口执行相同的任务,但它与 Spring 高度耦合,因此我们应该更喜欢destroy-method。那么让我们通过一个简单的例子来理解这两种方法。
Tip: It is good to go with JDBC Tutorial prior because it serves as a pre-requisite.
执行:
我们将通过简单地创建一个 Spring JDBC 项目,通过 @PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注解来解释 init() 和 destroy() 方法。所以我们先创建一个 Spring JDBC 项目。
第 1 步:在您首选的 IDE(IntelliJ IDEA 或 Eclipse)中创建一个简单的Java项目。
Tip: You can refer to below listed set of articles as follows:
- Creating First Java Application in IntelliJ IDEA
- How to Install Eclipse IDE For Java?
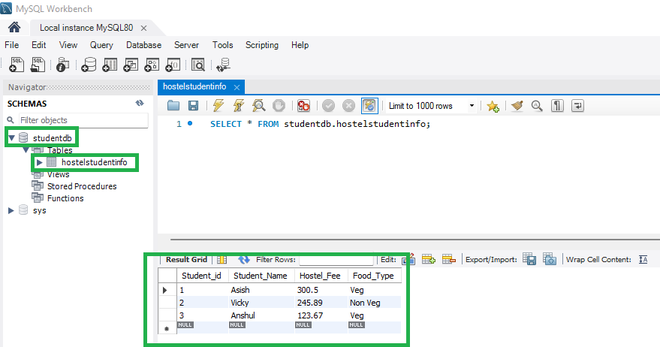
第 2 步:在数据库中创建一些表。在本文中,我们使用了 MySQL 数据库。我们的 MySQL 数据库中已经存在以下数据
所以这里的studentdb是我们的模式名, hostelstudentinfo是表名。同样,您可以创建自己的模式和表,并手动将一些数据放入该表中。
Tip: You can refer to below listed set of articles as follows:
- How to Install MySQL on Windows?
- How to Install SQL Workbench For MySQL on Windows?
第 3 步:转到Java项目并创建一个名为StudentDAO的类,在该类中,我们将创建一个方法selectAllRows()来获取 MySQL 数据库中存在的所有数据。我们还将声明我们的四个最重要的属性,以将我们的Java程序与下面列出的 MySQL 服务器连接起来,如下所示:
- 司机
- 网址
- 用户
- 密码
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate StudentDAO Class
// Importing required classes
import java.sql.*;
// Class
public class StudentDAO {
// Class data members
private String driver;
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
// Setter methods for
// Setter Injection
public void setDriver(String driver)
{
// This keyword refers to current instance itself
this.driver = driver;
}
// Setter
public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; }
// Setter
public void setUserName(String userName)
{
this.userName = userName;
}
// Setter
public void setPassword(String password)
{
this.password = password;
}
// Method
// To select all rows
public void selectAllRows()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
System.out.println("Retrieving all student data..");
// Loading drivers
// using forName() method
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
url, userName, password);
// Executing a query
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
// Storing it in a ResultSet
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(
"SELECT * FROM studentdb.hostelstudentinfo");
while (rs.next()) {
int studentId = rs.getInt(1);
String studentName = rs.getString(2);
double hostelFees = rs.getDouble(3);
String foodType = rs.getString(4);
System.out.println(studentId + " " + studentName
+ " " + hostelFees + " "
+ foodType);
}
// Closing the connection
// using close() method
con.close();
}
}XML
Java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Using ApplicationContext tom implement Spring IoC
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
// Get the bean studentDAO
StudentDAO studentDAO = context.getBean("studentDAO", StudentDAO.class);
// Calling the method
studentDAO.selectAllRows();
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate StudentDAO Class
// Importing required classes
import java.sql.*;
// Class
public class StudentDAO {
// Class data members
private String driver;
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
// Connection Object
Connection con;
// Statement Object
Statement stmt;
// Setter
public void setDriver(String driver)
{
this.driver = driver;
}
// Setter
public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; }
// Setter
public void setUserName(String userName)
{
this.userName = userName;
}
// Setter
public void setPassword(String password)
{
this.password = password;
}
// Method
// Create connection
public void createStudentDBConnection()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Loading driver using forName() method
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName,
password);
// Executing a query
stmt = con.createStatement();
}
// Method
// To select all rows
public void selectAllRows()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Display message
System.out.println("Retrieving all student data..");
// Create connection
createStudentDBConnection();
// Storing it in a ResultSet
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(
"SELECT * FROM studentdb.hostelstudentinfo");
while (rs.next()) {
int studentId = rs.getInt(1);
String studentName = rs.getString(2);
double hostelFees = rs.getDouble(3);
String foodType = rs.getString(4);
// Printing student attributes
System.out.println(studentId + " " + studentName
+ " " + hostelFees + " "
+ foodType);
}
// Closing connection
closeConnection()
}
// Method
public void deleteStudentRecord(int studentId)
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
System.out.println("Deleting student data..");
// Create connection
createStudentDBConnection();
stmt.executeUpdate(
"delete from studentdb.hostelstudentinfo where Student_id = "
+ studentId);
System.out.println("Record Deleted with the ID "
+ studentId);
// Close the connection
closeConnection();
}
// Method
// Close the connection
public void closeConnection() throws SQLException
{
con.close();
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate StudentDAO Class
// Importing required classes
import java.sql.*;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
// Class
public class StudentDAO {
// Class data members
private String driver;
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
// Connection Object
Connection con;
// Statement Object
Statement stmt;
// Setter
public void setDriver(String driver)
{
this.driver = driver;
}
// Setter
public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; }
// Setter
public void setUserName(String userName)
{
this.userName = userName;
}
// Setter
public void setPassword(String password)
{
this.password = password;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init()
throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException
{
createStudentDBConnection();
}
// Method 1
public void createStudentDBConnection()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Loading driver
// using forName() method
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
// using DriverManager
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName,
password);
// Executing query
stmt = con.createStatement();
}
// Method 2
public void selectAllRows()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Display command
System.out.println("Retrieving all student data..");
// Storing in a ResultSet
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(
"SELECT * FROM studentdb.hostelstudentinfo");
// Iterating
while (rs.next()) {
int studentId = rs.getInt(1);
String studentName = rs.getString(2);
double hostelFees = rs.getDouble(3);
String foodType = rs.getString(4);
// Printing corresponding student attributes
System.out.println(studentId + " " + studentName
+ " " + hostelFees + " "
+ foodType);
}
}
// Method 3
public void deleteStudentRecord(int studentId)
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
System.out.println("Delete student data..");
stmt.executeUpdate(
"delete from studentdb.hostelstudentinfo where Student_id = "
+ studentId);
System.out.println("Record Deleted with the ID "
+ studentId);
}
// Method 4
public void closeConnection() throws SQLException
{
con.close();
}
// Method 5
@PreDestroy public void destroy() throws SQLException
{
closeConnection();
}
}XML
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Application Class
// Importing required classes
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
// Application Class
public class Main {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Using ApplicationContext tom implement Spring IoC
ApplicationContext context
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"beans.xml");
// Getting the bean studentDAO
StudentDAO studentDAO = context.getBean(
"studentDAO", StudentDAO.class);
// Calling the method
// inside main() method
studentDAO.deleteStudentRecord(2);
studentDAO.selectAllRows();
}
}第 4 步:现在我们必须将外部 JAR 文件添加到 IntelliJ IDEA 项目中。 JAR(Java Archive)是一种包文件格式,通常用于将许多Java类文件和相关的元数据和资源(文本、图像等)聚合到一个文件中,以在Java平台上分发应用程序软件或库。简而言之,JAR 文件是包含 .class 文件、音频文件、图像文件或目录的压缩版本的文件。我们必须将以下外部 jar 文件添加到我们的Java项目中
- 春天
- MySQL 连接器
Tip: You can refer to the listed article: How to Add External JAR File to an IntelliJ IDEA Project for which user may download the jar file from the links provided below as follows:
- Spring
- MySQL Connector
第 5 步:让我们在beans.xml文件中创建 StudentDAO 类的 bean,并通过 setter 注入来注入属性的值。
Tip: You can refer to the listed article: Spring – Injecting Literal Values By Setter Injection.
文件:bean.xml
XML
第 6 步:创建 Main 类,让我们测试我们的应用程序是否运行良好。
文件:主要。Java
Java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Using ApplicationContext tom implement Spring IoC
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
// Get the bean studentDAO
StudentDAO studentDAO = context.getBean("studentDAO", StudentDAO.class);
// Calling the method
studentDAO.selectAllRows();
}
}
输出:
可以看到我们已经成功地从 MySQL 数据库中获取了数据。
Retrieving all student data..
1 Asish 300.5 Veg
2 Vicky 245.89 Non Veg
3 Anshul 123.67 VegSo what’s the problem with the above code? The problem is, suppose we want to define another method deleteStudentRecord(int studentId) in the StudentDAO class something like as represented in below code chunk as follows:
文件:StudentDAO 类
public void deleteStudentRecord(int studentId)
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Display command only
System.out.println("Deleting student data..");
// Loading driver
// using forname() method
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, password);
// Executing a query
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
stmt.executeUpdate("delete from studentdb.hostelstudentinfo where Student_id = " + studentId);
// Printing the deleted record to corresponding ID
System.out.println("Record Deleted with the ID " + studentId);
// Close the connection
// using close() method
con.close();
}现在您可以看到我们必须一次又一次地编写一些代码行。然后想想如果假设我们要执行 100 种不同的操作,我们必须一次又一次地编写相同的代码。所以我们能做些什么。我们可以在方法中编写通用代码,然后调用该方法。我们可以在名为createStudentDBConnection()的方法中编写类似这样的内容
public void createStudentDBConnection()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Loading driver
// using forName() method
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting connection
// using DriverManager
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, password);
// Executing query
stmt = con.createStatement();
}同样,我们也可以定义另一种方法来关闭连接。我们可以在名为closeConnection()的方法中编写类似这样的内容
public void closeConnection() throws SQLException
{
con.close();
}我们可以像这样在 selectAllRows() 和 deleteStudentRecord() 中调用这些方法。现在是StudentDAO 的完整代码。 Java类可以写成
文件:StudentDAO。Java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate StudentDAO Class
// Importing required classes
import java.sql.*;
// Class
public class StudentDAO {
// Class data members
private String driver;
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
// Connection Object
Connection con;
// Statement Object
Statement stmt;
// Setter
public void setDriver(String driver)
{
this.driver = driver;
}
// Setter
public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; }
// Setter
public void setUserName(String userName)
{
this.userName = userName;
}
// Setter
public void setPassword(String password)
{
this.password = password;
}
// Method
// Create connection
public void createStudentDBConnection()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Loading driver using forName() method
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName,
password);
// Executing a query
stmt = con.createStatement();
}
// Method
// To select all rows
public void selectAllRows()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Display message
System.out.println("Retrieving all student data..");
// Create connection
createStudentDBConnection();
// Storing it in a ResultSet
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(
"SELECT * FROM studentdb.hostelstudentinfo");
while (rs.next()) {
int studentId = rs.getInt(1);
String studentName = rs.getString(2);
double hostelFees = rs.getDouble(3);
String foodType = rs.getString(4);
// Printing student attributes
System.out.println(studentId + " " + studentName
+ " " + hostelFees + " "
+ foodType);
}
// Closing connection
closeConnection()
}
// Method
public void deleteStudentRecord(int studentId)
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
System.out.println("Deleting student data..");
// Create connection
createStudentDBConnection();
stmt.executeUpdate(
"delete from studentdb.hostelstudentinfo where Student_id = "
+ studentId);
System.out.println("Record Deleted with the ID "
+ studentId);
// Close the connection
closeConnection();
}
// Method
// Close the connection
public void closeConnection() throws SQLException
{
con.close();
}
}
但我们又在做同样的事情。我们在selectAllRows()和 deleteStudentRecord() 方法中一次又一次地调用createStudentDBConnection()和closeConnection ()方法。假设我们总共有 100 个这样的实用方法,那么我们必须调用这些方法 100 次。所以我们会告诉我们的 spring 框架,一旦你(spring 框架)创建了 bean,请执行createStudentDBConnection()方法。所以我们要告诉 Spring 框架的方式是添加@PostConstruct注解。总之,我们可以告诉你,Spring,一旦你创建了 StudentDAO 对象,请你自己创建createStudentDBConnection() 。不要等我们打电话。
Spring @PostConstruct Annotation: So generally, whenever we annotate a method in Spring Bean with @PostConstruct annotation, it gets executed after the spring bean is initialized. We can have only one method annotated with @PostConstruct annotation. This annotation is part of Common Annotations API and it’s part of JDK module javax.annotation-api.
注意:在项目中添加@PostConstruct 和@PreDestroy 注解
使用Java 9+ 的开发人员,@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注释都是Java EE 的一部分。由于Java EE 在Java 9 中已被弃用并在Java 11 中被删除,我们必须添加一个额外的依赖项才能使用这些注解:
如果有人使用 Maven,那么
javax.annotation
javax.annotation-api
1.3.2
否则,如果手动添加jar,如下:
- 访问链接并在文件列中,可以看到 pom 和 jar。
- 单击 jar,您的 jar 将被下载。
- 通过配置构建将其作为外部 jar 添加到类路径中。
One can refer to this article: Add External JAR File to an IntelliJ IDEA Project or refer article: Add External JAR File to an Eclipse Project.
注意:如果您使用的是Java 8 或更低版本,则无需执行上述操作。
所以现在我们可以把@PostConstruct注解 在createStudentDBConnection()之前是这样的
@PostConstruct
public void createStudentDBConnection()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Loading driver
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName,
password);
// Executing query
stmt = con.createStatement();
}介绍 init()
在实际应用程序中, init()方法是随处可见的方法。我们也可以说init()方法是一个标准名称。例如,在这个项目中,我们可以将createStudentDBConnection()方法标记为 init。这里createStudentDBConnection()是我们的 init() 方法。使用@PostConstruct注释方法以将其用作 init() 方法。我们不需要调用 init() 方法,我们的框架会为我们调用它。我们可以将我们的 init() 方法名称作为任何名称。我们可以说它init()或者我们可以说它createStudentDBConnection()或xyz() 。所以现在我们可以写同样的东西
@PostConstruct
public void init() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException
{
createStudentDBConnection();
}
// Method
public void createStudentDBConnection() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Loading driver
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, password);
// Executing query
stmt = con.createStatement();
}为什么是 init()?
- 您可以在 bean 初始化期间添加自定义代码/逻辑
- 它可用于设置数据库/套接字/文件等资源。
介绍destroy()
在从容器中删除 bean 之前,将调用 destroy() 方法。现在让我们来看看 closeConnection()方法。我们定义了这个方法来清理未使用的引用。例如在这个项目中的con变量。因此,我们可以通过将任何方法标记为@PreDestroy来将其设为 destroy() 方法。所以现在我们可以编写代码片段,如下所示:
// Method
public void closeConnection() throws SQLException
{
con.close();
}
// Annotation
@PreDestroy
// Method
public void destroy() throws SQLException
{
closeConnection();
}Spring @PreDestroy Annotation: When we annotate a Spring Bean method with PreDestroy annotation, it gets called when the bean instance is getting removed from the context. Remember that if your spring bean scope is “prototype” then it’s not completely managed by the spring container and the PreDestroy method won’t get called. If there is a method named shutdown or close then the spring container will try to automatically configure them as callback methods when the bean is being destroyed.
请注意,我们也可以在 closeConnection() 方法之前使用 @PreDestroy 注解。
文件:StudentDAO。Java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate StudentDAO Class
// Importing required classes
import java.sql.*;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
// Class
public class StudentDAO {
// Class data members
private String driver;
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
// Connection Object
Connection con;
// Statement Object
Statement stmt;
// Setter
public void setDriver(String driver)
{
this.driver = driver;
}
// Setter
public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; }
// Setter
public void setUserName(String userName)
{
this.userName = userName;
}
// Setter
public void setPassword(String password)
{
this.password = password;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init()
throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException
{
createStudentDBConnection();
}
// Method 1
public void createStudentDBConnection()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Loading driver
// using forName() method
Class.forName(driver);
// Getting a connection
// using DriverManager
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName,
password);
// Executing query
stmt = con.createStatement();
}
// Method 2
public void selectAllRows()
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
// Display command
System.out.println("Retrieving all student data..");
// Storing in a ResultSet
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(
"SELECT * FROM studentdb.hostelstudentinfo");
// Iterating
while (rs.next()) {
int studentId = rs.getInt(1);
String studentName = rs.getString(2);
double hostelFees = rs.getDouble(3);
String foodType = rs.getString(4);
// Printing corresponding student attributes
System.out.println(studentId + " " + studentName
+ " " + hostelFees + " "
+ foodType);
}
}
// Method 3
public void deleteStudentRecord(int studentId)
throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
System.out.println("Delete student data..");
stmt.executeUpdate(
"delete from studentdb.hostelstudentinfo where Student_id = "
+ studentId);
System.out.println("Record Deleted with the ID "
+ studentId);
}
// Method 4
public void closeConnection() throws SQLException
{
con.close();
}
// Method 5
@PreDestroy public void destroy() throws SQLException
{
closeConnection();
}
}
在运行应用程序之前,请确保您已在beans.xml文件中添加以下行以使用注释
文件:bean.xml
XML
文件:主要。Java
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Application Class
// Importing required classes
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
// Application Class
public class Main {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Using ApplicationContext tom implement Spring IoC
ApplicationContext context
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"beans.xml");
// Getting the bean studentDAO
StudentDAO studentDAO = context.getBean(
"studentDAO", StudentDAO.class);
// Calling the method
// inside main() method
studentDAO.deleteStudentRecord(2);
studentDAO.selectAllRows();
}
}
输出:
Delete student data..
Record Deleted with the ID 2
Retrieving all student data..
1 Asish 300.5 Veg
3 Anshul 123.67 Veg