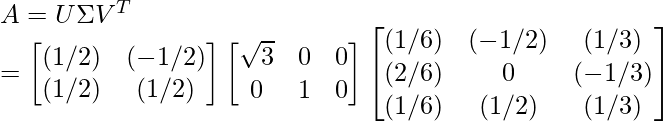奇异值分解
先决条件:矩阵对角化、特征向量计算和低秩近似
在深入研究 SVD 之前,让我们先简要了解一下什么是矩阵对角化技术以及它何时无法有效执行。
矩阵对角化
矩阵对角化是将方阵转换为特殊类型矩阵的过程,称为对角矩阵。该矩阵与基础矩阵具有相同的基本属性。在数学上,如果满足以下条件,任何输入矩阵 A 都可以简化为任何对角矩阵 D:
where,
P -> Modal Matrix: It is a (n x n) matrix that consists of eigen-vectors.
It is generally used in the process of diagonalization
and similarity transformation.然而,矩阵对角化技术对于 ( mxn)形式的矩阵失败,其中m ≠ n 。 (即当矩阵不是方阵时。这就是“奇异值分解”出现的地方,并为这个问题提供了一个很好的解决方案。
奇异值 (σ)
设A是秩为r 的任意 mxn 矩阵。将其与其转置(即A T A )相乘,会创建一个 nxn矩阵,该矩阵本质上是对称的以及半正定的。简单来说, A T A矩阵的所有特征值 (λ i…r )都是非负的(即大于 0)。
奇异值定义为获得的特征值的平方根。那是:
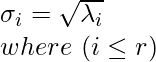
奇异值分解 (SVD)
设A为任意mxn矩阵。然后 SVD 将该矩阵划分为 2 个本质上正交的酉矩阵和一个包含奇异值的矩形对角矩阵,直到r 。在数学上,它表示为:
where,
Σ -> (m x n) orthogonal matrix
U -> (m x m) orthogonal matrix
V -> (n x n) diagonal matrix with first r rows having only singular values.
(Rest of the values are 0) 现在,了解如何计算矩阵U 、 V和Σ很重要。
计算正交矩阵 V
首先,我们计算与输入矩阵 A 相关联的特征向量 x i 。然后,我们通过将向量 x i 中的每个值除以其大小来找到对应于 x i的归一化向量 v i 。例如:
Let x = [1,2,4]
=> mag(x) or |x| = √(12 + 22 + 42) = √21.
Therefore, v = [(1/√21), (2/√21), (4/√21)]我们知道, A是一个mxn矩阵。因此,A T A 是一个所有特征值 > 0 的 xn 对称矩阵。因此,我们可以得到 A T A 的特征向量 v 1…n 使得:
where,
xi -> eigen vector
vi -> normalized eigen vector.
and
σi -> corresponding singular value.
λi -> corresponding eigen value.在计算 AAT的特征向量后,矩阵V将是:
where, v1, v2, ... vi are arranged column-wise into matrix V.计算正交矩阵 U
类似地,对于任何A ( mxn ) 矩阵, AA T是一个mxm对称矩阵,其中所有特征值 > 0。因此,我们可以得到AA T 的特征向量 x 1…n使得:
where,
xi -> eigen vector.
and
σi -> corresponding singular value.
λi -> corresponding eigen value.现在,我们使用以下等式来计算矩阵 U:
计算后,矩阵 U 将是:
where, u1, u2, ... ui are arranged column-wise into matrix U.计算对角矩阵Σ
此处,矩阵 A 具有 rank(A) = r,其中 r ≤ min (m,n)。
情况 1:如果m ≤ n ,比如 m = 2 & n = 4,那么假设所有 (σ i > 0),Σ 可以表示为:
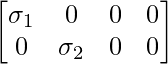
情况 2:如果 m ≥ n,假设 m = 5 & n = 3,那么假设所有 (σ i > 0),Σ 可以表示为:

特殊情况:当指定矩阵的秩时,假设 r = 3, m = 6 & n = 4。那么 Σ 可以表示为:

这意味着σ 4 ≤ 0 ,因此被丢弃。
NOTE: The number of singular values where σi > 0 can determine the rank of the matrix.
示例问题
考虑以下问题。找到具有值的 ( 2 x 3 ) 矩阵 A 的 SVD:
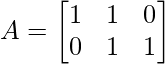
解决方案
让我们了解解决此类问题所需的每个步骤。
Step 1 - Find AT and then compute ATA.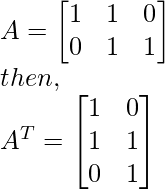
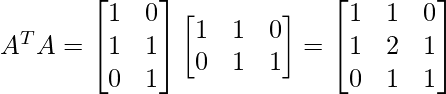
Step 2 - Find the eigen values associated with matrix ATA.
(Discussed in the prerequisite articles mentioned above)与 A T A 相关的特征值:λ = 0、1 和 3。
Step 3 - Find the singular values corresponding to the obtained
eigen values using formula:与 A T A 相关的奇异值:λ = 3, 1 & 0。
λ1 = 3 -> σ1 = √3
λ2 = 1 -> σ2 = 1
λ3 = 0 -> σ3 = 0Step 4 - Compute diagonal matrix Σ using the values of σ keeping
the above discussed cases in mind.由于 (m = 2 < n = 3),应用案例 1,矩阵 Σ 为:
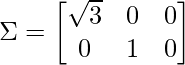
Step 5 - Find the eigen vectors & corresponding normalized eigen vectors
associated with matrix ATA.
(Discussed in the prerequisite articles mentioned above)NOTE: It is important to understand that normalized eigen vectors of ATA define the matrix V.
与 A T A 相关的特征向量:
For λ1 = 3 -> x1 = [1, 2, 1]
For λ2 = 1 -> x2 = [-1, 0, 1]
For λ3 = 0 -> x3 = [1, -1, 1]
where x1, x2 and x3 are eigen vectors of matrix ATA. 与 A T A 相关的归一化特征向量:
For x1 = [1, 2, 1] => v1 = [(1/√6), (2/√6), (1/√6)]
For x2 = [-1, 0, 1] => v2 = [(-1/√2), 0, (1/√2)]
For x3 = [1, -1, 1] => v3 = [(1/√3), (-1/√3), (1/√3)]
where v1, v2 and v3 are eigen vectors of matrix ATA. Step 6 - Use eigen vectors obtained to compute matrix V.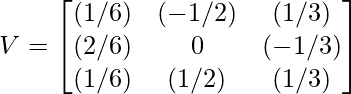
Step 7 - Use the above given equation to compute the orthogonal matrix U. 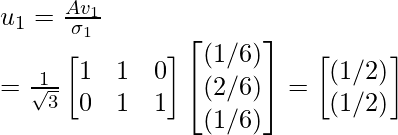
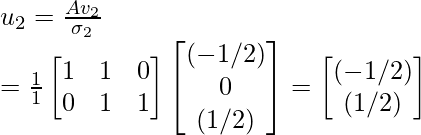
因此,正交矩阵 U 为:
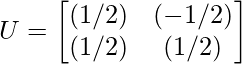
Step 8 - Compute the SVD of A using the equation given below:
(As discussed above)因此,使用SVD, A可以表示为: