基于比较的排序算法(合并排序,堆排序,快速排序等)的下限是Ω(nLogn),即它们不能比nLogn更好。
计数排序是一种线性时间排序算法,当元素的范围从1到k时,它以O(n + k)时间排序。
如果元素的范围是1到n 2怎么办?
我们不能使用计数排序,因为计数排序将花费O(n 2 ),这比基于比较的排序算法差。我们可以在线性时间内对这样的数组排序吗?
答案是基数排序。基数排序的想法是从最低有效位到最高有效位逐位进行排序。基数排序使用计数排序作为排序的子例程。
基数排序算法
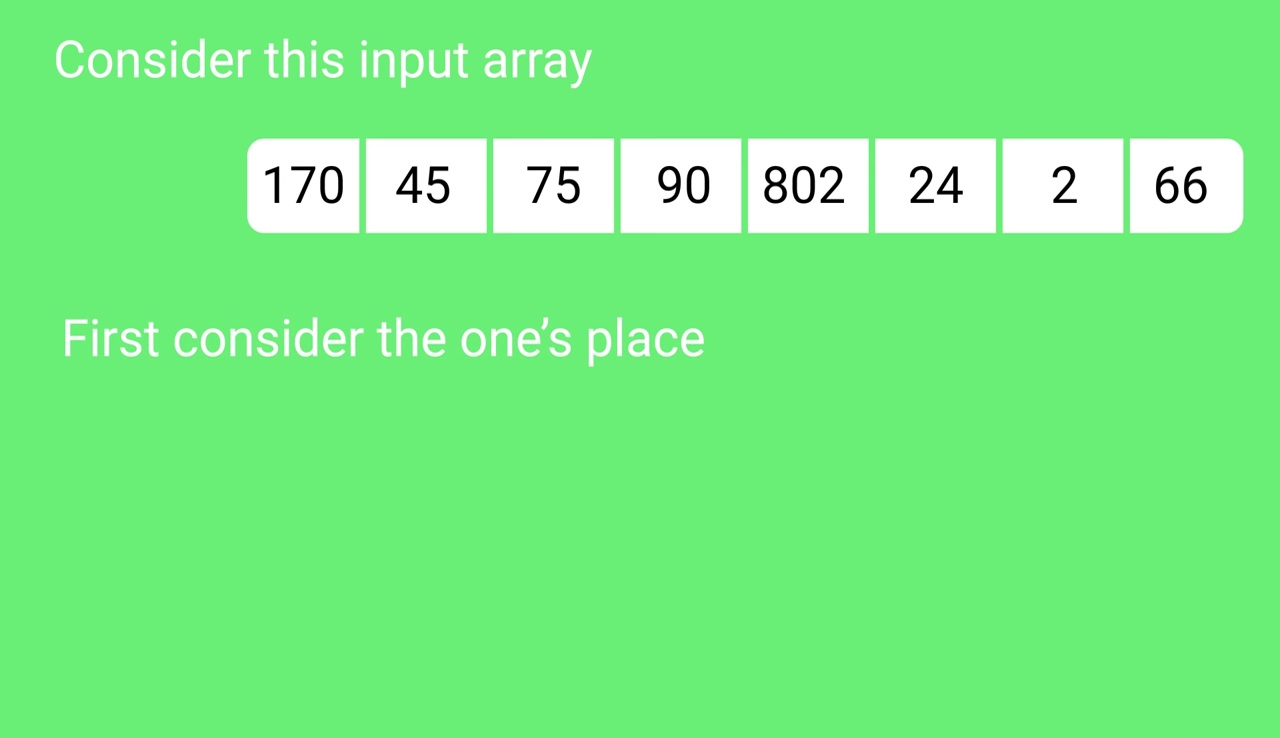
- 对于i从最低有效数字到最高有效数字变化的每个数字i,都要执行以下操作。
- 根据第i位使用计数排序(或任何稳定排序)对输入数组进行排序。
例子:
Original, unsorted list:
170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66
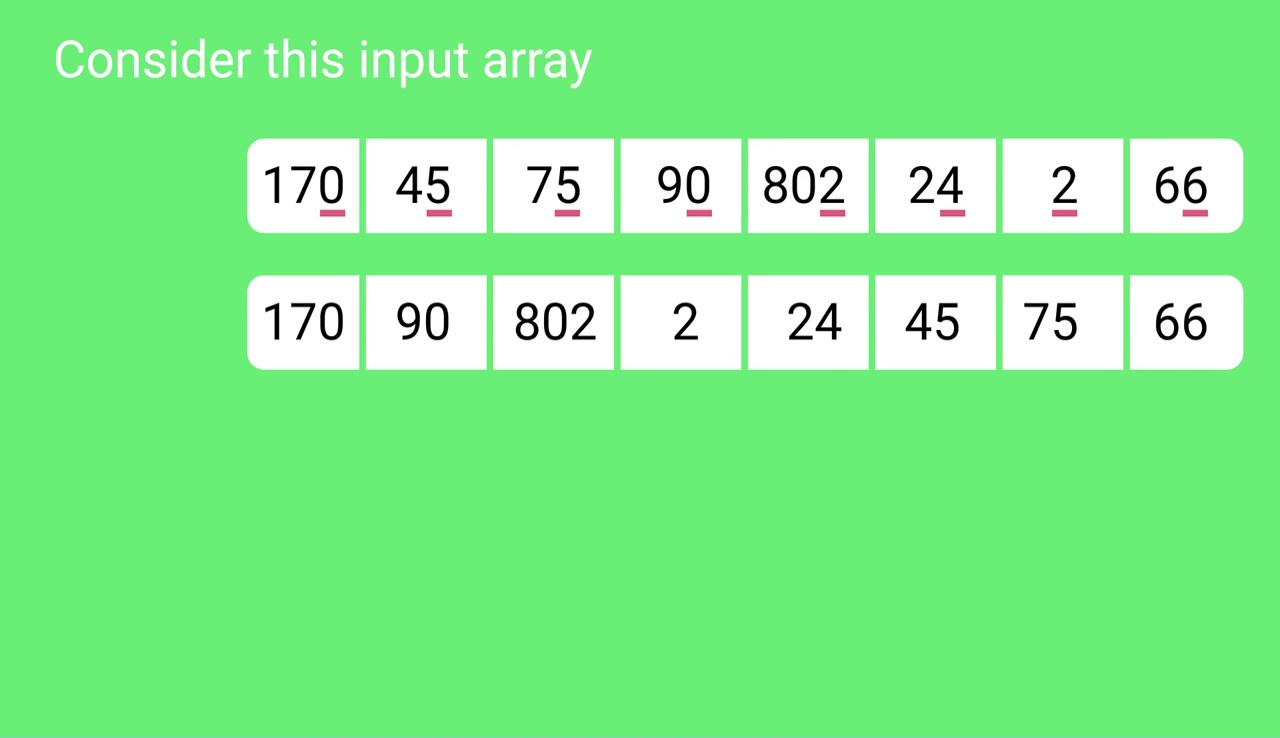
Sorting by least significant digit (1s place) gives:
[*Notice that we keep 802 before 2, because 802 occurred
before 2 in the original list, and similarly for pairs
170 & 90 and 45 & 75.]
170, 90, 802, 2, 24, 45, 75, 66
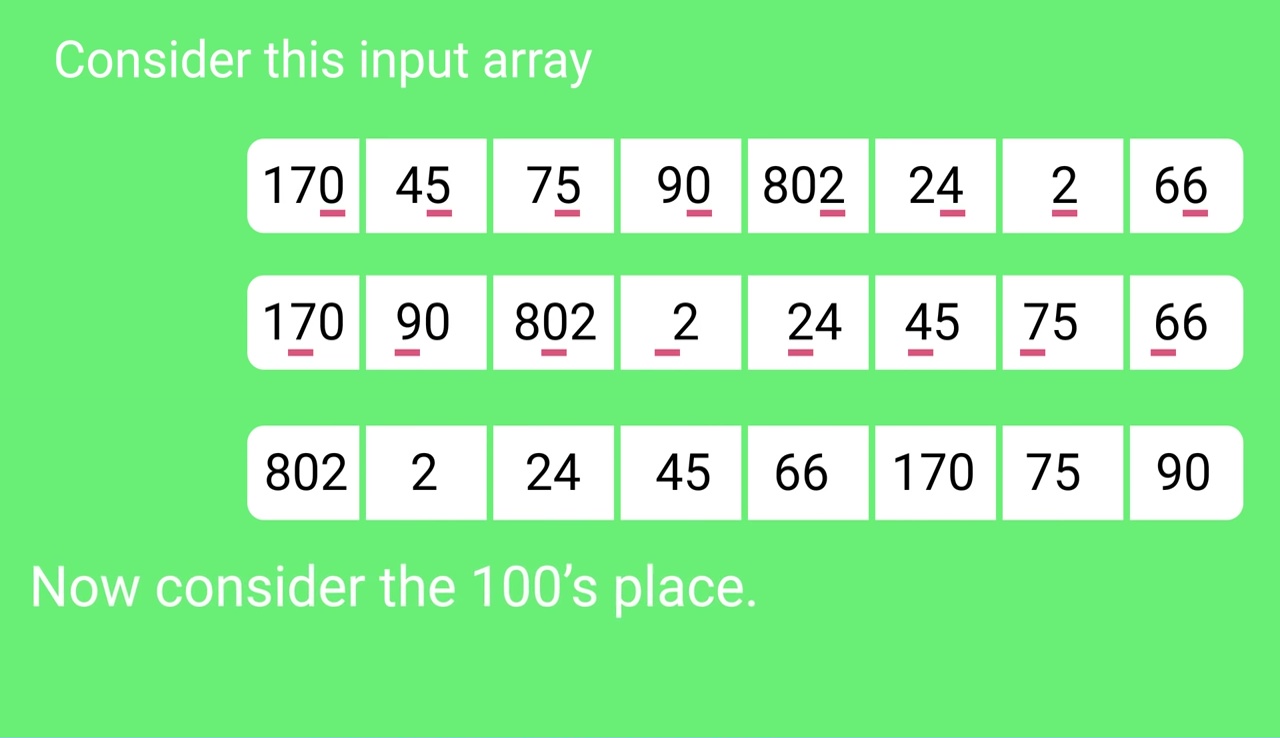
Sorting by next digit (10s place) gives:
[*Notice that 802 again comes before 2 as 802 comes before
2 in the previous list.]
802, 2, 24, 45, 66, 170, 75, 90
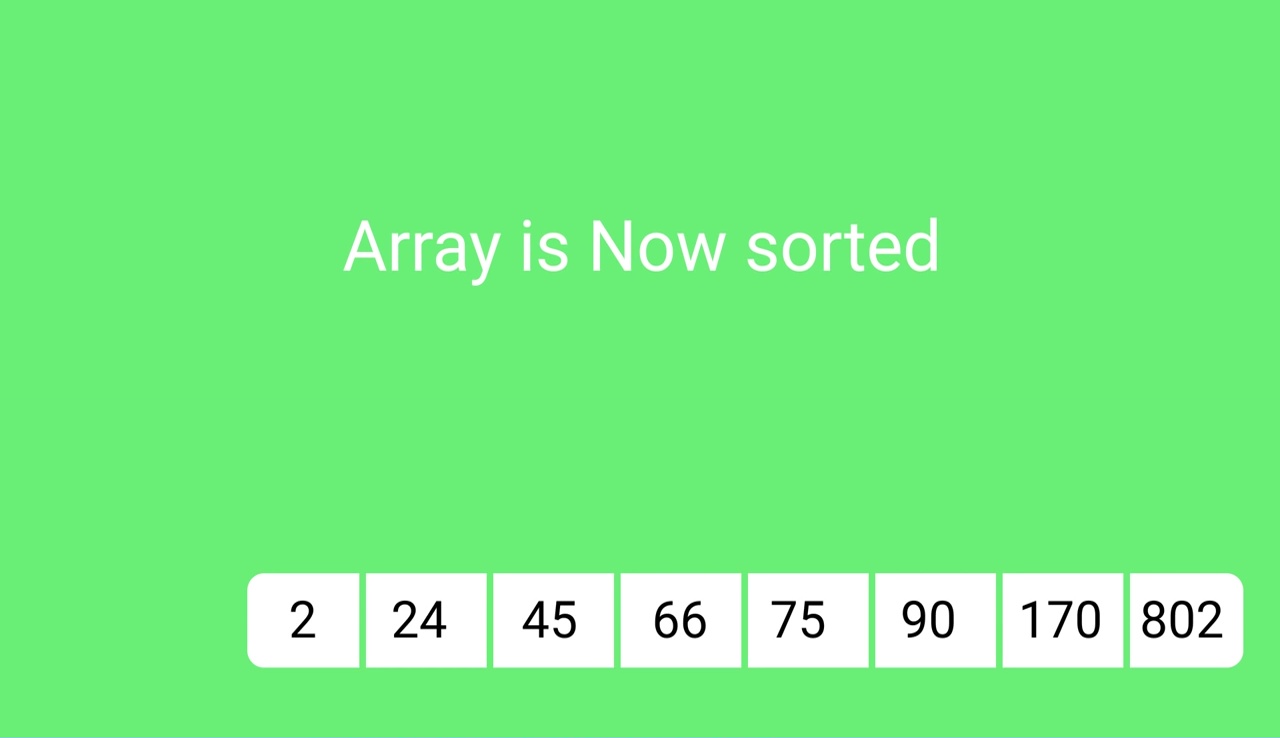
Sorting by the most significant digit (100s place) gives:
2, 24, 45, 66, 75, 90, 170, 802 Radix Sort的运行时间是几点?
设输入整数为d位。基数排序需要O(d *(n + b))时间,其中b是表示数字的基数,例如,对于十进制,b是10。d的值是什么?如果k是最大可能值,则d将为O(log b (k))。因此,总体时间复杂度为O((n + b)* log b (k))。它看起来比基于比较的排序算法对大k的时间复杂度更高。让我们首先限制k。令k <= n c ,其中c为常数。在这种情况下,复杂度变为O(nLog b (n))。但是它仍然没有超越基于比较的排序算法。
如果我们增大b的值怎么办?使时间复杂度线性化的b的值应该是多少?如果将b设置为n,则时间复杂度为O(n)。换句话说,如果数字以n为底(或者每个数字取对数2 (n)位),则可以对范围为1到n c的整数数组进行排序。
Radix Sort是否优于Quick-Sort等基于比较的排序算法?
如果我们每个数字都有2 n个对数位,那么对于各种各样的输入数字,Radix的运行时间似乎比快速排序要好。对于Radix Sort,隐藏在渐近符号中的常数因子更高,而Quick-Sort更有效地使用硬件缓存。同样,基数排序使用计数排序作为子例程,计数排序占用额外的空间来对数字进行排序。
基数排序的实现
以下是Radix Sort的简单实现。为简单起见,假定d的值为10。建议您在下面的代码中查看Counting Sort,以了解countSort()函数的详细信息。
C++
// C++ implementation of Radix Sort
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function to get maximum value in arr[]
int getMax(int arr[], int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// A function to do counting sort of arr[] according to
// the digit represented by exp.
void countSort(int arr[], int n, int exp)
{
int output[n]; // output array
int i, count[10] = { 0 };
// Store count of occurrences in count[]
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++;
// Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual
// position of this digit in output[]
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
// Build the output array
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i];
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--;
}
// Copy the output array to arr[], so that arr[] now
// contains sorted numbers according to current digit
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
// The main function to that sorts arr[] of size n using
// Radix Sort
void radixsort(int arr[], int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// Do counting sort for every digit. Note that instead
// of passing digit number, exp is passed. exp is 10^i
// where i is current digit number
for (int exp = 1; m / exp > 0; exp *= 10)
countSort(arr, n, exp);
}
// A utility function to print an array
void print(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function Call
radixsort(arr, n);
print(arr, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Radix sort Java implementation
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Radix {
// A utility function to get maximum value in arr[]
static int getMax(int arr[], int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// A function to do counting sort of arr[] according to
// the digit represented by exp.
static void countSort(int arr[], int n, int exp)
{
int output[] = new int[n]; // output array
int i;
int count[] = new int[10];
Arrays.fill(count, 0);
// Store count of occurrences in count[]
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++;
// Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains
// actual position of this digit in output[]
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
// Build the output array
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i];
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--;
}
// Copy the output array to arr[], so that arr[] now
// contains sorted numbers according to curent digit
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
// The main function to that sorts arr[] of size n using
// Radix Sort
static void radixsort(int arr[], int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// Do counting sort for every digit. Note that
// instead of passing digit number, exp is passed.
// exp is 10^i where i is current digit number
for (int exp = 1; m / exp > 0; exp *= 10)
countSort(arr, n, exp);
}
// A utility function to print an array
static void print(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
/*Driver Code*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66 };
int n = arr.length;
// Function Call
radixsort(arr, n);
print(arr, n);
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */Python
# Python program for implementation of Radix Sort
# A function to do counting sort of arr[] according to
# the digit represented by exp.
def countingSort(arr, exp1):
n = len(arr)
# The output array elements that will have sorted arr
output = [0] * (n)
# initialize count array as 0
count = [0] * (10)
# Store count of occurrences in count[]
for i in range(0, n):
index = (arr[i] / exp1)
count[int(index % 10)] += 1
# Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual
# position of this digit in output array
for i in range(1, 10):
count[i] += count[i - 1]
# Build the output array
i = n - 1
while i >= 0:
index = (arr[i] / exp1)
output[count[int(index % 10)] - 1] = arr[i]
count[int(index % 10)] -= 1
i -= 1
# Copying the output array to arr[],
# so that arr now contains sorted numbers
i = 0
for i in range(0, len(arr)):
arr[i] = output[i]
# Method to do Radix Sort
def radixSort(arr):
# Find the maximum number to know number of digits
max1 = max(arr)
# Do counting sort for every digit. Note that instead
# of passing digit number, exp is passed. exp is 10^i
# where i is current digit number
exp = 1
while max1 / exp > 0:
countingSort(arr, exp)
exp *= 10
# Driver code
arr = [170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66]
# Function Call
radixSort(arr)
for i in range(len(arr)):
print(arr[i])
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumra
# Edited by Patrick GallagherC#
// C# implementation of Radix Sort
using System;
class GFG {
public static int getMax(int[] arr, int n)
{
int mx = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] > mx)
mx = arr[i];
return mx;
}
// A function to do counting sort of arr[] according to
// the digit represented by exp.
public static void countSort(int[] arr, int n, int exp)
{
int[] output = new int[n]; // output array
int i;
int[] count = new int[10];
// initializing all elements of count to 0
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
count[i] = 0;
// Store count of occurrences in count[]
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]++;
// Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains
// actual
// position of this digit in output[]
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
// Build the output array
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10] - 1] = arr[i];
count[(arr[i] / exp) % 10]--;
}
// Copy the output array to arr[], so that arr[] now
// contains sorted numbers according to current
// digit
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = output[i];
}
// The main function to that sorts arr[] of size n using
// Radix Sort
public static void radixsort(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know number of digits
int m = getMax(arr, n);
// Do counting sort for every digit. Note that
// instead of passing digit number, exp is passed.
// exp is 10^i where i is current digit number
for (int exp = 1; m / exp > 0; exp *= 10)
countSort(arr, n, exp);
}
// A utility function to print an array
public static void print(int[] arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function Call
radixsort(arr, n);
print(arr, n);
}
// This code is contributed by DrRoot_
}PHP
= 0; $i--)
{
$output[$count[ ($arr[$i] /
$exp) % 10 ] - 1] = $arr[$i];
$count[ ($arr[$i] / $exp) % 10 ]--;
}
// Copy the output array to arr[], so
// that arr[] now contains sorted numbers
// according to current digit
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
$arr[$i] = $output[$i];
}
// The main function to that sorts arr[]
// of size n using Radix Sort
function radixsort(&$arr, $n)
{
// Find the maximum number to know
// number of digits
$m = max($arr);
// Do counting sort for every digit. Note
// that instead of passing digit number,
// exp is passed. exp is 10^i where i is
// current digit number
for ($exp = 1; $m / $exp > 0; $exp *= 10)
countSort($arr, $n, $exp);
}
// A utility function to print an array
function PrintArray(&$arr,$n)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . " ";
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(170, 45, 75, 90, 802, 24, 2, 66);
$n = count($arr);
// Function Call
radixsort($arr, $n);
PrintArray($arr, $n);
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
?>C++
// implementation of radix sort using bin/bucket sort
#include
using namespace std;
// structure for a single linked list to help further in the
// sorting
struct node {
int data;
node* next;
};
// function for creating a new node in the linked list
struct node* create(int x)
{
node* temp = new node();
temp->data = x;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// utility function to append node in the linked list
// here head is passed by reference, to know more about this
// search pass by reference
void insert(node*& head, int n)
{
if (head == NULL) {
head = create(n);
return;
}
node* t = head;
while (t->next != NULL)
t = t->next;
t->next = create(n);
}
// utility function to pop an element from front in the list
// for the sake of stability in sorting
int del(node*& head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return 0;
node* temp = head;
// storing the value of head before updating
int val = head->data;
// updation of head to next node
head = head->next;
delete temp;
return val;
}
// utility function to get the number of digits in the
// max_element
int digits(int n)
{
int i = 1;
if (n < 10)
return 1;
while (n > (int)pow(10, i))
i++;
return i;
}
void radix_sort(vector& arr)
{
// size of the array to be sorted
int sz = arr.size();
// getting the maximum element in the array
int max_val = *max_element(arr.begin(), arr.end());
// getting digits in the maximum element
int d = digits(max_val);
// creating buckets to store the pointers
node** bins;
// array of pointers to linked list of size 10 as
// integers are decimal numbers so they can hold numbers
// from 0-9 only, that's why size of 10
bins = new node*[10];
// intialising the hash array with null to all
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
bins[i] = NULL;
// first loop working for a constan time only and inner
// loop is iterating through the array to store elements
// of array in the linked list by their digits value
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++) // bins updation
insert(bins[(arr[j] / (int)pow(10, i)) % 10],
arr[j]);
int x = 0, y = 0;
// write back to the array after each pass
while (x < 10) {
while (bins[x] != NULL)
arr[y++] = del(bins[x]);
x++;
}
}
}
// a utility function to print the sorted array
void print(vector arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector arr = { 573, 25, 415, 12, 161, 6 };
// function call
radix_sort(arr);
print(arr);
return 0;
} 2 24 45 66 75 90 170 802 以下是使用存储桶排序技术时实现基数排序的另一种方法,在查看代码时可能看起来并不简单,但是如果您尝试一下,那么很容易就可以了解有关存储桶排序的更多信息,请访问https: //www.geeksforgeeks.org/bucket-sort-2并了解该技术背后的逻辑。
C++
// implementation of radix sort using bin/bucket sort
#include
using namespace std;
// structure for a single linked list to help further in the
// sorting
struct node {
int data;
node* next;
};
// function for creating a new node in the linked list
struct node* create(int x)
{
node* temp = new node();
temp->data = x;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// utility function to append node in the linked list
// here head is passed by reference, to know more about this
// search pass by reference
void insert(node*& head, int n)
{
if (head == NULL) {
head = create(n);
return;
}
node* t = head;
while (t->next != NULL)
t = t->next;
t->next = create(n);
}
// utility function to pop an element from front in the list
// for the sake of stability in sorting
int del(node*& head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return 0;
node* temp = head;
// storing the value of head before updating
int val = head->data;
// updation of head to next node
head = head->next;
delete temp;
return val;
}
// utility function to get the number of digits in the
// max_element
int digits(int n)
{
int i = 1;
if (n < 10)
return 1;
while (n > (int)pow(10, i))
i++;
return i;
}
void radix_sort(vector& arr)
{
// size of the array to be sorted
int sz = arr.size();
// getting the maximum element in the array
int max_val = *max_element(arr.begin(), arr.end());
// getting digits in the maximum element
int d = digits(max_val);
// creating buckets to store the pointers
node** bins;
// array of pointers to linked list of size 10 as
// integers are decimal numbers so they can hold numbers
// from 0-9 only, that's why size of 10
bins = new node*[10];
// intialising the hash array with null to all
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
bins[i] = NULL;
// first loop working for a constan time only and inner
// loop is iterating through the array to store elements
// of array in the linked list by their digits value
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++) // bins updation
insert(bins[(arr[j] / (int)pow(10, i)) % 10],
arr[j]);
int x = 0, y = 0;
// write back to the array after each pass
while (x < 10) {
while (bins[x] != NULL)
arr[y++] = del(bins[x]);
x++;
}
}
}
// a utility function to print the sorted array
void print(vector arr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector arr = { 573, 25, 415, 12, 161, 6 };
// function call
radix_sort(arr);
print(arr);
return 0;
}
6 12 25 161 415 573 时间复杂度与第一种方法相同,只是通过另一种方法的实现。
快照:

基数测验
GeeksforGeeks / GeeksQuiz上的其他排序算法:
- 选择排序
- 气泡排序
- 插入排序
- 合并排序
- 堆排序
- 快速排序
- 计数排序
- 桶分类
- 壳排序