实现循环缓冲区的Java程序
当数据不断地从一个地方移动到另一个地方或从一个进程移动到另一个进程或经常被访问时,它不能存储在永久内存位置,例如硬盘驱动器,因为它们需要时间来检索数据。这种类型的数据需要快速访问并存储在临时存储位置,例如称为缓冲区的 RAM。
缓冲区示例:
- 当任何视频在线流式传输时,数据(音频和视频)会在视频播放之前缓冲。在此缓冲过程中,数据被下载并存储在 RAM 中,并在需要时随时访问。
- Word 文档在保存文档之前将内容和用户所做的更改存储在缓冲区中。
什么是循环缓冲区?
循环缓冲区或环形缓冲区是一个循环队列,允许以连续的方式使用内存。循环缓冲区遵循先进先出原则,即先进先出。
Circular Buffers can be implemented in two ways, using an array or a linked list.
方法 1:使用数组
由于添加的元素类型未知,因此在构造函数中初始化空对象数组及其容量。维护两个指针,即head 和tail,用于元素的插入和删除。 head 指向第一个元素,tail 指向最后一个元素。

使用数组的循环缓冲区
元素的插入
最初,头部为 0,尾部为 -1,大小为 0。
需要插入元素的索引使用以下公式计算: –
int index = (tail + 1) % capacity
array[index] = element;尾指针和大小在插入元素时递增 1。当数组的大小等于其容量时,缓冲区已满,无法容纳更多元素。
删除元素:
检索头指针处的元素,头指针加一,如果减一,则缓冲区的大小。
int index = head % capacity;
E element = (E) array[index];例子:
Input : [5, 6, 7, 1 ,4]
Output : The elements are printed in the order :-
5
6
7
1
4下面是上述方法的实现
Java
// Java program to implement a
// Circular Buffer using an array
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
class CircularBuffer {
// Initial Capacity of Buffer
private int capacity = 0;
// Initial Size of Buffer
private int size = 0;
// Head pointer
private int head = 0;
// Tail pointer
private int tail = -1;
private Object[] array;
// Constructor
CircularBuffer(int capacity)
{
// Initializing the capacity of the array
this.capacity = capacity;
// Initializing the array
array = new Object[capacity];
}
// Addition of elements
public void add(Object element) throws Exception
{
// Calculating the index to add the element
int index = (tail + 1) % capacity;
// Size of the array increases as elements are added
size++;
// Checking if the array is full
if (size == capacity) {
throw new Exception("Buffer Overflow");
}
// Storing the element in the array
array[index] = element;
// Incrementing the tail pointer to point
// to the element added currently
tail++;
}
// Deletion of elements
public Object get() throws Exception
{
// Checking if the array is empty
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("Empty Buffer");
}
// Calculating the index of the element to be
// deleted
int index = head % capacity;
// Getting the element
Object element = array[index];
// Incrementing the head pointer to point
// to the next element
head++;
// Decrementing the size of the array as the
// elements are deleted
size--;
// Returning the first element
return element;
}
// Retrieving the first element without deleting it
public Object peek() throws Exception
{
// Checking if the array is empty
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("Empty Buffer");
}
// Calculating the index of the
// element to be deleted
int index = head % capacity;
// Getting the element
Object element = array[index];
// Returning the element
return element;
}
// Checking if the array is empty
public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }
// Size of the array
public int size() { return size; }
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Creating the Circular Buffer
CircularBuffer cb = new CircularBuffer(10);
// Adding elements to the circular Buffer
cb.add(5);
cb.add(6);
cb.add(7);
cb.add(1);
cb.add(4);
// Printing the elements
System.out.println(
"The elements are printed in the order :-");
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
}
}Java
// Java program to implement a Circular
// Buffer using a Linked List
// A Generic Node class is used to create a Linked List
class Node {
// Data Stored in each Node of the Linked List
E data;
// Pointer to the next node in the Linked List
Node next;
// Node class constructor used to initializes
// the data in each Node
Node(E data) { this.data = data; }
}
class CircularBufferLL {
// Head node
Node head;
// Tail Node
Node tail;
int size = 0;
int capacity = 0;
// Constructor
CircularBufferLL(int capacity)
{
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// Addition of Elements
public void add(E element) throws Exception
{
// Size of buffer increases as elements
// are added to the Linked List
size++;
// Checking if the buffer is full
if (size == capacity) {
throw new Exception("Buffer Overflow");
}
// Checking if the buffer is empty
if (head == null) {
head = new Node<>(element);
tail = head;
return;
}
// Node element to be linked
Node temp = new Node<>(element);
// Referencing the last element to the head node
temp.next = head;
// Updating the tail reference to the
// latest node added
tail.next = temp;
// Updating the tail to the latest node added
tail = temp;
}
// Retrieving the head element
public E get() throws Exception
{
// Checking if the buffer is empty
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("Empty Buffer");
}
// Getting the element
E element = head.data;
// Updating the head pointer
head = head.next;
// Updating the tail reference to
// the new head pointer
tail.next = head;
// Decrementing the size
size--;
if (size == 0) {
// Removing any references present
// when the buffer becomes empty
head = tail = null;
}
return element;
}
// Retrieving the head element without deleting
public E peek() throws Exception
{
// Checking if the buffer is empty
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("Empty Buffer");
}
// Getting the element
E element = head.data;
return element;
}
// Checking if the buffer is empty
public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }
// Retrieving the size of the buffer
public int size() { return size; }
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Creating the Circular Buffer
CircularBufferLL cb
= new CircularBufferLL<>(10);
// Adding elements to the circular Buffer
cb.add(5);
cb.add(6);
cb.add(7);
cb.add(1);
cb.add(4);
// Printing the elements
System.out.println(
"The elements are printed in the order :-");
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
}
} The elements are printed in the order :-
5
6
7
1
4时间复杂度: O(1),插入和删除。
方法 2:使用链表
创建了一个通用节点类,它充当创建循环缓冲区的助手类。
维护两个指针,即head 和tail,用于元素的插入和删除。 head 指向第一个元素,tail 指向最后一个元素。
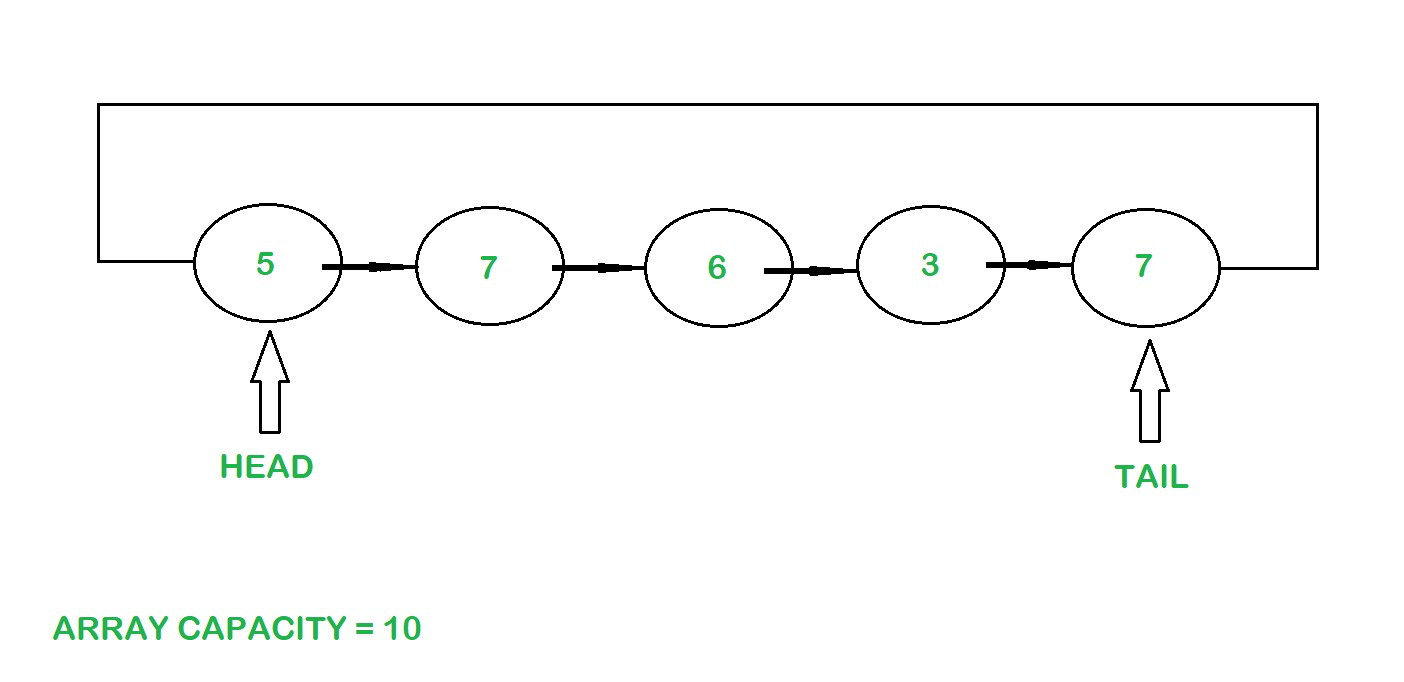
使用链表的循环缓冲区
元素的插入:
- 最初头部和尾部为空,大小为 0。
- 元素被添加到链表的尾部,尾部的引用更改为头指针。
- 缓冲区的大小随着元素添加到链表中而增加。
- 当数组的大小等于其容量时,缓冲区已满,无法容纳更多元素。
删除元素:
头指针处的元素被检索,头指针的引用更改为下一个元素和缓冲区的大小(如果减一)。
例子 :
Input : [5, 6, 7, 1 ,4]
Output: The elements are printed in the order :
5
6
7
1
4下面是上述方法的实现:
Java
// Java program to implement a Circular
// Buffer using a Linked List
// A Generic Node class is used to create a Linked List
class Node {
// Data Stored in each Node of the Linked List
E data;
// Pointer to the next node in the Linked List
Node next;
// Node class constructor used to initializes
// the data in each Node
Node(E data) { this.data = data; }
}
class CircularBufferLL {
// Head node
Node head;
// Tail Node
Node tail;
int size = 0;
int capacity = 0;
// Constructor
CircularBufferLL(int capacity)
{
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// Addition of Elements
public void add(E element) throws Exception
{
// Size of buffer increases as elements
// are added to the Linked List
size++;
// Checking if the buffer is full
if (size == capacity) {
throw new Exception("Buffer Overflow");
}
// Checking if the buffer is empty
if (head == null) {
head = new Node<>(element);
tail = head;
return;
}
// Node element to be linked
Node temp = new Node<>(element);
// Referencing the last element to the head node
temp.next = head;
// Updating the tail reference to the
// latest node added
tail.next = temp;
// Updating the tail to the latest node added
tail = temp;
}
// Retrieving the head element
public E get() throws Exception
{
// Checking if the buffer is empty
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("Empty Buffer");
}
// Getting the element
E element = head.data;
// Updating the head pointer
head = head.next;
// Updating the tail reference to
// the new head pointer
tail.next = head;
// Decrementing the size
size--;
if (size == 0) {
// Removing any references present
// when the buffer becomes empty
head = tail = null;
}
return element;
}
// Retrieving the head element without deleting
public E peek() throws Exception
{
// Checking if the buffer is empty
if (size == 0) {
throw new Exception("Empty Buffer");
}
// Getting the element
E element = head.data;
return element;
}
// Checking if the buffer is empty
public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }
// Retrieving the size of the buffer
public int size() { return size; }
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Creating the Circular Buffer
CircularBufferLL cb
= new CircularBufferLL<>(10);
// Adding elements to the circular Buffer
cb.add(5);
cb.add(6);
cb.add(7);
cb.add(1);
cb.add(4);
// Printing the elements
System.out.println(
"The elements are printed in the order :-");
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
System.out.println(cb.get());
}
}
The elements are printed in the order :-
5
6
7
1
4时间复杂度: O(1),插入和删除。