最大化 N 叉树中从根到叶节点的路径总和
给定一棵由N个节点组成的通用树,任务是找到从根到叶节点的路径的最大和。
例子:
Input:
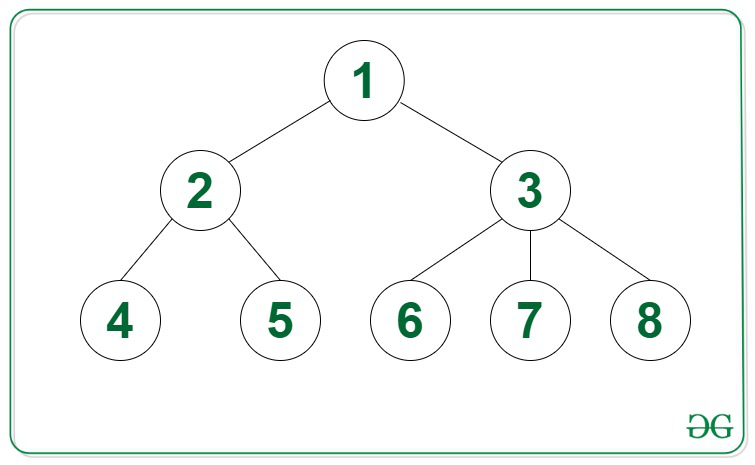
Output: 12
Explanation: The path sum to every leaf from the root are:
For node 4: 1 -> 2 -> 4 = 7
For node 5: 1 -> 2 -> 5 = 8
For node 6: 1 -> 3 -> 6 = 10
For node 7: 1 -> 3 -> 7 = 11
For node 8: 1 -> 3 -> 8 = 12 (maximum)
The maximum path sum is 12 i.e., from root 1 to leaf 8.
方法:给定问题可以通过对给定树执行 DFS 遍历来解决。这个想法是通过跟踪每个路径中节点的值之和来从给定通用树的根节点执行 DFS 遍历,如果出现任何叶节点,则最大化在 a 中获得的当前路径和的值变量,比如说maxSum 。
执行 DFS 遍历后,打印maxSum的值作为结果最大和路径。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node in the tree
struct Node {
int val;
vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a
// new node in the tree
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->val = key;
return temp;
}
// Recursive function to calculate the
// maximum sum in a path using DFS
void DFS(Node* root, int sum, int& ans)
{
// If current node is a leaf node
if (root->child.size() == 0) {
ans = max(ans, sum);
return;
}
// Traversing all children of
// the current node
for (int i = 0;
i < root->child.size(); i++) {
// Recursive call for all
// the children nodes
DFS(root->child[i],
sum + root->child[i]->val, ans);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Generic Tree
Node* root = newNode(1);
(root->child).push_back(newNode(2));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(3));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(4));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(newNode(6));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(5));
(root->child[1])->child.push_back(newNode(7));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(newNode(8));
// Stores the maximum sum of a path
int maxSumPath = 0;
// Function Call
DFS(root, root->val, maxSumPath);
cout << maxSumPath;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
// Stores the maximum sum of a path
static int maxSumPath = 0;
// Structure of a node in the tree
static class Node {
public int val;
public Vector child;
public Node(int key)
{
val = key;
child = new Vector();
}
}
// Utility function to create a
// new node in the tree
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node(key);
return temp;
}
// Recursive function to calculate the
// maximum sum in a path using DFS
static void DFS(Node root, int sum)
{
// If current node is a leaf node
if (root.child.size() == 0) {
maxSumPath = Math.max(maxSumPath, sum);
return;
}
// Traversing all children of
// the current node
for (int i = 0; i < root.child.size(); i++) {
// Recursive call for all
// the children nodes
DFS(root.child.get(i), sum + root.child.get(i).val);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Given Generic Tree
Node root = newNode(1);
(root.child).add(newNode(2));
(root.child).add(newNode(3));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode(4));
(root.child.get(1).child).add(newNode(6));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode(5));
(root.child.get(1)).child.add(newNode(7));
(root.child.get(1).child).add(newNode(8));
// Function Call
DFS(root, root.val);
System.out.print(maxSumPath);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07. Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Stores the maximum sum of a path
maxSumPath = 0
# Structure of a node in the tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.val = key
self.child = []
# Utility function to create a
# new node in the tree
def newNode(key):
temp = Node(key)
return temp
# Recursive function to calculate the
# maximum sum in a path using DFS
def DFS(root, Sum):
global maxSumPath
# If current node is a leaf node
if (len(root.child) == 0):
maxSumPath = max(maxSumPath, Sum)
return
# Traversing all children of
# the current node
for i in range(len(root.child)):
# Recursive call for all
# the children nodes
DFS(root.child[i], Sum + root.child[i].val)
# Given Generic Tree
root = newNode(1)
(root.child).append(newNode(2))
(root.child).append(newNode(3))
(root.child[0].child).append(newNode(4))
(root.child[1].child).append(newNode(6))
(root.child[0].child).append(newNode(5))
(root.child[1]).child.append(newNode(7))
(root.child[1].child).append(newNode(8))
# Function Call
DFS(root, root.val)
print(maxSumPath)
# This code is contributed by rameshtravel07.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Stores the maximum sum of a path
static int maxSumPath = 0;
// Structure of a node in the tree
class Node {
public int val;
public List child;
public Node(int key)
{
val = key;
child = new List();
}
}
// Utility function to create a
// new node in the tree
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node(key);
return temp;
}
// Recursive function to calculate the
// maximum sum in a path using DFS
static void DFS(Node root, int sum)
{
// If current node is a leaf node
if (root.child.Count == 0) {
maxSumPath = Math.Max(maxSumPath, sum);
return;
}
// Traversing all children of
// the current node
for (int i = 0;
i < root.child.Count; i++) {
// Recursive call for all
// the children nodes
DFS(root.child[i],
sum + root.child[i].val);
}
}
static void Main() {
// Given Generic Tree
Node root = newNode(1);
(root.child).Add(newNode(2));
(root.child).Add(newNode(3));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode(4));
(root.child[1].child).Add(newNode(6));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode(5));
(root.child[1]).child.Add(newNode(7));
(root.child[1].child).Add(newNode(8));
// Function Call
DFS(root, root.val);
Console.Write(maxSumPath);
}
}
// This code is contributed by mukesh07. Javascript
输出:
12时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)