Java中的Java类
Java中的Java .io.FilterInputStream 类
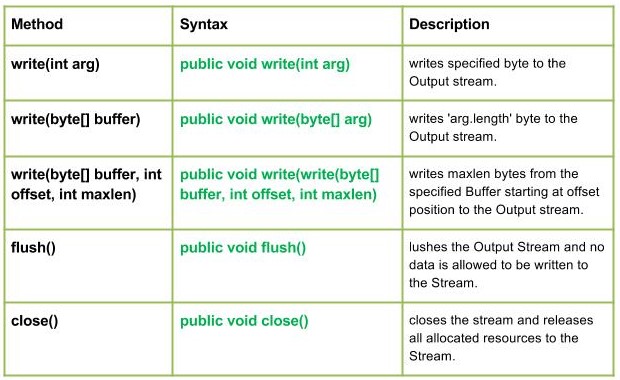
Java.io.FilterOutputStream类是所有过滤输出流的类的超类。 FilterOutputStream 类的 write() 方法过滤数据并将其写入底层流,过滤是根据 Streams 完成的。
宣言 :
public class FilterOutputStream
extends OutputStream构造函数:
- FilterOutputStream(OutputStream geekout) :创建一个输出流过滤器。
方法:
- write(int arg) : Java.io.FilterOutputStream.write(int arg)将指定字节写入输出流。
句法 :
public void write(int arg)
Parameters :
arg : Source Bytes
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.- 执行 :
Java
// Java program illustrating the working of work(int arg)
// method
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// OutputStream, FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream
// initially null
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
// FileInputStream used here
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
char c;
int a;
try
{
// create output streams
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("GEEKS.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
// write(int arg) : Used to write 'M' in the file
// - "ABC.txt"
geek_filter.write(77);
// Flushes the Output Stream
geek_filter.flush();
// Creating Input Stream
geekinput = new FileInputStream("GEEKS.txt");
// read() method of FileInputStream :
// reading the bytes and converting next bytes to int
a = geekinput.read();
/* Since, read() converts bytes to int, so we
convert int to char for our program output*/
c = (char)a;
// print character
System.out.println("Character written by" +
" FilterOutputStream : " + c);
}
catch(IOException except)
{
// if any I/O error occurs
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally{
// releases any system resources associated with
// the stream
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}Java
// Java program illustrating the working of work(byte
// buffer) method
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// OutputStream, FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream
// initially null
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
// FileInputStream used here
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
byte[] buffer = {77, 79, 72, 73, 84};
char c;
int a;
try
{
// create output streams
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
// writes buffer to the output stream
geek_filter.write(buffer);
// forces byte contents to written out to the stream
geek_filter.flush();
// create input streams
geekinput = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
while ((a=geekinput.read())!=-1)
{
// converts integer to the character
c = (char)a;
// prints
System.out.print(c);
}
}
catch(IOException except)
{
// if any I/O error occurs
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally
{
// releases any system resources associated
// with the stream
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}Java
// Java program illustrating the working of
// write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen),
// flush(), close() method
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// OutputStream, FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream
// initially null
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
// FileInputStream used here
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
byte[] buffer = {65, 66, 77, 79, 72, 73, 84};
char c;
int a;
try
{
// create output streams
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
// write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) :
// writes buffer to the output stream
// Here offset = 2, so it won't read first two bytes
// then maxlen = 5, so it will print max of 5 characters
geek_filter.write(buffer, 2, 5);
// forces byte contents to written out to the stream
geek_filter.flush();
// create input streams
geekinput = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
while ((a = geekinput.read())!=-1)
{
// converts integer to the character
c = (char)a;
// prints
System.out.print(c);
}
}
catch(IOException except)
{
// if any I/O error occurs
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally
{
// releases any system resources associated
// with the stream
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}- 笔记 :
在我使用GEEKS.txt文件的程序中,该程序将创建一个新文件,其名称为代码中给出的名称并写入其中。
输出 :
Character written by FilterOutputStream : M- write(byte[] buffer) : Java.io.FilterOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer)将'arg.length'字节写入输出流。
句法 :
public void write(byte[] arg)
Parameters :
buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.- 执行 :
Java
// Java program illustrating the working of work(byte
// buffer) method
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// OutputStream, FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream
// initially null
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
// FileInputStream used here
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
byte[] buffer = {77, 79, 72, 73, 84};
char c;
int a;
try
{
// create output streams
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
// writes buffer to the output stream
geek_filter.write(buffer);
// forces byte contents to written out to the stream
geek_filter.flush();
// create input streams
geekinput = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
while ((a=geekinput.read())!=-1)
{
// converts integer to the character
c = (char)a;
// prints
System.out.print(c);
}
}
catch(IOException except)
{
// if any I/O error occurs
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally
{
// releases any system resources associated
// with the stream
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}
- 笔记 :
在我使用GEEKS.txt文件的程序中,程序将创建一个代码中给出的名称的新文件并写入其中。
输出 :
MOHIT- write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) : Java.io.FilterOutputStream.write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)将 maxlen 个字节从指定的 Buffer 开始从偏移位置写入输出流。
句法 :
public void write(write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)
Parameters :
buffer : Source Buffer to be written to the Output Stream
Return :
buffer : Source Buffer to be written
offset : Starting offset
maxlen : max no. of bytes to bewriten to the Output Stream
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.- flush() : Java.io.FilterOutputStream.flush()刷新输出流,不允许将数据写入流。
句法 :
public void flush()
Parameters :
------
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.- close() : Java.io.FilterOutputStream.close()关闭流并将所有分配的资源释放到流。
句法 :
public void close()
Parameters :
------
Return :
void
Exception :
In case any I/O error occurs.Java程序说明:write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen), flush(), close() 方法
Java
// Java program illustrating the working of
// write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen),
// flush(), close() method
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// OutputStream, FileInputStream & FilterOutputStream
// initially null
OutputStream geek_out = null;
FilterOutputStream geek_filter = null;
// FileInputStream used here
FileInputStream geekinput = null;
byte[] buffer = {65, 66, 77, 79, 72, 73, 84};
char c;
int a;
try
{
// create output streams
geek_out = new FileOutputStream("ABC.txt");
geek_filter = new FilterOutputStream(geek_out);
// write(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) :
// writes buffer to the output stream
// Here offset = 2, so it won't read first two bytes
// then maxlen = 5, so it will print max of 5 characters
geek_filter.write(buffer, 2, 5);
// forces byte contents to written out to the stream
geek_filter.flush();
// create input streams
geekinput = new FileInputStream("ABC.txt");
while ((a = geekinput.read())!=-1)
{
// converts integer to the character
c = (char)a;
// prints
System.out.print(c);
}
}
catch(IOException except)
{
// if any I/O error occurs
System.out.print("Write Not working properly");
}
finally
{
// releases any system resources associated
// with the stream
if (geek_out != null)
geek_out.close();
if (geek_filter != null)
geek_filter.close();
}
}
}
笔记 :
在我使用GEEKS.txt文件的程序中,程序将创建一个代码中给出的名称的新文件并写入其中。
输出 :
MOHIT