带有示例的Python逻辑运算符
运算符用于对值和变量执行操作。这些是执行算术和逻辑计算的特殊符号。运算符操作的值称为Operand 。
Table of Content
- Logical operators
- Logical AND operator
- Logical OR operator
- Logical NOT operator
- Order of evaluation of logical operators
逻辑运算符
在Python中,逻辑运算符用于条件语句(真或假)。它们执行逻辑与、逻辑或和逻辑非操作。
| OPERATOR | DESCRIPTION | SYNTAX |
|---|---|---|
| and | Logical AND: True if both the operands are true | x and y |
| or | Logical OR: True if either of the operands is true | x or y |
| not | Logical NOT: True if operand is false | not x |
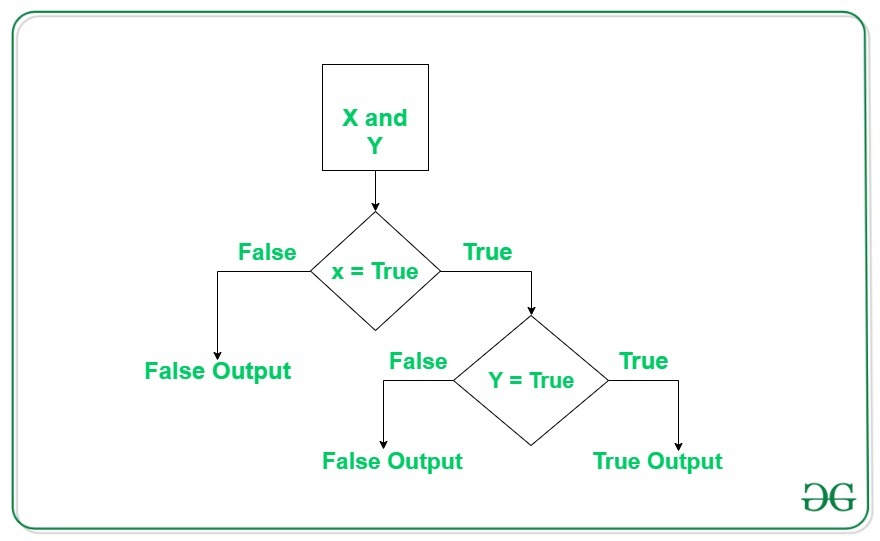
逻辑与运算符
如果两个操作数都为 True ,则逻辑运算符返回True ,否则返回False 。
示例 #1:
# Python program to demonstrate
# logical and operator
a = 10
b = 10
c = -10
if a > 0 and b > 0:
print("The numbers are greater than 0")
if a > 0 and b > 0 and c > 0:
print("The numbers are greater than 0")
else:
print("Atleast one number is not greater than 0")
输出:
The numbers are greater than 0
Atleast one number is not greater than 0
示例 #2:
# Python program to demonstrate
# logical and operator
a = 10
b = 12
c = 0
if a and b and c:
print("All the numbers have boolean value as True")
else:
print("Atleast one number has boolean value as False")
输出:
Atleast one number has boolean value as False
注意:如果在使用 and运算符时第一个表达式的计算结果为 false,则不会计算其他表达式。
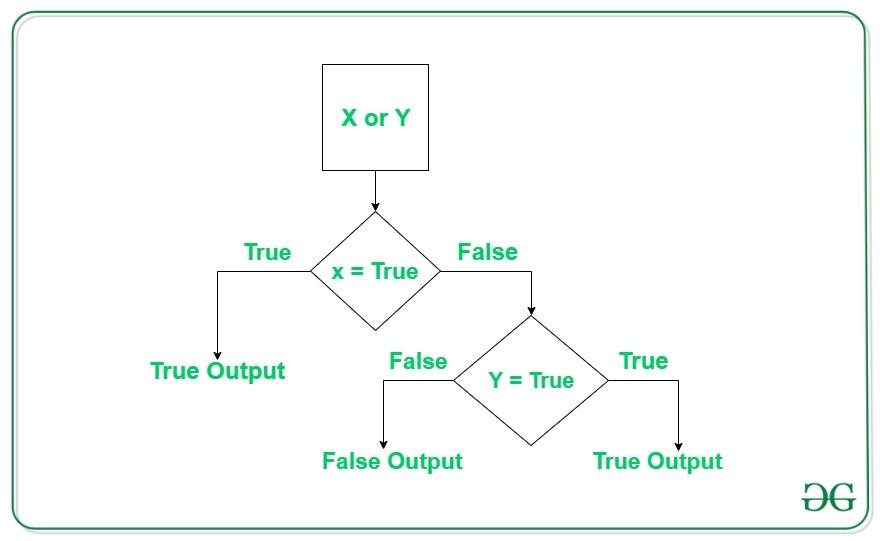
逻辑或运算符
如果任一操作数为 True,则逻辑或运算符返回 True。
示例 #1:
# Python program to demonstrate
# logical or operator
a = 10
b = -10
c = 0
if a > 0 or b > 0:
print("Either of the number is greater than 0")
else:
print("No number is greater than 0")
if b > 0 or c > 0:
print("Either of the number is greater than 0")
else:
print("No number is greater than 0")
输出:
Either of the number is greater than 0
No number is greater than 0
示例 #2:
# Python program to demonstrate
# logical and operator
a = 10
b = 12
c = 0
if a or b or c:
print("Atleast one number has boolean value as True")
else:
print("All the numbers have boolean value as False")
输出:
Atleast one number has boolean value as True
注意:如果在使用 or运算符时第一个表达式的计算结果为 True,则不会计算进一步的表达式。
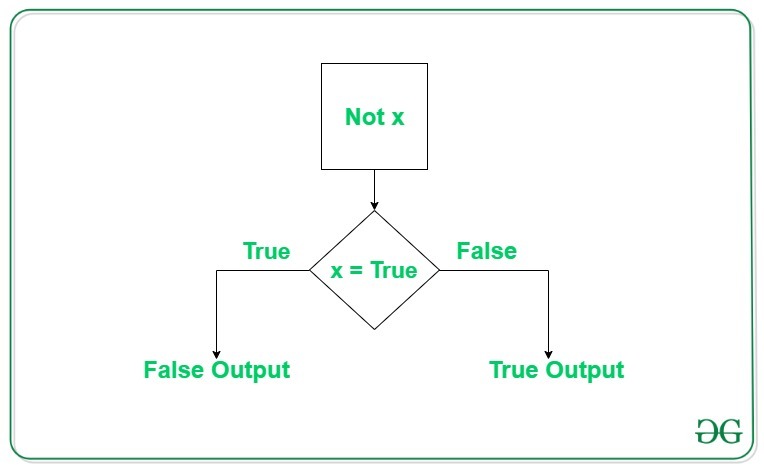
逻辑非运算符
逻辑非运算符使用单个布尔值。如果布尔值为True ,则返回False ,反之亦然。
例子:
# Python program to demonstrate
# logical not operator
a = 10
if not a:
print("Boolean value of a is True")
if not (a%3 == 0 or a%5 == 0):
print("10 is not divisible by either 3 or 5")
else:
print("10 is divisible by either 3 or 5")
输出:
10 is divisible by either 3 or 5
逻辑运算符的求值顺序
在多个运算符的情况下, Python总是从左到右计算表达式。这可以通过下面的例子来验证。
例子:
# Python program to demonstrate
# order of evaluation of logical
# operators
def order(x):
print("Method called for value:", x)
return True if x > 0 else False
a = order
b = order
c = order
if a(-1) or b(5) or c(10):
print("Atleast one of the number is positive")
输出:
Method called for value: -1
Method called for value: 5
Atleast one of the number is positive