Django REST Framework 中的可浏览 API
Django REST 框架中的可浏览 API 功能为不同的资源生成 HTML 输出。它有助于通过任何 Web 浏览器与 RESTful Web 服务进行交互。要启用此功能,我们应该为请求标头中的 Content-Type 键指定 text/html。它帮助我们使用 Web 浏览器浏览 API 并可以发出不同的 HTTP 请求。在本节中,我们将使用 Django REST API 框架中的可浏览 API 功能。
To check how to setup Django RESt Framework and create a API visit – How to Create a basic API using Django Rest Framework ?
创建一个简单的项目来演示可浏览的 API——
让我们创建应用程序机器人所需的模型、序列化程序和视图。
创建模型
在 Django 中,模型是以面向对象的方式处理数据库的类。每个模型类引用一个数据库表,模型类中的每个属性引用一个数据库列。在这里,我们将创建以下模型:
- RobotCategory(机器人类别)
- 制造商(制造商详细信息)
- 机器人(机器人详情)
RobotCategory 模型需要:
- 机器人类别名称
制造商模型要求:
- 生产商名称
机器人模型需要:
- 机器人名称
- RobotCategory 模型的外键
- 制造商模型的外键
- 货币
- 价钱
- 生产日期
让我们看看我们的机器人 Restful Web 服务中的 HTTP 动词、范围语义。HTTP Verb Scope Semantics URL GET Robot Category Retrieve a Robot Category http://localhost:8000/robocategory/{id}/ GET Collection of Robot Category Retrieve all Robot Category in the collection http://localhost:8000/robocategory/ POST Collection of Robot Category Create a new Robot Category in the collection http://localhost:8000/robocategory/{id}/ PUT Robot Category Update a Robot Category http://localhost:8000/robocategory/{id}/ DELETE Robot Category Delete a Robot Category http://localhost:8000/robocategory/{id}/ GET Manufacturer Retrieve a Manufacturer http://localhost:8000/manufacturer/{id}/ GET Collection of Manufacturer Retrieve all Manufacturer in the collection http://localhost:8000/manufacturer/ POST Collection of Manufacturer Create a Manufacturer in the collection http://localhost:8000/manufacturer/{id}/ PUT Manufacturer Update a Manufacturer http://localhost:8000/manufacturer/{id}/ DELETE Manufacturer Delete a Manufacturer http://localhost:8000/manufacturer/{id}/ GET Robot Retrieve a Robot http://localhost:8000/robot/{id}/ GET Collection of Robot Retrieve all Robot in the collection http://localhost:8000/robot/ POST Collection of Robot Create a Robot in the collection http://localhost:8000/robot/{id}/ PUT Robot Update a Robot http://localhost:8000/robot/{id}/ DELETE Robot Delete a Robot http://localhost:8000/robot/{id}/
让我们为机器人类别、制造商、机器人及其关系创建模型。您可以在 models.py 文件中添加以下代码。
Python3
from django.db import models
class RobotCategory(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=150, unique=True)
class Meta:
ordering = ('name',)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Manufacturer(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=150, unique=True)
class Meta:
ordering = ('name',)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Robot(models.Model):
CURRENCY_CHOICES = (
('INR', 'Indian Rupee'),
('USD', 'US Dollar'),
('EUR', 'Euro'),
)
name = models.CharField(max_length=150, unique=True)
robot_category = models.ForeignKey(
RobotCategory,
related_name='robots',
on_delete=models.CASCADE)
manufacturer = models.ForeignKey(
Manufacturer,
related_name='robots',
on_delete=models.CASCADE)
currency = models.CharField(
max_length=3,
choices= CURRENCY_CHOICES,
default='INR')
price = models.IntegerField()
manufacturing_date = models.DateTimeField()
class Meta:
ordering = ('name',)
def __str__(self):
return self.namePython3
from rest_framework import serializers
from robots.models import RobotCategory, Manufacturer, Robot
class RobotCategorySerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
robots = serializers.HyperlinkedRelatedField(
many=True,
read_only=True,
view_name='robot-detail')
class Meta:
model = RobotCategory
fields = '__all__'
class ManufacturerSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
robots = serializers.HyperlinkedRelatedField(
many=True,
read_only=True,
view_name='robot-detail')
class Meta:
model = Manufacturer
fields = '__all__'
class RobotSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
robot_category = serializers.SlugRelatedField(
queryset=RobotCategory.objects.all(), slug_field='name')
manufacturer = serializers.SlugRelatedField(
queryset=Manufacturer.objects.all(), slug_field='name')
currency = serializers.ChoiceField(
choices=Robot.CURRENCY_CHOICES)
currency_name = serializers.CharField(
source='get_currency_display',
read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = Robot
fields = '__all__'Python3
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework import generics
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.reverse import reverse
from robots.models import RobotCategory, Manufacturer, Robot
from robots.serializers import RobotCategorySerializer, \
ManufacturerSerializer, RobotSerializer
class ApiRoot(generics.GenericAPIView):
name = 'api-root'
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return Response({
'robot-categories': reverse(RobotCategoryList.name, request=request),
'manufacturers': reverse(ManufacturerList.name, request=request),
'robots': reverse(RobotList.name, request=request)
})
class RobotCategoryList(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = RobotCategory.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotCategorySerializer
name = 'robotcategory-list'
class RobotCategoryDetail(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
queryset = RobotCategory.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotCategorySerializer
name = 'robotcategory-detail'
class ManufacturerList(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = Manufacturer.objects.all()
serializer_class = ManufacturerSerializer
name= 'manufacturer-list'
class ManufacturerDetail(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
queryset = Manufacturer.objects.all()
serializer_class = ManufacturerSerializer
name = 'manufacturer-detail'
class RobotList(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = Robot.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotSerializer
name = 'robot-list'
class RobotDetail(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
queryset = Robot.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotSerializer
name = 'robot-detail'Python3
from django.urls import path
from robots import views
urlpatterns = [
path('robocategory/',
views.RobotCategoryList.as_view(),
name='robotcategory-list'),
path('robocategory//',
views.RobotCategoryDetail.as_view(),
name='robotcategory-detail'),
path('manufacturer/',
views.ManufacturerList.as_view(),
name='manufacturer-list'),
path('manufacturer//',
views.ManufacturerDetail.as_view(),
name='manufacturer-detail'),
path('robot/',
views.RobotList.as_view(),
name='robot-list'),
path('robot//',
views.RobotDetail.as_view(),
name='robot-detail'),
path('',
views.ApiRoot.as_view(),
name=views.ApiRoot.name)
] Python3
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('', include('robots.urls')),
]这里我们有三个类,它们是 django.db.models.Model 类的子类:
- 机器人类别
- 制造商
- 机器人
Robot 类与 RobotCategory 模型和制造商模型保持多对一的关系。这种关系是通过使用 django.db.models.ForeignKey 类来实现的。代码如下:
robot_category = models.ForeignKey(
RobotCategory,
related_name='robots',
on_delete=models.CASCADE)
manufacturer = models.ForeignKey(
Manufacturer,
related_name='robots',
on_delete=models.CASCADE)related_name 参数创建反向关系。此处related_name 中的值“robots”创建了从RobotCategory 到Robot 和Manufacturer 到Robot 的反向关系。这有助于获取属于机器人类别并基于制造商的所有机器人。
接下来,您可以执行迁移过程并应用所有生成的迁移。您可以使用以下命令
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
创建序列化程序
现在,我们需要序列化 RobotCategory、Manufacturer 和 Robot 实例。在这里,我们将使用 HyperlinkedModelSerializer 来处理模型关系。您可以查看 DRF Serializer Relations 主题以详细了解。
蟒蛇3
from rest_framework import serializers
from robots.models import RobotCategory, Manufacturer, Robot
class RobotCategorySerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
robots = serializers.HyperlinkedRelatedField(
many=True,
read_only=True,
view_name='robot-detail')
class Meta:
model = RobotCategory
fields = '__all__'
class ManufacturerSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
robots = serializers.HyperlinkedRelatedField(
many=True,
read_only=True,
view_name='robot-detail')
class Meta:
model = Manufacturer
fields = '__all__'
class RobotSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
robot_category = serializers.SlugRelatedField(
queryset=RobotCategory.objects.all(), slug_field='name')
manufacturer = serializers.SlugRelatedField(
queryset=Manufacturer.objects.all(), slug_field='name')
currency = serializers.ChoiceField(
choices=Robot.CURRENCY_CHOICES)
currency_name = serializers.CharField(
source='get_currency_display',
read_only=True)
class Meta:
model = Robot
fields = '__all__'
RobotCategorySerializer 和ManufacturerSerializer 类是HyperlinkedModelSerializer 类的子类,反向关系(RobotCategory 到Robot 和Manufacturer 到Robot)使用HyperlinkedRelatedField 表示,其中许多和read_only 属性设置为True。 view_name —robot-detail — 允许可浏览的 API 功能为用户提供点击工具,以呈现超链接。
RobotSerializer 类也是 HyperlinkedModelSerializer 类的子类。 RobotSerializer 类声明了两个属性——robot_category 和制造商——它们保存了一个 serializers.SlugRelatedField 的实例。 SlugRelated Field 通过唯一的 slug 属性表示关系。
创建视图
让我们利用 Django REST Framework 提供的基于类的通用视图来处理 HTTP 请求并提供适当的 HTTP 响应。您可以查看基于 DRF 类的视图以获取详细说明。
蟒蛇3
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework import generics
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.reverse import reverse
from robots.models import RobotCategory, Manufacturer, Robot
from robots.serializers import RobotCategorySerializer, \
ManufacturerSerializer, RobotSerializer
class ApiRoot(generics.GenericAPIView):
name = 'api-root'
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return Response({
'robot-categories': reverse(RobotCategoryList.name, request=request),
'manufacturers': reverse(ManufacturerList.name, request=request),
'robots': reverse(RobotList.name, request=request)
})
class RobotCategoryList(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = RobotCategory.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotCategorySerializer
name = 'robotcategory-list'
class RobotCategoryDetail(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
queryset = RobotCategory.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotCategorySerializer
name = 'robotcategory-detail'
class ManufacturerList(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = Manufacturer.objects.all()
serializer_class = ManufacturerSerializer
name= 'manufacturer-list'
class ManufacturerDetail(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
queryset = Manufacturer.objects.all()
serializer_class = ManufacturerSerializer
name = 'manufacturer-detail'
class RobotList(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = Robot.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotSerializer
name = 'robot-list'
class RobotDetail(generics.RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView):
queryset = Robot.objects.all()
serializer_class = RobotSerializer
name = 'robot-detail'
在这里,我们的视图类从 rest_framework.generics 导入,我们利用了两个基于类的通用视图——ListCreateAPIView 和 RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView。
您可以注意到 ApiRoot 类是generics.GenericAPIView的子类,它为我们的 Web 服务的根创建了一个端点。它使用可浏览的 API 功能方便浏览资源。
class ApiRoot(generics.GenericAPIView):
name = 'api-root'
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return Response({
'robot-categories': reverse(RobotCategoryList.name, request=request),
'manufacturers': reverse(ManufacturerList.name, request=request),
'robots': reverse(RobotList.name, request=request)
}) get 方法返回一个 Response 对象(作为字符串的键/值对),该对象具有视图的描述性名称及其 URL。
设置 URL Conf
转到应用程序(机器人)文件夹并创建一个名为 urls.py 的新文件。您可以添加以下代码:
蟒蛇3
from django.urls import path
from robots import views
urlpatterns = [
path('robocategory/',
views.RobotCategoryList.as_view(),
name='robotcategory-list'),
path('robocategory//',
views.RobotCategoryDetail.as_view(),
name='robotcategory-detail'),
path('manufacturer/',
views.ManufacturerList.as_view(),
name='manufacturer-list'),
path('manufacturer//',
views.ManufacturerDetail.as_view(),
name='manufacturer-detail'),
path('robot/',
views.RobotList.as_view(),
name='robot-list'),
path('robot//',
views.RobotDetail.as_view(),
name='robot-detail'),
path('',
views.ApiRoot.as_view(),
name=views.ApiRoot.name)
]
它定义了必须在请求中匹配的 URL 模式,以便为 views.py 文件中定义的基于类的视图执行特定方法。现在我们必须设置根 URL 配置。您可以添加以下代码:
蟒蛇3
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('', include('robots.urls')),
]
如何使用可浏览 API 向 API 发出请求?
让我们编写并发送 HTTP 请求以在响应中生成 text/html 内容。 RESTFul Web 服务使用 BrowsableAPIRenderer 类来生成 HTML 内容。接受 text/html 的 HTTPie 命令如下:
http -v :8000/robot/ “Accept:text/html”
分享命令提示符截图供大家参考
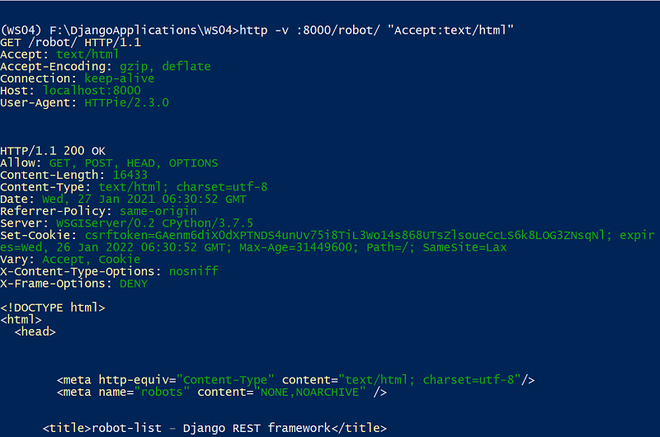
在使用可浏览 API 之前,让我们使用 HTTPie 命令为机器人类别、制造商和机器人创建一个新条目。命令如下:
http POST :8000/robocategory/ name=”Articulated Robots”
http POST :8000/manufacturer/ name=”Fanuc”
http POST :8000/robot/ name=”FANUC M-710ic/50″ robot_category=”Articulated Robots” manufacturer=”Fanuc” currency=”USD” price=37000 manufacturing_date=”2019-10-12 00:00:00+00:00″
获取 HTTP 请求
现在,让我们使用浏览器浏览“机器人”Restful Web 服务。您可以使用以下网址。
http://localhost:8000/
分享浏览器截图供大家参考
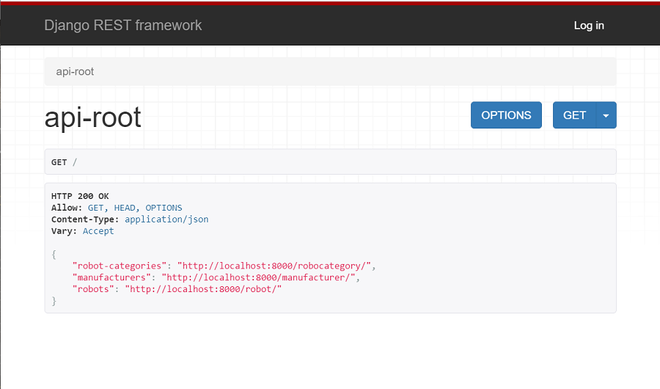
您可以点击机器人类别、制造商和机器人对应的链接并查看数据。分享显示robots结果的浏览器截图(http://localhost:8000/robot/)
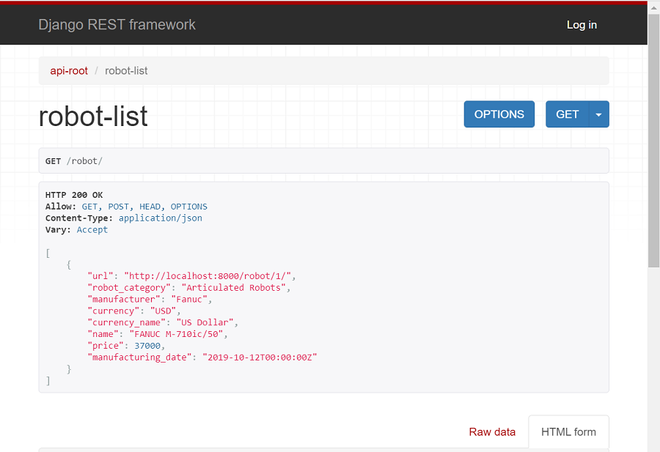
POST HTTP 请求
接下来,让我们创建一个新的机器人类别。您可以浏览以下链接并向下滚动。
http://localhost:8000/robocategory/
分享浏览器截图供大家参考
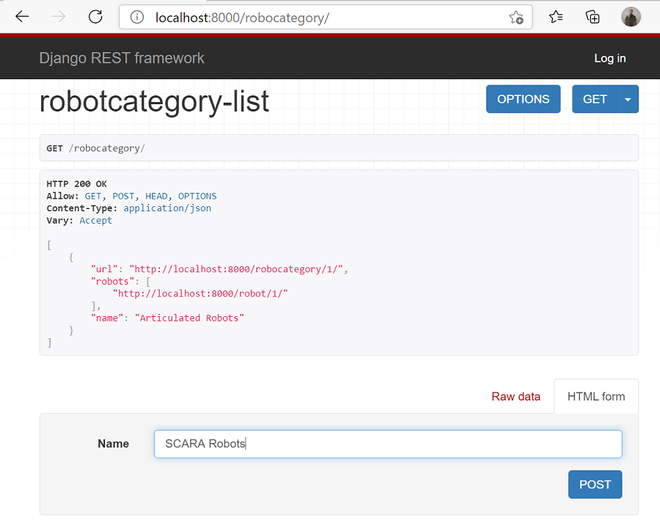
您可以键入新机器人类别的名称,然后单击 POST 按钮。在这里,它以 HTML 形式显示。如果您选择原始数据,请选择媒体类型为 application/json,将新的机器人类别名称填充到名称字段,然后单击 POST 按钮。分享截图供大家参考。
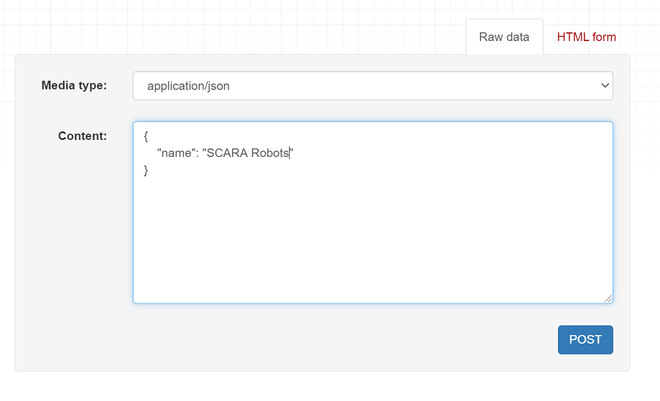
分享输出截图
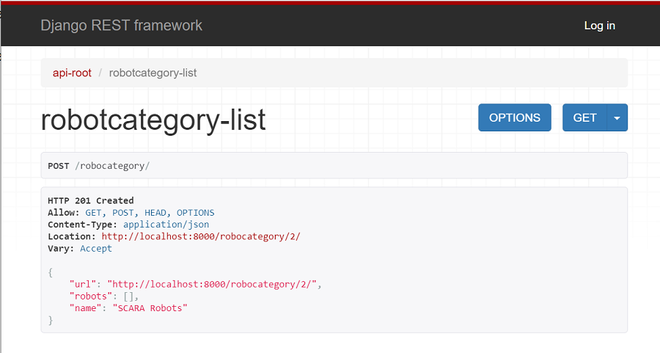
让我们创建一个新的制造商,您可以浏览以下网址
http://localhost:8000/manufacturer/
分享浏览器截图
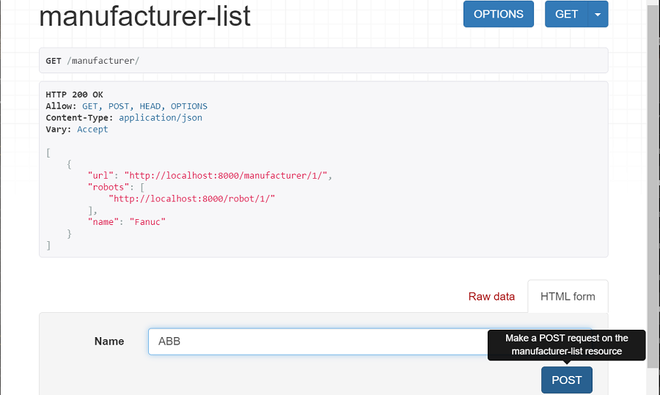
您可以输入制造商名称 (ABB) 并单击 POST 按钮。浏览器显示输出如下图
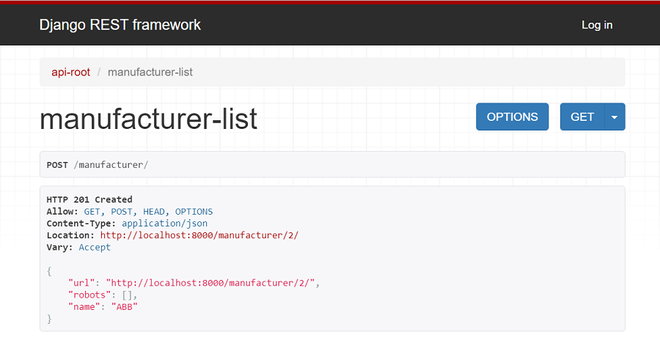
最后,让我们为机器人创建一个新条目。您可以浏览以下网址并向下滚动。
http://localhost:8000/robot/
让我们填充数据。分享浏览器截图供大家参考
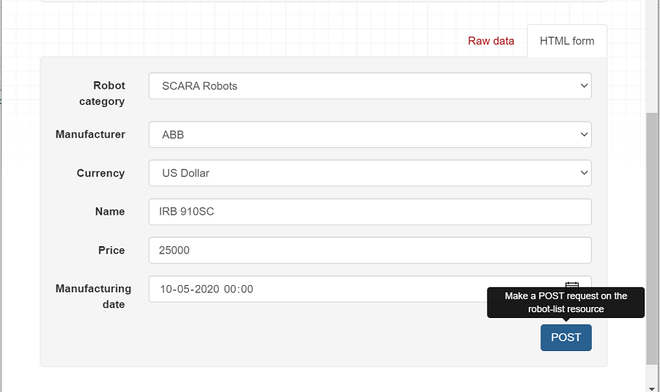
在这里,您可以注意到机器人类别、制造和货币是下拉字段。填充条目后,您可以单击 POST 按钮。在显示输出的屏幕截图下方共享。
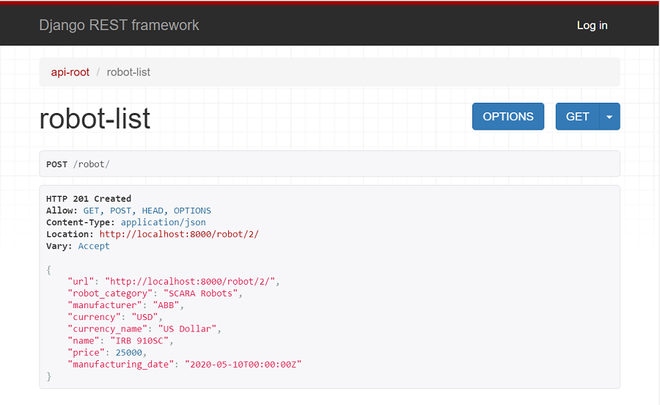
PUT HTTP 请求
让我们编辑 pk 值为 2 的机器人的价格。您可以浏览以下 URL 并向下滚动。
http://localhost:8000/robot/2/
分享浏览器截图。您可以将价格更改为 27000,然后单击 PUT 按钮。
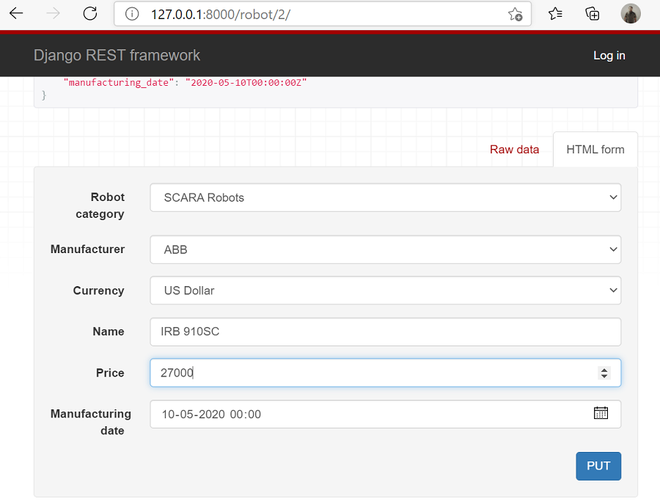
分享输出的截图。

删除 HTTP 请求
您可以创建一个新的测试条目并使用 pk 值浏览 URL。
http://localhost:8000/robot/2/
您会注意到一个 DELETE 按钮。下面分享浏览器截图:
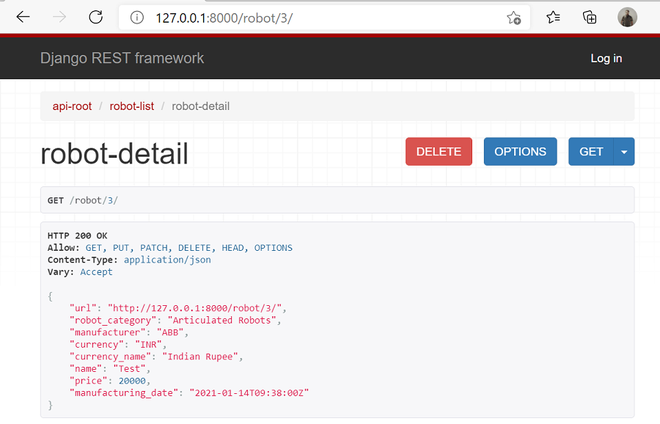
单击“删除”按钮时,浏览器会确认相同。您可以单击确认窗口中的删除按钮。下面分享截图。
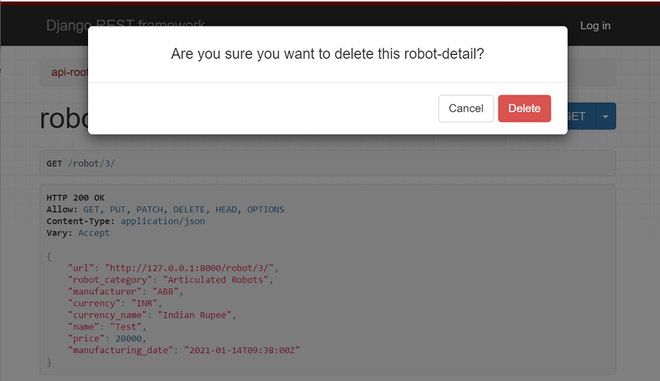
如果删除成功,则会显示以下输出。
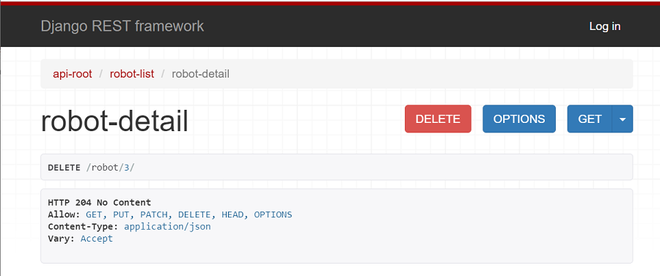
让我们总结一下
通过本节,我们了解了如何使用 Django REST API 框架中的可浏览 API 功能。我们编写并发送了生成文本/html 内容作为响应的 HTTP 请求,并在 Web 浏览器中分析了响应。