Java中的 LinkedTransferQueue 示例
Java中的LinkedTransferQueue类是Java集合框架的一部分。它是在 JDK 1.7 中引入的,属于Java.util.concurrent包。它实现了TransferQueue并提供了基于链接节点的无界功能。 LinkedTransferQueue 中的元素按 FIFO 顺序排列,头部指向队列中时间最长的元素,尾部指向队列中时间最短的元素。由于它的异步特性,size() 会遍历整个集合,所以它不是 O(1) 时间的操作。如果在遍历过程中修改了这个集合,它也可能给出不准确的大小。不能保证以原子方式执行 addAll、removeAll、retainAll、containsAll、equals 和 toArray 等批量操作。例如,与 addAll 操作同时操作的迭代器可能只观察到一些添加的元素。
LinkedTransferQueue 使用了消息传递应用程序。消息从生产者线程传递到消费者线程有两个方面。
- put(E e):如果生产者想要排队元素而不等待消费者,则使用此方法。但是,如果队列已满,它会等到空间可用。
- transfer(E e):该方法一般用于将元素传递给等待接收的线程,如果没有线程等待则等待等待线程一到达就进入等待状态元素将被转移到其中。
LinkedTransferQueue 的层次结构
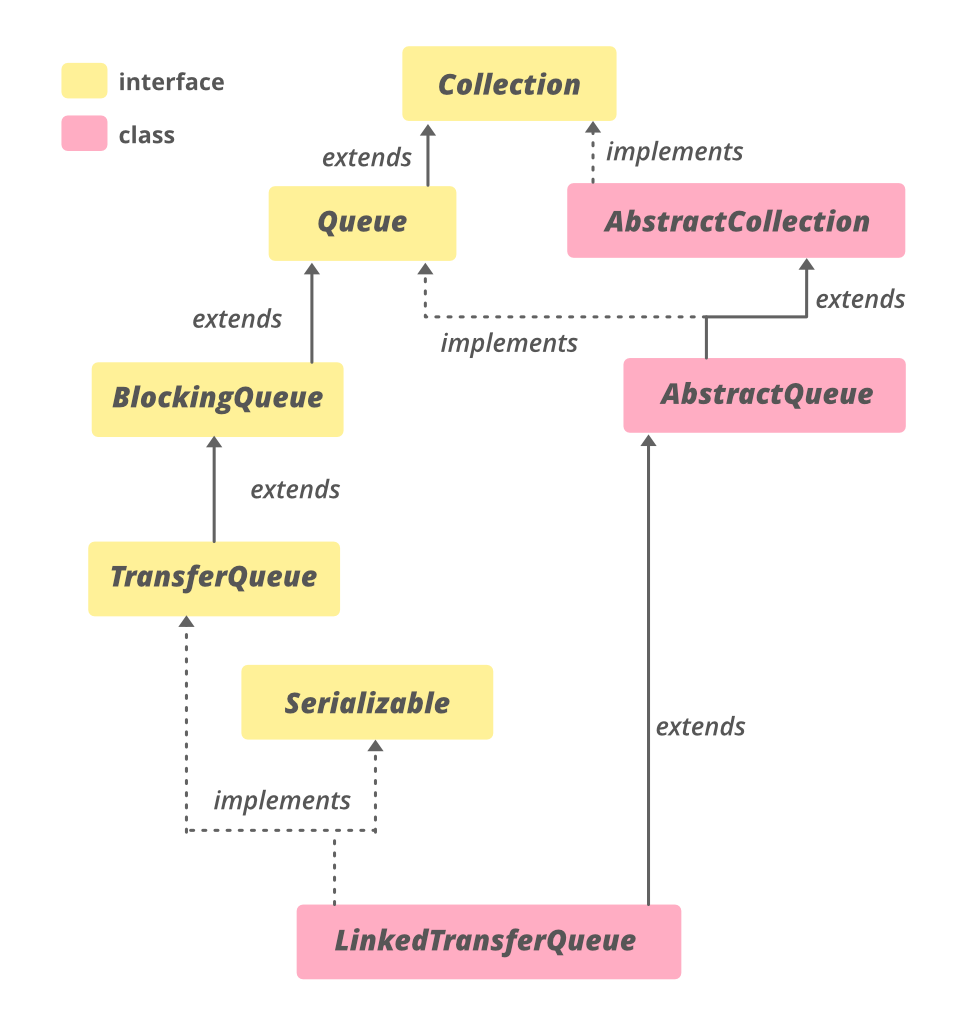
它实现了 Serializable 、 Iterable
宣言:
public class LinkedTransferQueue
这里, E是这个集合维护的元素的类型。
LinkedTransferQueue 的构造函数
为了创建 LinkedTransferQueue 的实例,我们需要从Java.util.concurrent包中导入它。
1. LinkedTransferQueue() :该构造函数用于构造一个空队列。
LinkedTransferQueue
2. LinkedTransferQueue(Collection
LinkedTransferQueue
示例 1:用Java说明 LinkedTransferQueue 的示例程序
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedTransferQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// create object of LinkedTransferQueue
// using LinkedTransferQueue() constructor
LinkedTransferQueue LTQ
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Add numbers to end of LinkedTransferQueue
LTQ.add(7855642);
LTQ.add(35658786);
LTQ.add(5278367);
LTQ.add(74381793);
// print Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue1: " + LTQ);
// create object of LinkedTransferQueue
// using LinkedTransferQueue(Collection c)
// constructor
LinkedTransferQueue LTQ2
= new LinkedTransferQueue(LTQ);
// print Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue2: " + LTQ2);
}
} Java
// Java code to illustrate
// methods of LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedTransferQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// create object of LinkedTransferQueue
LinkedTransferQueue LTQ
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Add numbers to end of LinkedTransferQueue
// using add() method
LTQ.add(7855642);
LTQ.add(35658786);
LTQ.add(5278367);
LTQ.add(74381793);
// prints the Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue: " + LTQ);
// prints the size of Queue after removal
// using size() method
System.out.println("Size of Linked Transfer Queue: "
+ LTQ.size());
// removes the front element and prints it
// using poll() method
System.out.println("First element: " + LTQ.poll());
// prints the Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue: " + LTQ);
// prints the size of Queue after removal
// using size() method
System.out.println("Size of Linked Transfer Queue: "
+ LTQ.size());
// Add numbers to end of LinkedTransferQueue
// using offer() method
LTQ.offer(20);
// prints the Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue: " + LTQ);
// prints the size of Queue after removal
// using size() method
System.out.println("Size of Linked Transfer Queue: "
+ LTQ.size());
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate adding
// elements to LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the queue
LinkedTransferQueue queue
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Adding elements to this queue
for (int i = 10; i <= 14; i++)
queue.add(i);
// Add the element using offer() method
System.out.println("adding 15 "
+ queue.offer(15, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// Adding elements to this queue
for (int i = 16; i <= 20; i++)
queue.put(i);
// Printing the elements of the queue
System.out.println(
"The elements in the queue are:");
for (Integer i : queue)
System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
// create another queue to demonstrate transfer
// method
LinkedTransferQueue g
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run()
{
try {
System.out.println("Transferring"
+ " an element");
// Transfer a String element
// using transfer() method
g.transfer("is a computer"
+ " science portal.");
System.out.println(
"Element "
+ "transfer is complete");
}
catch (InterruptedException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
}
catch (NullPointerException e2) {
System.out.println(e2);
}
}
})
.start();
try {
// Get the transferred element
System.out.println("Geeks for Geeks "
+ g.take());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate removing
// elements of LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
class RemoveElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the queue
LinkedTransferQueue queue
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Adding elements to this queue
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
queue.add(i);
// Printing the elements of the queue
System.out.println(
"The elements in the queue are:");
for (Integer i : queue)
System.out.print(i + " ");
// remove() method will remove the specified
// element from the queue
queue.remove(1);
queue.remove(5);
// Printing the elements of the queue
System.out.println("\nRemaining elements in queue : ");
for (Integer i : queue)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
} Java
// Java Program Demonstrate iterating
// over LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
class LinkedTransferQueueIteratorExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the queue
LinkedTransferQueue queue
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Adding elements to this queue
queue.add("Gfg");
queue.add("is");
queue.add("fun!!");
// Returns an iterator over the elements
Iterator iterator = queue.iterator();
// Printing the elements of the queue
while (iterator.hasNext())
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
} Linked Transfer Queue1: [7855642, 35658786, 5278367, 74381793]
Linked Transfer Queue2: [7855642, 35658786, 5278367, 74381793]示例 2:
Java
// Java code to illustrate
// methods of LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedTransferQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException
{
// create object of LinkedTransferQueue
LinkedTransferQueue LTQ
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Add numbers to end of LinkedTransferQueue
// using add() method
LTQ.add(7855642);
LTQ.add(35658786);
LTQ.add(5278367);
LTQ.add(74381793);
// prints the Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue: " + LTQ);
// prints the size of Queue after removal
// using size() method
System.out.println("Size of Linked Transfer Queue: "
+ LTQ.size());
// removes the front element and prints it
// using poll() method
System.out.println("First element: " + LTQ.poll());
// prints the Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue: " + LTQ);
// prints the size of Queue after removal
// using size() method
System.out.println("Size of Linked Transfer Queue: "
+ LTQ.size());
// Add numbers to end of LinkedTransferQueue
// using offer() method
LTQ.offer(20);
// prints the Queue
System.out.println("Linked Transfer Queue: " + LTQ);
// prints the size of Queue after removal
// using size() method
System.out.println("Size of Linked Transfer Queue: "
+ LTQ.size());
}
}
Linked Transfer Queue: [7855642, 35658786, 5278367, 74381793]
Size of Linked Transfer Queue: 4
First element: 7855642
Linked Transfer Queue: [35658786, 5278367, 74381793]
Size of Linked Transfer Queue: 3
Linked Transfer Queue: [35658786, 5278367, 74381793, 20]
Size of Linked Transfer Queue: 4基本操作
1.添加元素
LinkedTransferQueue 提供了多种方法来添加或插入元素。它们是add(E e)、put(E e)、offer(E e)、transfer(E e)。当 transfer() 等待一个或多个接收线程时,add、put 和 offer 方法不关心是否有其他线程访问队列。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate adding
// elements to LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.concurrent.*;
class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the queue
LinkedTransferQueue queue
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Adding elements to this queue
for (int i = 10; i <= 14; i++)
queue.add(i);
// Add the element using offer() method
System.out.println("adding 15 "
+ queue.offer(15, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
// Adding elements to this queue
for (int i = 16; i <= 20; i++)
queue.put(i);
// Printing the elements of the queue
System.out.println(
"The elements in the queue are:");
for (Integer i : queue)
System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
// create another queue to demonstrate transfer
// method
LinkedTransferQueue g
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run()
{
try {
System.out.println("Transferring"
+ " an element");
// Transfer a String element
// using transfer() method
g.transfer("is a computer"
+ " science portal.");
System.out.println(
"Element "
+ "transfer is complete");
}
catch (InterruptedException e1) {
System.out.println(e1);
}
catch (NullPointerException e2) {
System.out.println(e2);
}
}
})
.start();
try {
// Get the transferred element
System.out.println("Geeks for Geeks "
+ g.take());
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
adding 15 true
The elements in the queue are:
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
Transferring an element
Geeks for Geeks is a computer science portal.
Element transfer is complete2. 移除元素
LinkedTransferQueue 提供的 remove() 方法用于删除该队列中存在的元素。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate removing
// elements of LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
class RemoveElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the queue
LinkedTransferQueue queue
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Adding elements to this queue
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
queue.add(i);
// Printing the elements of the queue
System.out.println(
"The elements in the queue are:");
for (Integer i : queue)
System.out.print(i + " ");
// remove() method will remove the specified
// element from the queue
queue.remove(1);
queue.remove(5);
// Printing the elements of the queue
System.out.println("\nRemaining elements in queue : ");
for (Integer i : queue)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
The elements in the queue are:
1 2 3 4 5
Remaining elements in queue :
2 3 4 3. 迭代
LinkedTransferQueue 的 iterator() 方法用于以正确的顺序返回此队列中元素的迭代器。
Java
// Java Program Demonstrate iterating
// over LinkedTransferQueue
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
class LinkedTransferQueueIteratorExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the queue
LinkedTransferQueue queue
= new LinkedTransferQueue();
// Adding elements to this queue
queue.add("Gfg");
queue.add("is");
queue.add("fun!!");
// Returns an iterator over the elements
Iterator iterator = queue.iterator();
// Printing the elements of the queue
while (iterator.hasNext())
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
}
Gfg is fun!!
LinkedTransferQueue 的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this queue contains the specified element. |
| drainTo(Collection c) | Removes all available elements from this queue and adds them to the given collection. |
| drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements) | Removes at most the given number of available elements from this queue and adds them to the given collection. |
| forEach(Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this queue contains no elements. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue in proper sequence. |
| offer(E e) | Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue. |
| offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue. |
| put(E e) | Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue. |
| remainingCapacity() | Always returns Integer.MAX_VALUE because a LinkedTransferQueue is not capacity constrained. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue, if it is present. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | Removes all of this collection’s elements that are also contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| retainAll(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| size() | Returns the number of elements in this queue. |
| spliterator() | Returns a Spliterator over the elements in this queue. |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in proper sequence. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in proper sequence; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| transfer(E e) | Transfers the element to a consumer, waiting if necessary to do so. |
| tryTransfer(E e) | Transfers the element to a waiting consumer immediately, if possible. |
| tryTransfer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | Transfers the element to a consumer if it is possible to do so before the timeout elapses. |
在类Java.util.AbstractQueue 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this queue. |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this queue. |
| element() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. |
| remove() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. |
在类Java.util.AbstractCollection 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this collection. |
在接口Java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, waiting up to the specified wait time if necessary for an element to become available. |
| take() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, waiting if necessary until an element becomes available. |
在接口Java.util.Collection 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this collection (optional operation). |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this collection (optional operation). |
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this collection for equality. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this collection. |
| parallelStream() | Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
| stream() | Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
| toArray(IntFunction | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection, using the provided generator function to allocate the returned array. |
在接口Java.util.Queue 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| element() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. |
| peek() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| poll() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| remove() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. |
在接口Java .util.concurrent.TransferQueue 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| getWaitingConsumerCount() | Returns an estimate of the number of consumers waiting to receive elements via BlockingQueue.take() or timed poll. |
| hasWaitingConsumer() | Returns true if there is at least one consumer waiting to receive an element via BlockingQueue.take() or timed poll. |
参考: Java : Java