Java中的泛化和专业化
普通班?
粗略地说,一个讲述主要特征但不讲述具体细节的类。位于继承层次结构顶部的类可以说是General。
具体类?
一个非常特殊并说明具体细节的类。位于继承层次结构底部的类可以说是特定的。
示例 1:
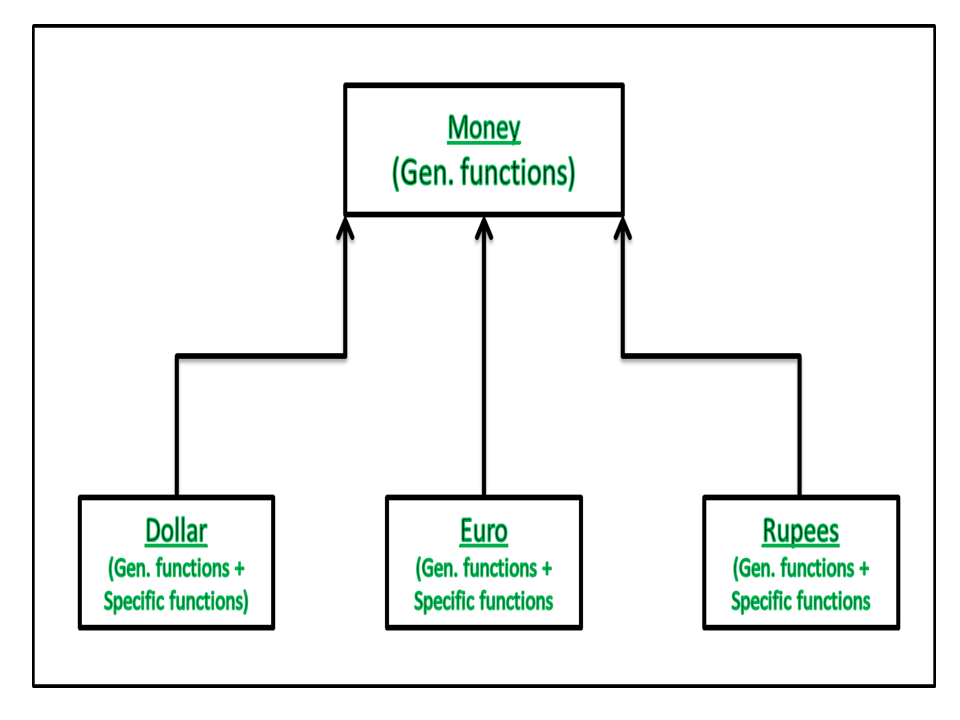 相对一般类别:货币相对特定类别:美元、欧元、卢比
相对一般类别:货币相对特定类别:美元、欧元、卢比
示例 2:
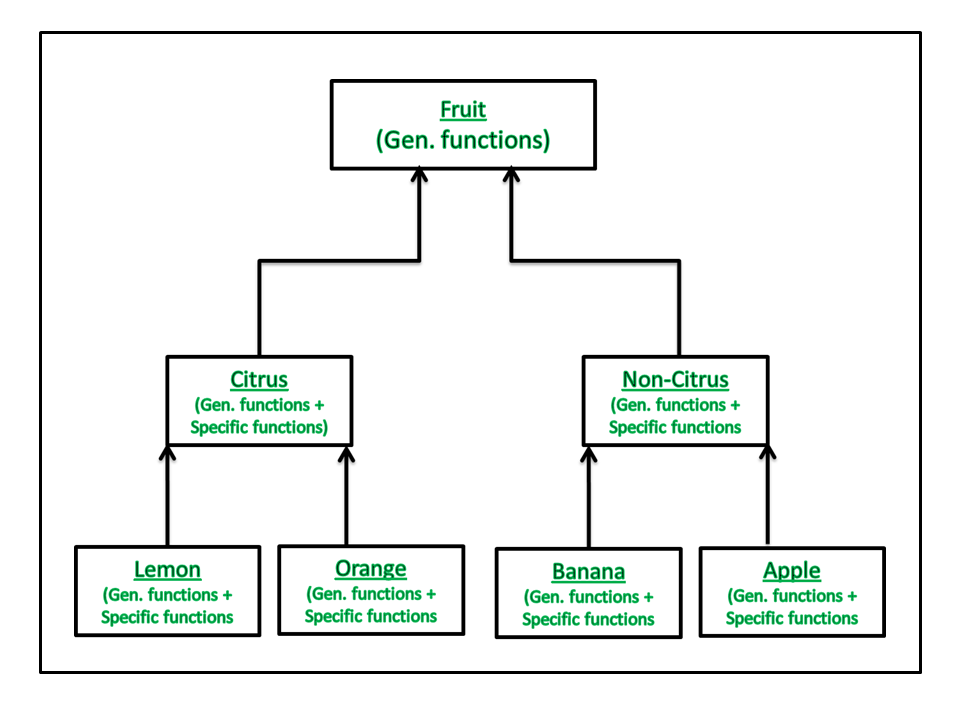 柠檬、橙子比柑橘类更具体香蕉、苹果比非柑橘类柑橘类更具体、非柑橘类比水果更具体水果是最普通的类
柠檬、橙子比柑橘类更具体香蕉、苹果比非柑橘类柑橘类更具体、非柑橘类比水果更具体水果是最普通的类
将一种类类型转换为另一种类类型?
我们可以在Java中将对一种类类型的引用转换为另一种类类型。但是为了发生转换,类应该通过继承的方式相互关联。
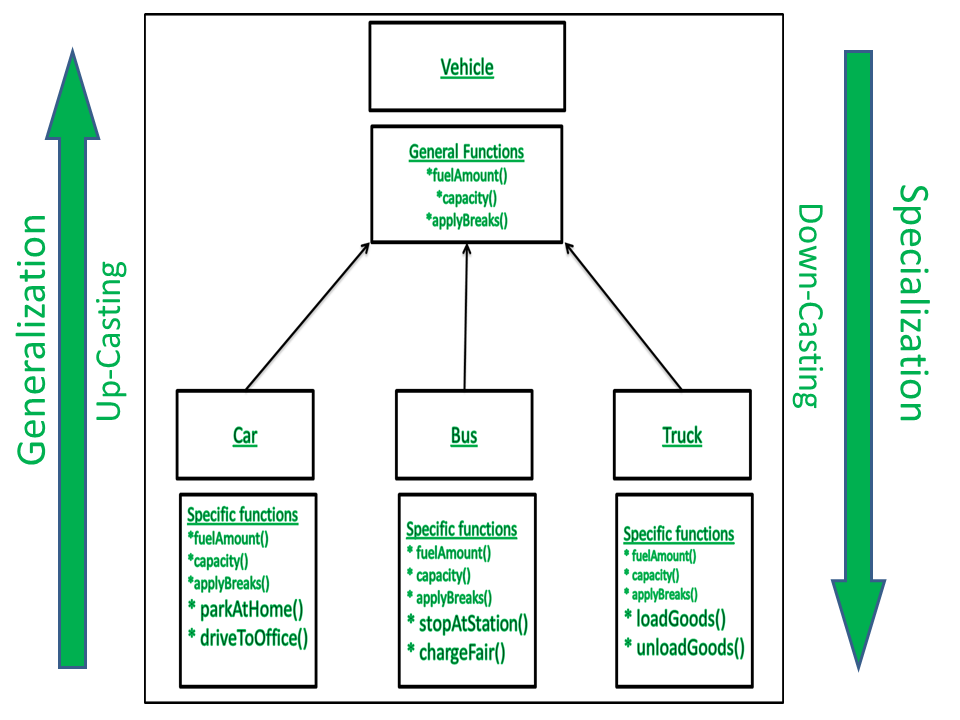
所以,
- Vehicle 和 Bus 的引用可以相互转换。
- Vehicle 和 Car 的引用可以相互转换。
- Vehicle 和 Truck 的引用可以相互转换。
- Bus、Car 和 Truck 的引用不能相互转换。
概括
将子类类型转换为超类类型称为“泛化”,因为我们正在使子类变得更加通用并且其范围正在扩大。这也称为加宽或上铸。扩大是安全的,因为类将变得更加普遍。
例如,如果我们说 Car 是 Vehicle,则不会有异议。因此, Java编译器在泛化时不会要求强制转换运算符。
例子:
Java
class Father {
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
public void play()
{
System.out.println("Enjoying son");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// father is a superclass reference
Father father;
// new operator returns a subclass reference
father = (Father) new Son();
// which is widened using casting
// and stored in father variable
// Though casting is done but it is not needed
father.work();
// Uncomment next line to see the error
// father.play();
}
}Java
class Father {
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
@Override
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Son");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// father is the super class reference
Father father;
// new operator returns a subclass reference
father = (Father) new Son();
// which is widened using casting
// and stored in father variable
// Though casting is done but it is not needed
// subclass method is invoked
father.work();
}
}Java
class Father {
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
public void play()
{
System.out.println("Enjoying son");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
// son is a sub class reference
Son son;
// new operator returns a superclass reference
// which is narrowed using casting
// and stored in son variable
// This will throw exception
son = (Son) new Father();
// Through a narrowed reference of the superclass
// we can neither access superclass method
// and nor the subclass methods
// Below lines will show
// an error when uncommented
// son.work();
// son.play();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}Java
class Father {
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
public void play()
{
System.out.println("Enjoying son");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// son is a subclass reference
Father father;
// new operator returns a subclass reference
// which is stored in the father variable
// father stores a Father class reference
// because of implicit casting
father = new Son();
// father is narrowed
Son son = (Son)father;
son.work(); // works well
son.play(); // works well
}
}输出:
Earning Father
因此,在扩展或泛化中,我们可以访问所有超类方法,但不能访问子类方法。
示例:现在假设我们覆盖子类中的超类方法
Java
class Father {
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
@Override
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Son");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// father is the super class reference
Father father;
// new operator returns a subclass reference
father = (Father) new Son();
// which is widened using casting
// and stored in father variable
// Though casting is done but it is not needed
// subclass method is invoked
father.work();
}
}
输出:
Earning Son
专业化
将超类类型转换为子类类型称为“专业化”。在这里,我们从更一般的形式下降到特定的形式,因此范围缩小了。因此,这称为缩小或向下投射。
缩小范围并不安全,因为类别将变得越来越具体,从而引起越来越多的疑问。例如,如果我们说 Vehicle 是 Car,我们需要一个证明。因此,在这种情况下, Java编译器专门要求进行强制转换。这称为显式转换。
示例:在不允许窄化时显示
Java
class Father {
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
public void play()
{
System.out.println("Enjoying son");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
// son is a sub class reference
Son son;
// new operator returns a superclass reference
// which is narrowed using casting
// and stored in son variable
// This will throw exception
son = (Son) new Father();
// Through a narrowed reference of the superclass
// we can neither access superclass method
// and nor the subclass methods
// Below lines will show
// an error when uncommented
// son.work();
// son.play();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
java.lang.ClassCastException: Father cannot be cast to Son
例子:
Java
class Father {
public void work()
{
System.out.println("Earning Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
public void play()
{
System.out.println("Enjoying son");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// son is a subclass reference
Father father;
// new operator returns a subclass reference
// which is stored in the father variable
// father stores a Father class reference
// because of implicit casting
father = new Son();
// father is narrowed
Son son = (Son)father;
son.work(); // works well
son.play(); // works well
}
}
输出:
Earning Father
Enjoying son
结论:
- 当超类引用(指超类对象)被缩小时,使用该引用我们既不能访问子类的方法也不能访问超类的方法。
- 当子类引用(指子类对象)被扩大然后再次缩小时,使用该引用我们可以访问子类以及超类的所有方法。这与简单的基类引用相同,即引用超类方法已被继承的基类对象。