Solidity – 数组
数组是存储相同数据类型元素的固定集合的数据结构,其中每个元素都有一个称为索引的特定位置。我们不需要创建许多相同类型的单独变量,而是声明一个所需大小的数组并将元素存储在数组中,并且可以使用索引进行访问。在 Solidity 中,数组可以是固定大小或动态大小。数组有一个连续的内存位置,其中最低的索引对应于第一个元素,而最高的表示最后一个元素
创建一个数组
要在 Solidity 中声明数组,应指定元素的数据类型和元素的数量。数组的大小必须是正整数并且数据类型应该是有效的 Solidity 类型
句法:
[size] =
固定大小的数组
数组的大小应该是预定义的。元素的总数不应超过数组的大小。如果未指定数组的大小,则创建足够大小的数组,足以容纳初始化。
示例:在下面的示例中,创建了合约类型来演示如何声明和初始化固定大小的数组。
Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// creating a fixed-size array
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Declaring state variables
// of type array
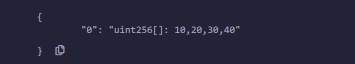
uint[6] data1;
// Defining function to add
// values to an array
function array_example() public returns (
int[5] memory, uint[6] memory){
int[5] memory data
= [int(50), -63, 77, -28, 90];
data1
= [uint(10), 20, 30, 40, 50, 60];
return (data, data1);
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// creating a dynamic array
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Declaring state variable
// of type array. One is fixed-size
// and the other is dynamic array
uint[] data
= [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
int[] data1;
// Defining function to
// assign values to dynamic array
function dynamic_array() public returns(
uint[] memory, int[] memory){
data1
= [int(-60), 70, -80, 90, -100, -120, 140];
return (data, data1);
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// accessing elements of an array
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Declaring an array
uint[6] data;
// Defining function to
// assign values to array
function array_example(
) public payable returns (uint[6] memory){
data
= [uint(10), 20, 30, 40, 50, 60];
return data;
}
// Defining function to access
// values from the array
// from a specific index
function array_element(
) public payable returns (uint){
uint x = data[2];
return x;
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// how to find length of an array
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Declaring an array
uint[6] data;
// Defining a function to
// assign values to an array
function array_example(
) public payable returns (uint[6] memory){
data = [uint(10), 20, 30, 40, 50, 60];
return data;
}
// Defining a function to
// find the length of the array
function array_length(
) public returns(uint) {
uint x = data.length;
return x;
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Push operation
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Defining the array
uint[] data = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
// Defining the function to push
// values to the array
function array_push(
) public returns(uint[] memory){
data.push(60);
data.push(70);
data.push(80);
return data;
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Pop operation
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Defining an array
uint[] data
= [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
// Defining a function to
// pop values from the array
function array_pop(
) public returns(uint[] memory){
data.pop();
return data;
}
}输出 :
动态数组:
数组的大小在声明时没有预定义。随着元素的添加,数组的大小会发生变化,并且在运行时,数组的大小将被确定。
示例:在下面的示例中,创建了合约类型来演示如何创建和初始化动态数组。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// creating a dynamic array
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Declaring state variable
// of type array. One is fixed-size
// and the other is dynamic array
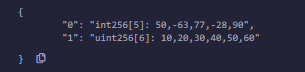
uint[] data
= [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
int[] data1;
// Defining function to
// assign values to dynamic array
function dynamic_array() public returns(
uint[] memory, int[] memory){
data1
= [int(-60), 70, -80, 90, -100, -120, 140];
return (data, data1);
}
}
输出 :
数组操作
1.访问数组元素:使用索引访问数组的元素。如果要访问第 i 个元素,则必须访问第 (i-1) 个索引。
示例:在下面的示例中,合约类型首先初始化一个数组 [数据] ,然后检索特定索引 2 处的值。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// accessing elements of an array
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Declaring an array
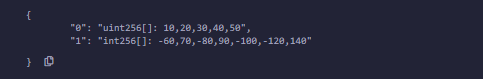
uint[6] data;
// Defining function to
// assign values to array
function array_example(
) public payable returns (uint[6] memory){
data
= [uint(10), 20, 30, 40, 50, 60];
return data;
}
// Defining function to access
// values from the array
// from a specific index
function array_element(
) public payable returns (uint){
uint x = data[2];
return x;
}
}
输出 :
2. 数组长度:数组长度用于检查数组中存在的元素数量。内存数组的大小在声明时是固定的,而动态数组是在运行时定义的,因此需要操作长度。
示例:在下面的示例中,合约类型首先初始化一个数组[数据] ,然后计算数组的长度。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// how to find length of an array
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Declaring an array
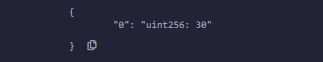
uint[6] data;
// Defining a function to
// assign values to an array
function array_example(
) public payable returns (uint[6] memory){
data = [uint(10), 20, 30, 40, 50, 60];
return data;
}
// Defining a function to
// find the length of the array
function array_length(
) public returns(uint) {
uint x = data.length;
return x;
}
}
输出 :
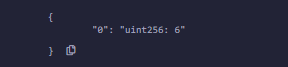
3. Push: Push 用于在动态数组中添加新元素时使用。新元素总是添加到数组的最后一个位置。
示例:在下面的示例中,合约类型首先初始化一个数组[数据] , 然后更多的值被推入数组。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Push operation
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Defining the array
uint[] data = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
// Defining the function to push
// values to the array
function array_push(
) public returns(uint[] memory){
data.push(60);
data.push(70);
data.push(80);
return data;
}
}
输出 :
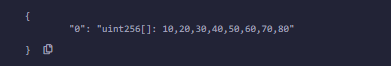
4. Pop:当要在任何动态数组中删除数组的最后一个元素时使用 Pop。
示例:在下面的示例中,合约类型首先初始化一个数组[数据] , 然后使用pop函数从数组中删除值。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Pop operation
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract Types {
// Defining an array
uint[] data
= [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
// Defining a function to
// pop values from the array
function array_pop(
) public returns(uint[] memory){
data.pop();
return data;
}
}
输出 :