Shell 脚本 - 替换
有些表达方式传达了特殊的含义。换句话说,他们不是他们看起来的样子。每当遇到这样的表达式时,shell 都会执行替换。因此,替换被定义为由 shell 执行的一种机制,其中它用表达式的实际值替换表达式的值。
转义序列:
转义序列是一组字符,在用作字符串字面量时不代表其实际值。下面列出了一些转义序列:Sr. No. Escape Sequences Significance (actual value) 1 \n new line 2 \f form feed 3 \r carriage return 4 \b backspace 5 \t horizontal tab 6 \v vertical tab 7 \\ backslash
Shell 将转义序列替换为其实际值。
例子:
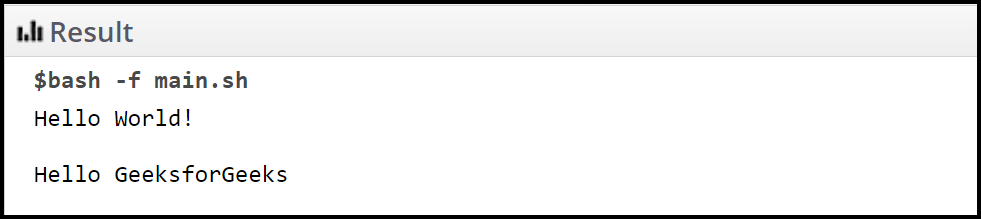
在这个 shell 脚本中,首先我们使用了一个 echo 命令来打印一个字符串。请注意,我们在字符串末尾使用了转义序列 (\n)。它会在打印字符后添加一个字符串。
#!/bin/sh
// Print the string
echo -e "Hello World! \n"
// Print the string
echo -e "Hello GeeksforGeeks"输出:
变量替换:
shell 允许我们根据变量的初始化状态来操作变量的值。Sr No. Expression Significance 1 ${myVariable} substitute the value of myVariable. 2 ${myVariable:-value} If myVariable is not-set (or null) then the value is substituted for myVariable. 3 ${myVariable:=value} If myVariable is not-set (or null), then it is set to value. 4 ${myVariable:? message} If myVariable is not-set (or null) then the message is printed as standard error. 5 ${myVariable:+value} If myVariable is set then the value is substituted for myVariable.
例子:
这些表达式在下面的 shell 脚本中演示。
#!/bin/sh
# If myVariable is unset or null
# then assign 12 to it
echo ${myVariable:- 11}
echo "1. The value of myVariable is ${myVariable}"
# If myVariable is unset or null
# then assign "GeeksforGeeks" to it
echo ${myVariable:="GeeksforGeeks"}
echo "2. Value of myVariable is ${myVariable}"
# unset myVariable
unset myVariable
# If myVariable is set then substitute
# the value
echo ${myVariable:+"GeeksforGeeks"}
echo "3. Value of myVariable is $myVariable"
myVariable="GeeksforGeeks"
# If myVariable is set then substitute
# the value
echo ${myVariable:+"Bhuwanesh"}
echo "4. Value of myVariable is $myVariable"
# If myVaraible is not-set or null then
# print the message
echo ${myVariable:?"message"}
echo "5. Value of myVariable is ${myVariable}"
unset myVariable
# If myVaraible is not-set or null then
# print the message
echo ${myVariable:?"message"}
echo "6. Value of myVariable is ${myVariable}"输出:

命令替换:
命令替换是程序员在 bash 脚本中遵循的一种机制。在这种机制中,命令的输出会替换命令本身。 Bash 通过执行命令然后用命令的标准输出替换命令替换来操作扩展。简而言之,UNIX 命令的输出被捆绑,然后用作命令。
为了更好地理解它,让我们考虑一个例子。 Linux 中的 seq 命令用于以 INCREMENT 为步长打印从 START 到 END 的数字。
句法:
seq START INCREMENT END 返回类型:
Prints numbers from START to END each in the new line by the difference of INCREMENT.
例子:
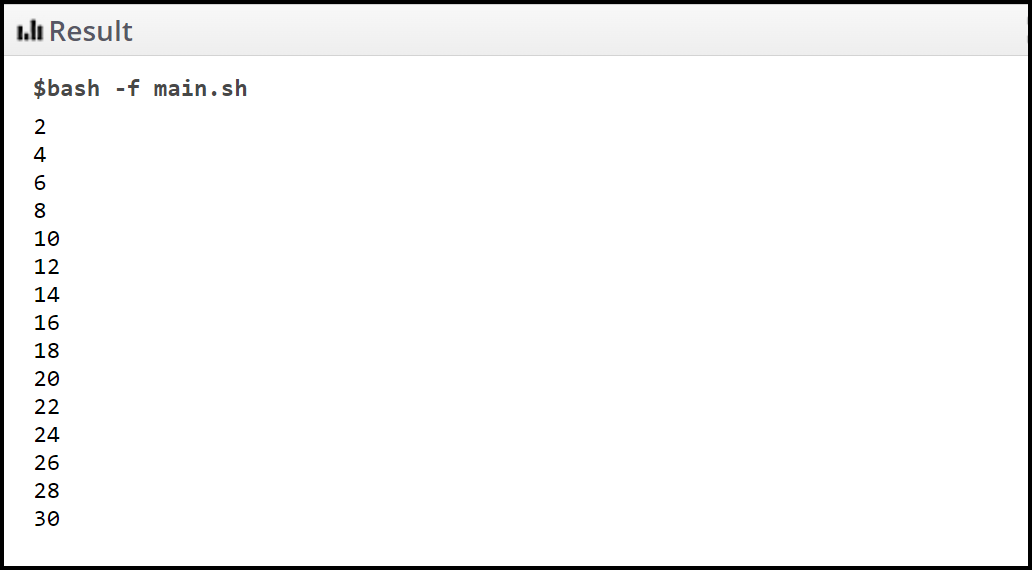
在下面的脚本中,我们打印从 2 到 20 的数字,相差 2。换句话说,我们打印的偶数最多为 30。
#!/bin/bash
# your code goes here
seq 2 2 30输出:
我们可以将上述命令的输出用作新命令。考虑下面的脚本,
例子:
#!/bin/bash
# your code goes here
echo $(seq 2 2 20)输出:
