Ruby 中的运算符优先级
运算符用于对操作数执行不同类型的操作。在具有多个具有不同优先级的运算符的表达式中首先执行哪个运算符由运算符优先级决定。当两个具有相同优先级的运算符出现在表达式中时,使用关联性。例如,'*' 和'/' 具有相同的优先级,因此表达式“100 / 10 * 10”被视为“(100 / 10) * 10”。 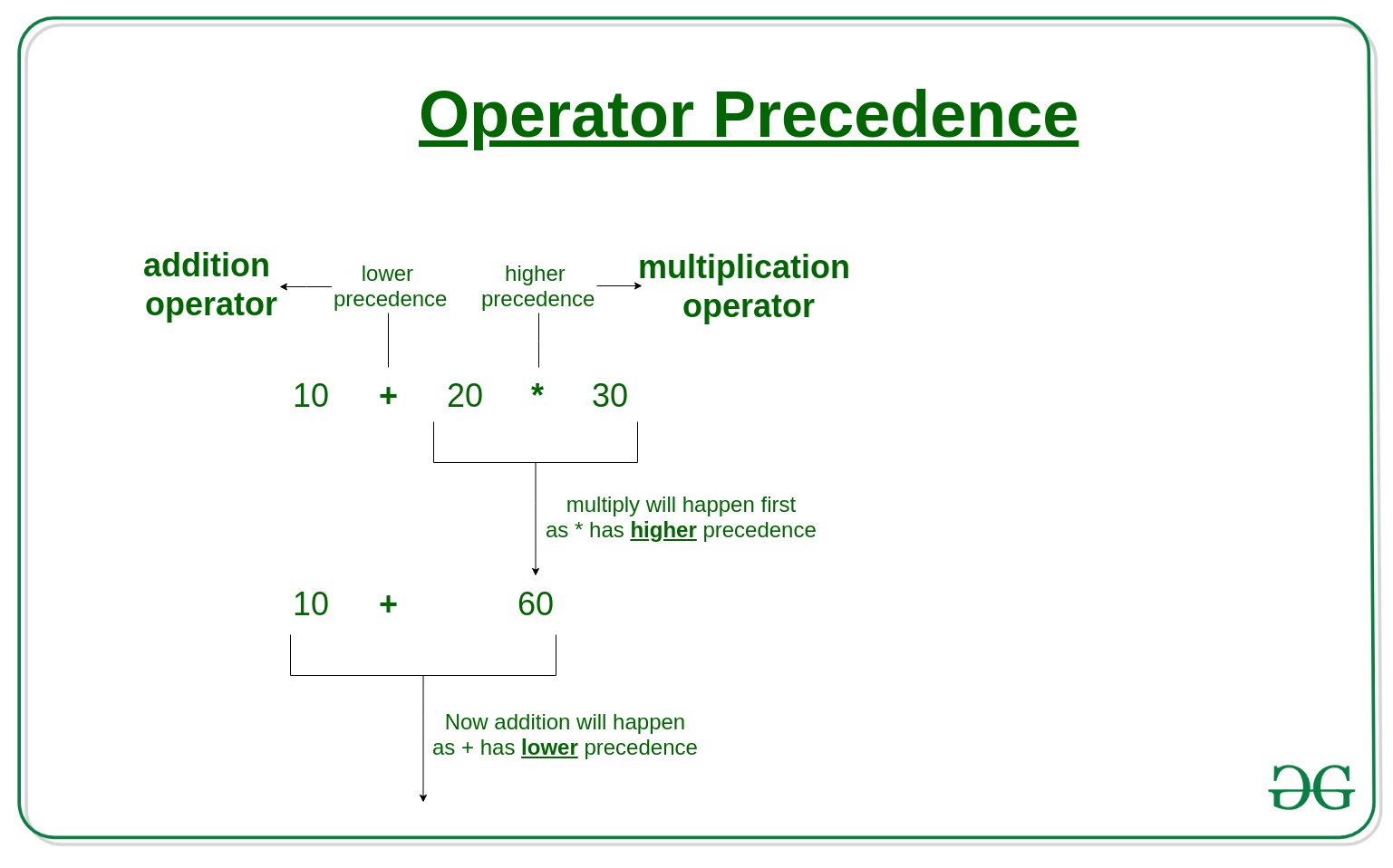
10 + 20 * 30 is calculated as 10 + (20 * 30)
and not as (10 + 20) * 30在下表中,优先级最高的运算符出现在表的顶部,而优先级最低的运算符出现在底部。
Operator | Category |
|---|---|
| [ ] [ ]= | Element reference, element set |
| ** | Exponentiation |
| !, ~, + | Boolean NOT, bitwise complement, unary plus |
| *, /, % | Multiplication, division, modulo (remainder) |
| +, – | Addition (or concatenation), subtraction |
| < <, > > | Bitwise shift-left (or append), bitwise shift-right |
| & | Bitwise AND |
| |, ^ | Bitwise OR, bitwise XOR |
| >, >=, <, <= | Ordering |
| <=>, ==, ===, !=, =~, !~ | Equality, pattern matching, comparison |
| && | Logical AND |
| || | Boolean OR |
| | | | Logical OR |
| .., …= | Range creation and Boolean flip-flops |
| ?, : | Conditional |
| modifier-rescue | Exception-handling modifier |
| =, +=, -=, etc. | Assignment |
| defined? | Test variable definition and type |
| not | Boolean NOT (low precedence) |
| or, and | Boolean OR, Boolean AND |
| modifier-if, modifier-unless, modifier-while, modifier-until | Conditional and loop modifiers |
| begin/end | blocks |
下面是运算符优先级的示例。
例子 :
# Ruby program to show Operators Precedence
a = 20;
b = 10;
c = 15;
d = 5;
e = 0
# operators with the highest precedence
# will operate first
e = a + b * c / d;
# step 1: 20 + (10 * 15) /5
# step 2: 20 + (150 /5)
# step 3:(20 + 30)
puts"Value of a + b * c / d is : #{e}"
输出 :
Value of a + b * c / d is : 50在上面的示例中,乘法和除法具有相同的优先级。所以它会像 20 + (10 * 15) /5 一样工作。在加法之后首先执行乘法而不是除法,因为加法的优先级较低。