PostgreSQL – 内连接
在 PostgreSQL 中,只要条件满足,INNER JOIN 关键字就会从两个表中选择所有行。该关键字将通过组合来自两个表中条件满足的所有行来创建结果集,即公共字段的值将相同。
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column1, table1.column2, table2.column1, ....
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
table1: First table.
table2: Second table
matching_column: Column common to both the tables.我们来分析一下上面的语法:
- 首先,使用 SELECT 语句指定我们希望从中选择数据的表。
- 其次,我们指定主表。
- 第三,我们指定主表连接到的表。
下面的维恩图说明了 PostgreSQL INNER JOIN 子句的工作: 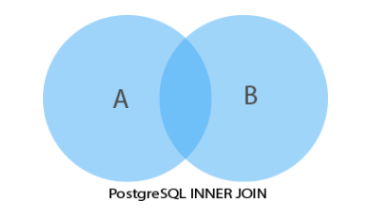
在本文中,我们将使用示例 DVD 租赁数据库,此处进行了说明,可以通过单击示例中的此链接进行下载。
现在,让我们看几个例子。
示例 1:
在这里,我们将使用 INNER JOIN 子句将“customer”表连接到“payment”表。
SELECT
customer.customer_id,
first_name,
last_name,
email,
amount,
payment_date
FROM
customer
INNER JOIN payment ON payment.customer_id = customer.customer_id;输出: 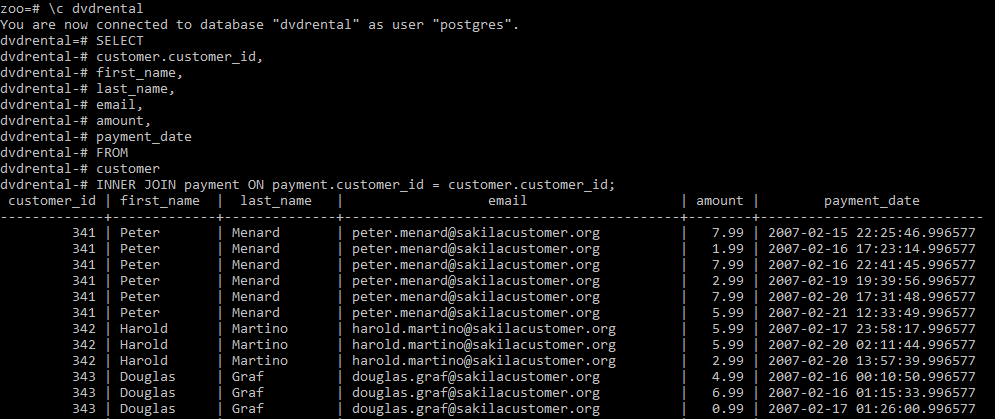
示例 2:
在这里,我们将使用 INNER JOIN 子句将“customer”表连接到“payment”表,并使用 ORDER BY 子句对它们进行排序:
SELECT
customer.customer_id,
first_name,
last_name,
email,
amount,
payment_date
FROM
customer
INNER JOIN payment ON payment.customer_id = customer.customer_id
ORDER BY
customer.customer_id;输出: 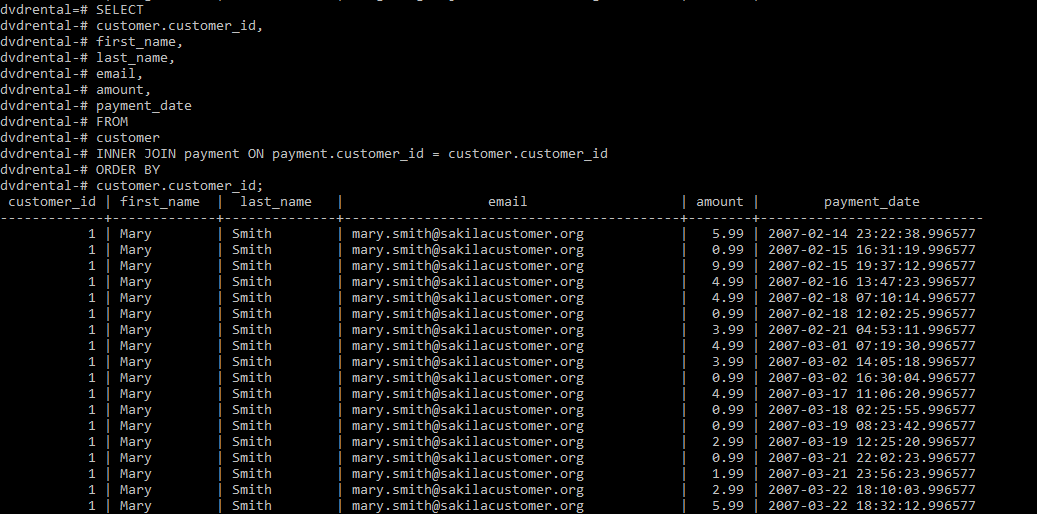
示例 3:
在这里,我们将使用 INNER JOIN 子句将“customer”表连接到“payment”表,并使用 WHERE 子句过滤它们:
SELECT
customer.customer_id,
first_name,
last_name,
email,
amount,
payment_date
FROM
customer
INNER JOIN payment ON payment.customer_id = customer.customer_id
WHERE
customer.customer_id = 15;
输出: 
示例 4:
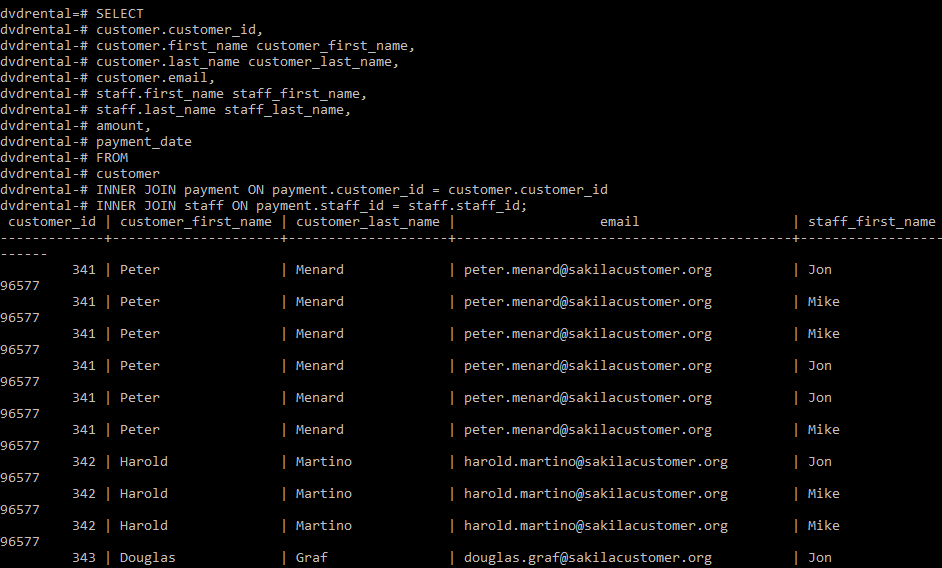
这里我们将使用 INNER JOIN 子句建立三个表之间的关系:员工、付款和客户。
SELECT
customer.customer_id,
customer.first_name customer_first_name,
customer.last_name customer_last_name,
customer.email,
staff.first_name staff_first_name,
staff.last_name staff_last_name,
amount,
payment_date
FROM
customer
INNER JOIN payment ON payment.customer_id = customer.customer_id
INNER JOIN staff ON payment.staff_id = staff.staff_id;输出: