使用类在Java中实现链表
先决条件:链表数据结构
像数组一样,链表是一种线性数据结构。与数组不同,链表元素不存储在连续位置,元素使用指针链接,如下所示。
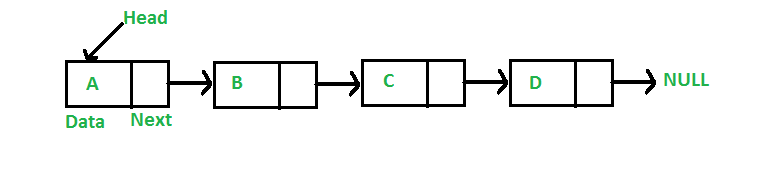
在Java中,LinkedList 可以表示为一个类,而 Node 可以表示为一个单独的类。 LinkedList 类包含 Node 类类型的引用。
Java
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// Next is by default initialized
// as null
Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// This inner class is made static
// so that main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list, int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// **************DELETION BY KEY**************
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY
public static LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,
int key)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted
if (currNode != null && currNode.data == key) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the key is somewhere other than at head
//
// Search for the key to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null && currNode.data != key) {
// If currNode does not hold key
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// If the key was present, it should be at currNode
// Therefore the currNode shall not be null
if (currNode != null) {
// Since the key is at currNode
// Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
}
//
// CASE 3: The key is not present
//
// If key was not present in linked list
// currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION BY KEY******
//
// Delete node with value 1
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteByKey(list, 1);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 4
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteByKey(list, 4);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteByKey(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION
public static LinkedList
deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list, int index)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If index is 0, then head node itself is to be
// deleted
if (index == 0 && currNode != null) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the index is greater than 0 but less than the
// size of LinkedList
//
// The counter
int counter = 0;
// Count for the index to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null) {
if (counter == index) {
// Since the currNode is the required
// position Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
break;
}
else {
// If current position is not the index
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
counter++;
}
}
// If the position element was found, it should be
// at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be
// null
//
// CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the
// LinkedList
//
// In this case, the currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION AT POSITION******
//
// Delete node at position 0
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteAtPosition(list, 0);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 2
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteAtPosition(list, 2);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteAtPosition(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// **************INSERTION**************
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// **************TRAVERSAL**************
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("\nLinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
// **************DELETION BY KEY**************
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY
public static LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,
int key)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted
if (currNode != null && currNode.data == key) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the key is somewhere other than at head
//
// Search for the key to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null && currNode.data != key) {
// If currNode does not hold key
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// If the key was present, it should be at currNode
// Therefore the currNode shall not be null
if (currNode != null) {
// Since the key is at currNode
// Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
}
//
// CASE 3: The key is not present
//
// If key was not present in linked list
// currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************DELETION AT A POSITION**************
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION
public static LinkedList
deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list, int index)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If index is 0, then head node itself is to be
// deleted
if (index == 0 && currNode != null) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the index is greater than 0 but less than the
// size of LinkedList
//
// The counter
int counter = 0;
// Count for the index to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null) {
if (counter == index) {
// Since the currNode is the required
// position Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
break;
}
else {
// If current position is not the index
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
counter++;
}
}
// If the position element was found, it should be
// at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be
// null
//
// CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the
// LinkedList
//
// In this case, the currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION BY KEY******
//
// Delete node with value 1
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteByKey(list, 1);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 4
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteByKey(list, 4);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteByKey(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION AT POSITION******
//
// Delete node at position 0
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteAtPosition(list, 0);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 2
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteAtPosition(list, 2);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteAtPosition(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}创建和插入
在本文中,列表中的插入是在最后完成的,即在给定链表的最后一个节点之后添加新节点。例如,如果给定的链表是 5->10->15->20->25 并且要插入 30,则链表变为 5->10->15->20->25->30 .
由于链表通常由其头指针表示,因此需要遍历链表直到最后一个节点,然后将倒数第二个节点更改为新节点。
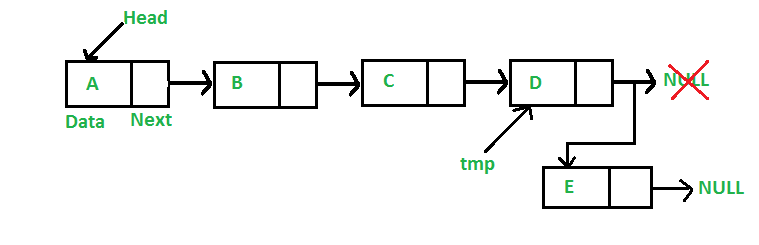
Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// This inner class is made static
// so that main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list, int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}
输出
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 遍历
对于遍历,下面是一个通用函数printList(),它通过从头节点到最后一个节点遍历列表来打印任何给定列表。
Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}
输出
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 KEY删除
删除过程可以理解为:
待办事项:
给定一个“键”,删除链表中该键的第一次出现。
怎么做:
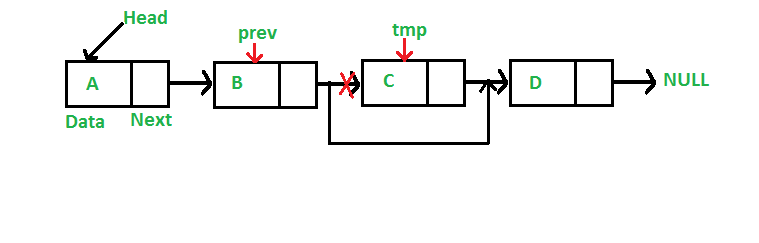
要从链表中删除节点,请执行以下步骤。
- 在列表中搜索第一次出现的键
- 现在,三个条件中的任何一个都可以存在:
- 案例一:钥匙在头部找到
- 在这种情况下,将节点的头部更改为当前头部的下一个节点。
- 释放被替换的头节点的内存。
- 在这种情况下,将节点的头部更改为当前头部的下一个节点。
- 情况2:钥匙在中间或最后找到,除了头部
- 在这种情况下,查找要删除的节点的前一个节点。
- 将下一个上一个节点更改为当前节点的下一个节点。
- 释放被替换节点的内存。
- 在这种情况下,查找要删除的节点的前一个节点。
- 情况3:在列表中找不到key
- 在这种情况下,无需进行任何操作。
- 在这种情况下,无需进行任何操作。
- 案例一:钥匙在头部找到
Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// **************DELETION BY KEY**************
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY
public static LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,
int key)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted
if (currNode != null && currNode.data == key) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the key is somewhere other than at head
//
// Search for the key to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null && currNode.data != key) {
// If currNode does not hold key
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// If the key was present, it should be at currNode
// Therefore the currNode shall not be null
if (currNode != null) {
// Since the key is at currNode
// Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
}
//
// CASE 3: The key is not present
//
// If key was not present in linked list
// currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION BY KEY******
//
// Delete node with value 1
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteByKey(list, 1);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 4
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteByKey(list, 4);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteByKey(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}
输出
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 found and deleted
LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
4 found and deleted
LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
10 not found
LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
删除位置
这个删除过程可以理解为:
待办事项:
给定一个'position' ,从链表中删除该位置的节点。
怎么做:
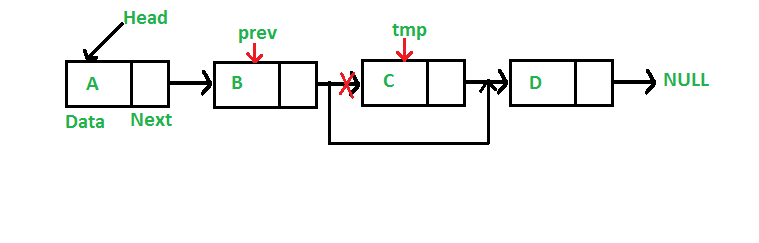
步骤如下:
- 通过计算节点的索引来遍历列表
- 对于每个索引,将索引匹配为与位置相同
- 现在,三个条件中的任何一个都可以存在:
- 情况1:位置为0,即要删除头部
- 在这种情况下,将节点的头更改为当前头的下一个节点。
- 释放被替换的头节点的内存。
- 在这种情况下,将节点的头更改为当前头的下一个节点。
- 情况2:位置大于0但小于列表大小,即在中间或最后,头部除外
- 在这种情况下,查找要删除的节点的前一个节点。
- 将前一个节点的下一个节点更改为当前节点的下一个节点。
- 释放被替换节点的内存。
- 在这种情况下,查找要删除的节点的前一个节点。
- 情况3:位置大于列表的大小,即在列表中找不到位置
- 在这种情况下,无需进行任何操作。
- 在这种情况下,无需进行任何操作。
- 情况1:位置为0,即要删除头部
Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION
public static LinkedList
deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list, int index)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If index is 0, then head node itself is to be
// deleted
if (index == 0 && currNode != null) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the index is greater than 0 but less than the
// size of LinkedList
//
// The counter
int counter = 0;
// Count for the index to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null) {
if (counter == index) {
// Since the currNode is the required
// position Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
break;
}
else {
// If current position is not the index
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
counter++;
}
}
// If the position element was found, it should be
// at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be
// null
//
// CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the
// LinkedList
//
// In this case, the currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION AT POSITION******
//
// Delete node at position 0
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteAtPosition(list, 0);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 2
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteAtPosition(list, 2);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteAtPosition(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}
输出
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
0 position element deleted
LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
2 position element deleted
LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
10 position element not found
LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
所有操作
下面是一起应用每个操作的完整程序:
Java
import java.io.*;
// Java program to implement
// a Singly Linked List
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
// Linked list Node.
// Node is a static nested class
// so main() can access it
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// **************INSERTION**************
// Method to insert a new node
public static LinkedList insert(LinkedList list,
int data)
{
// Create a new node with given data
Node new_node = new Node(data);
new_node.next = null;
// If the Linked List is empty,
// then make the new node as head
if (list.head == null) {
list.head = new_node;
}
else {
// Else traverse till the last node
// and insert the new_node there
Node last = list.head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
// Insert the new_node at last node
last.next = new_node;
}
// Return the list by head
return list;
}
// **************TRAVERSAL**************
// Method to print the LinkedList.
public static void printList(LinkedList list)
{
Node currNode = list.head;
System.out.print("\nLinkedList: ");
// Traverse through the LinkedList
while (currNode != null) {
// Print the data at current node
System.out.print(currNode.data + " ");
// Go to next node
currNode = currNode.next;
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
// **************DELETION BY KEY**************
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by KEY
public static LinkedList deleteByKey(LinkedList list,
int key)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If head node itself holds the key to be deleted
if (currNode != null && currNode.data == key) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the key is somewhere other than at head
//
// Search for the key to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null && currNode.data != key) {
// If currNode does not hold key
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// If the key was present, it should be at currNode
// Therefore the currNode shall not be null
if (currNode != null) {
// Since the key is at currNode
// Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " found and deleted");
}
//
// CASE 3: The key is not present
//
// If key was not present in linked list
// currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(key + " not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************DELETION AT A POSITION**************
// Method to delete a node in the LinkedList by POSITION
public static LinkedList
deleteAtPosition(LinkedList list, int index)
{
// Store head node
Node currNode = list.head, prev = null;
//
// CASE 1:
// If index is 0, then head node itself is to be
// deleted
if (index == 0 && currNode != null) {
list.head = currNode.next; // Changed head
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
// Return the updated List
return list;
}
//
// CASE 2:
// If the index is greater than 0 but less than the
// size of LinkedList
//
// The counter
int counter = 0;
// Count for the index to be deleted,
// keep track of the previous node
// as it is needed to change currNode.next
while (currNode != null) {
if (counter == index) {
// Since the currNode is the required
// position Unlink currNode from linked list
prev.next = currNode.next;
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element deleted");
break;
}
else {
// If current position is not the index
// continue to next node
prev = currNode;
currNode = currNode.next;
counter++;
}
}
// If the position element was found, it should be
// at currNode Therefore the currNode shall not be
// null
//
// CASE 3: The index is greater than the size of the
// LinkedList
//
// In this case, the currNode should be null
if (currNode == null) {
// Display the message
System.out.println(
index + " position element not found");
}
// return the List
return list;
}
// **************MAIN METHOD**************
// method to create a Singly linked list with n nodes
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
//
// ******INSERTION******
//
// Insert the values
list = insert(list, 1);
list = insert(list, 2);
list = insert(list, 3);
list = insert(list, 4);
list = insert(list, 5);
list = insert(list, 6);
list = insert(list, 7);
list = insert(list, 8);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION BY KEY******
//
// Delete node with value 1
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteByKey(list, 1);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 4
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteByKey(list, 4);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node with value 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteByKey(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
//
// ******DELETION AT POSITION******
//
// Delete node at position 0
// In this case the key is ***at head***
deleteAtPosition(list, 0);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 2
// In this case the key is present ***in the
// middle***
deleteAtPosition(list, 2);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
// Delete node at position 10
// In this case the key is ***not present***
deleteAtPosition(list, 10);
// Print the LinkedList
printList(list);
}
}
输出
LinkedList: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 found and deleted
LinkedList: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
4 found and deleted
LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
10 not found
LinkedList: 2 3 5 6 7 8
0 position element deleted
LinkedList: 3 5 6 7 8
2 position element deleted
LinkedList: 3 5 7 8
10 position element not found
LinkedList: 3 5 7 8