Java Java类
IO 中的管道提供了同时在 JVM 中运行的两个线程之间的链接。因此,管道既可用作源,也可用作目标。
- PipedInputStream 也使用 PipedOutputStream 进行管道传输。因此,可以使用 PipedOutputStream 写入数据,也可以使用 PipedInputStream 写入数据。但是,同时使用两个线程会为线程创建死锁。
- 如果向连接的管道输出流提供数据字节的线程不再活动,则称该管道已损坏。
宣言:
public class PipedInputStream
extends InputStream构造函数:
- PipedInputStream() :创建一个未连接的 PipedInputStream。
- PipedInputStream(int pSize) :创建一个 PipedInputStream,它没有与指定的管道大小连接。
- PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream outStream) :创建一个 PipedInputStream,它连接到 PipedOutputStream – 'outStream'。
- PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream outStream, int pSize) :创建一个管道输入流,该输入流连接到具有指定管道大小的管道输出流。
方法:
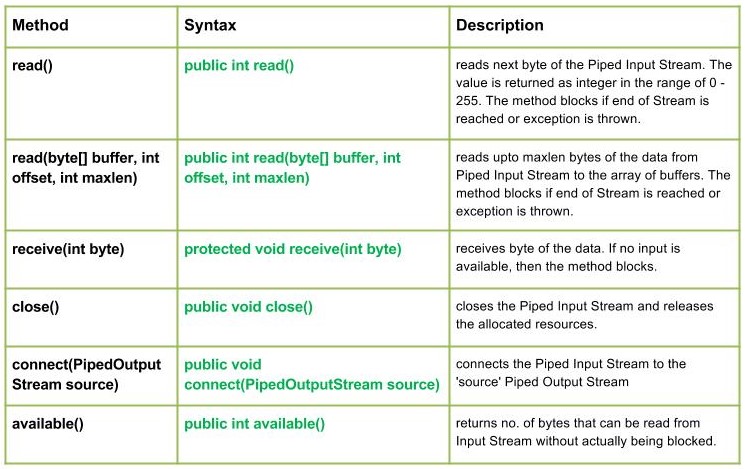
- int read():从此管道输入流中读取数据的下一个字节。值字节作为 int 返回,范围为 0 到 255。此方法阻塞,直到输入数据可用,检测到流的结尾,或抛出异常。
// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PipedInputStream geek_input = new PipedInputStream(); PipedOutputStream geek_output = new PipedOutputStream(); try { // Use of connect() : connecting geek_input with geek_output geek_input.connect(geek_output); // Use of read() method : geek_output.write(71); System.out.println("using read() : " + (char)geek_input.read()); geek_output.write(69); System.out.println("using read() : " + (char)geek_input.read()); geek_output.write(75); System.out.println("using read() : " + (char)geek_input.read()); } catch (IOException except) { except.printStackTrace(); } } }输出 :
using read() : G using read() : E using read() : K - read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) : Java.io.PipedInputStream.read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen)从 Piped Input Stream 读取数据的 maxlen 字节到缓冲区数组。如果到达 Stream 的末尾或抛出异常,该方法将阻塞。
句法 :public int read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : the destination buffer into which the data is to be read offset : starting in the destination array - 'buffer'. maxlen : maximum length of array to be read Return : next 'maxlen' bytes of the data as an integer value return -1 is end of stream is reached Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. -> NullPointerException : if buffer is null. -> IndexOutOfBoundsException : if offset is -ve or maxlen is -ve or maxlen > buffer.length - offset. - receive(int byte) : Java.io.PipedInputStream.receive(int byte)接收数据的字节。如果没有可用的输入,则方法阻塞。
句法 :protected void receive(int byte) Parameters : byte : the bytes of the data received Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs or pipe is broken. - close() : Java.io.PipedInputStream.close()关闭管道输入流并释放分配的资源。
句法 :public void close() Parameters : -------------- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. - connect(PipedOutputStream source) : Java.io.PipedInputStream.connect(PipedOutputStream source)将管道输入流连接到“源”管道输出流,如果“源”是带有其他流的管道,则会引发 IO 异常
句法 :public void connect(PipedOutputStream source) Parameters : source : the Piped Output Stream to be connected to Return : void Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs. - available() : Java.io.PipedInputStream.available()返回no。可以从输入流中读取而不会被实际阻塞的字节数。
句法 :public int available() Parameters : ------------- Return : no. of bytes that can be read from Input Stream without actually being blocked. 0, if the stream is already closed but by invoking close() method Exception : -> IOException : if in case IO error occurs.解释 PipedInputStream 类方法工作的Java程序:
// Java program illustrating the working of PipedInputStream // connect(), read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen), // close(), available() import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PipedInputStream geek_input = new PipedInputStream(); PipedOutputStream geek_output = new PipedOutputStream(); try { // Use of connect() : connecting geek_input with geek_output geek_input.connect(geek_output); geek_output.write(71); geek_output.write(69); geek_output.write(69); geek_output.write(75); geek_output.write(83); // Use of available() : System.out.println("Use of available() : " + geek_input.available()); // Use of read(byte[] buffer, int offset, int maxlen) : byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; // destination 'buffer' geek_input.read(buffer, 0, 5); String str = new String(buffer); System.out.println("Using read(buffer, offset, maxlen) : " + str); // USe of close() method : System.out.println("Closing the stream"); geek_input.close(); } catch (IOException except) { except.printStackTrace(); } } }输出:
Use of available() : 5 Using read(buffer, offset, maxlen) : GEEKS Closing the stream下一篇: Java Java类