Node.js NPM uuid
NPM(Node Package Manager) 是 Node.js 包的包管理器。有一个名为“shortid”的 NPM 包用于创建短的非顺序 url 友好的唯一 ID。唯一 id 是由加密强的随机值创建的,这就是它非常安全的原因。它支持 Node、React Native、Chrome、Safari、Firefox 等跨平台。
安装命令:
npm install uuid将包导入本地文件的语法
const {v4 : uuidv4} = require('uuid')
创建唯一 ID 的语法
const newId = uuidv4()
在 shortid 模块上定义了一些方法来创建唯一 id 和自定义 id。一些方法如下图所示:Method Work uuid.NIL The nil UUID string (all zeros) uuid.parse() Convert UUID string to array of bytes uuid.validate() Test a string to see if it is a valid UUID uuid.v1() Create a version 1 (timestamp) UUID uuid.v3() Create a version 3 (namespace w/ MD5) UUID uuid.v4() Create a version 4 (random) UUID uuid.v5() Create a version 5 (namespace w/ SHA-1) UUID uuid.stringify() Convert array of bytes to UUID string
示例 1:此示例说明如何生成和使用 uuid 包创建唯一 id。
filename-index.js:此文件包含创建唯一 ID 并将其与用户信息附加并保存到数据库的所有逻辑。
const express = require('express')
const bodyParser = require('body-parser')
const {v4 : uuidv4} = require('uuid')
const formTemplet = require('./form')
const repo = require('./repository')
const app = express()
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000
// The body-parser middleware to parse form data
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended : true}))
// Get route to display HTML form
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(formTemplet({}))
})
// Post route to handle form submission logic and
app.post('/', (req, res) => {
// Fetching user inputs
const {name, email} = req.body
// Creating new unique id
const userId = uuidv4()
// Saving record to the database
// with attaching userid to each record
repo.create({
userId,
name,
email
})
res.send('Information submitted!')
})
// Server setup
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server start on port ${port}`)
})
文件名——repository.js:该文件包含创建数据库并与之交互的所有逻辑。
// Importing node.js file system module
const fs = require('fs')
class Repository {
constructor(filename) {
// Filename where data are going to store
if(!filename) {
throw new Error(
'Filename is required to create a datastore!')
}
this.filename = filename
try {
fs.accessSync(this.filename)
} catch(err) {
// If file not exist it is created
// with empty array
fs.writeFileSync(this.filename, '[]')
}
}
// Get all existing records
async getAll() {
return JSON.parse(
await fs.promises.readFile(this.filename, {
encoding : 'utf8'
})
)
}
// Create new record
async create(attrs){
// Fetch all existing records
const records = await this.getAll()
// All the existing records with new
// record push back to database
records.push(attrs)
await fs.promises.writeFile(
this.filename,
JSON.stringify(records, null, 2)
)
return attrs
}
}
// The 'datastore.json' file created at runtime
// and all the information provided via signup form
// store in this file in JSON formet.
module.exports = new Repository('datastore.json')
文件名 - form.js:此文件包含呈现表单的所有逻辑。
module.exports = ({errors}) => {
return `
`
}
输出:
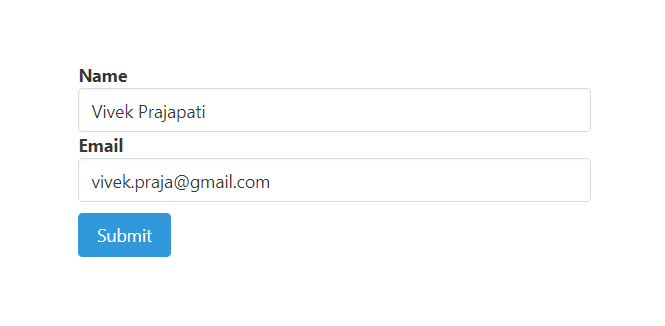
提交信息1

提交信息2
数据库:
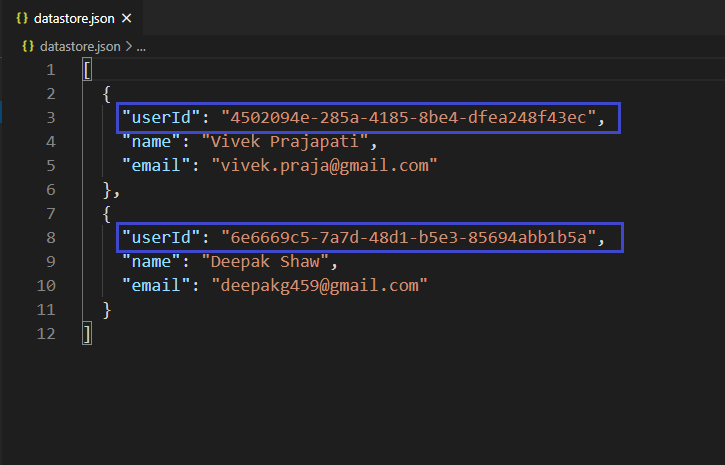
提交信息后的数据库
示例 2:此示例说明如何使用 uuid.parse() 和 uuid.stringify() 方法。
filename-index.js:此文件包含创建唯一 id 并将其与用户信息附加并保存到数据库的所有逻辑,还将 id 转换为解析的字节并将解析的字节转换为字符串id。
const express = require('express')
const bodyParser = require('body-parser')
const {
v4 : uuidv4,
parse:uuidParse,
stringify : uuidStringify
} = require('uuid')
const formTemplet = require('./form')
const repo = require('./repository')
const app = express()
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000
// The body-parser middleware to parse form data
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended : true}))
// Get route to display HTML form
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(formTemplet({}))
})
// Post route to handle form submission logic and
app.post('/', (req, res) => {
// Fetching user inputs
const {name, email} = req.body
// Creating new unique id
const userId = uuidv4()
const parsedId = uuidParse(userId)
const stringfyId = uuidStringify(parsedId)
console.log(`parsedId : ${parsedId}\n`)
console.log(`StringifyId : ${stringfyId}\n`)
// Saving record to the database
// with attaching userid to each record
repo.create({
userId,
name,
email
})
res.send('Information submitted!')
})
// Server setup
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server start on port ${port}`)
})
文件名——repository.js:该文件包含创建数据库并与之交互的所有逻辑。
// Importing node.js file system module
const fs = require('fs')
class Repository {
constructor(filename) {
// Filename where datas are going to store
if(!filename) {
throw new Error(
'Filename is required to create a datastore!')
}
this.filename = filename
try {
fs.accessSync(this.filename)
} catch(err) {
// If file not exist it is created
// with empty array
fs.writeFileSync(this.filename, '[]')
}
}
// Get all existing records
async getAll() {
return JSON.parse(
await fs.promises.readFile(this.filename, {
encoding : 'utf8'
})
)
}
// Create new record
async create(attrs){
// Fetch all existing records
const records = await this.getAll()
// All the existing records with new
// record push back to database
records.push(attrs)
await fs.promises.writeFile(
this.filename,
JSON.stringify(records, null, 2)
)
return attrs
}
}
// The 'datastore.json' file created at runtime
// and all the information provided via signup form
// store in this file in JSON formet.
module.exports = new Repository('datastore.json')
文件名 - form.js :此文件包含呈现表单的所有逻辑。
const getError = (errors, prop) => {
try {
return errors.mapped()[prop].msg
} catch (error) {
return ''
}
}
module.exports = ({errors}) => {
return `
`
}
输出:

提交信息

解析 id 和 stringify id
数据库:

提交信息后的数据库
注意:我们在 form.js 文件中使用了一些 Bulma 类来设计我们的内容。