Java中的包装类
Wrapper 类是其对象包装或包含原始数据类型的类。当我们为包装类创建一个对象时,它包含一个字段,在这个字段中,我们可以存储原始数据类型。换句话说,我们可以将原始值包装到包装类对象中。
需要包装类
- 它们将原始数据类型转换为对象。如果我们希望修改传递给方法的参数(因为原始类型是按值传递的),则需要对象。
- Java.util 包中的类只处理对象,因此包装类在这种情况下也有帮助。
- Collection 框架中的数据结构,例如 ArrayList 和 Vector,只存储对象(引用类型)而不存储原始类型。
- 需要一个对象来支持多线程中的同步。
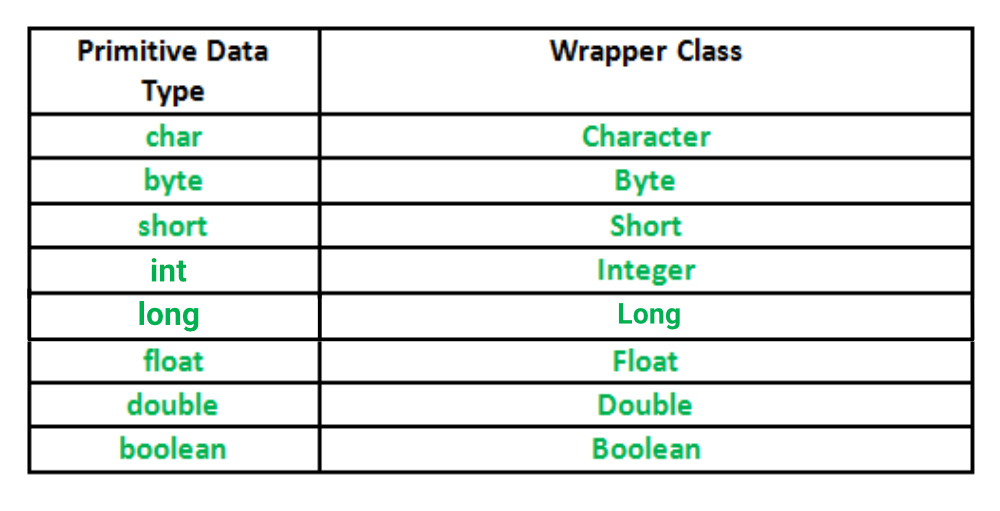
原始数据类型及其对应的包装类
自动装箱和拆箱
自动装箱:将原始类型自动转换为其相应包装类的对象称为自动装箱。例如 - 将 int 转换为 Integer,将 long 转换为 Long,将 double 转换为 Double 等。
例子:
// Java program to demonstrate Autoboxing
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Autoboxing
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char ch = 'a';
// Autoboxing- primitive to Character object conversion
Character a = ch;
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
// Autoboxing because ArrayList stores only objects
arrayList.add(25);
// printing the values from object
System.out.println(arrayList.get(0));
}
}
输出:
25拆箱:这只是自动装箱的逆过程。将包装类的对象自动转换为其相应的原始类型称为拆箱。例如 – 将 Integer 转换为 int、Long 转换为 long、Double 转换为 double 等。
// Java program to demonstrate Unboxing
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Unboxing
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Character ch = 'a';
// unboxing - Character object to primitive conversion
char a = ch;
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add(24);
// unboxing because get method returns an Integer object
int num = arrayList.get(0);
// printing the values from primitive data types
System.out.println(num);
}
}
输出:
24执行
// Java program to demonstrate Wrapping and UnWrapping
// in Java Classes
class WrappingUnwrapping
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// byte data type
byte a = 1;
// wrapping around Byte object
Byte byteobj = new Byte(a);
// int data type
int b = 10;
//wrapping around Integer object
Integer intobj = new Integer(b);
// float data type
float c = 18.6f;
// wrapping around Float object
Float floatobj = new Float(c);
// double data type
double d = 250.5;
// Wrapping around Double object
Double doubleobj = new Double(d);
// char data type
char e='a';
// wrapping around Character object
Character charobj=e;
// printing the values from objects
System.out.println("Values of Wrapper objects (printing as objects)");
System.out.println("Byte object byteobj: " + byteobj);
System.out.println("Integer object intobj: " + intobj);
System.out.println("Float object floatobj: " + floatobj);
System.out.println("Double object doubleobj: " + doubleobj);
System.out.println("Character object charobj: " + charobj);
// objects to data types (retrieving data types from objects)
// unwrapping objects to primitive data types
byte bv = byteobj;
int iv = intobj;
float fv = floatobj;
double dv = doubleobj;
char cv = charobj;
// printing the values from data types
System.out.println("Unwrapped values (printing as data types)");
System.out.println("byte value, bv: " + bv);
System.out.println("int value, iv: " + iv);
System.out.println("float value, fv: " + fv);
System.out.println("double value, dv: " + dv);
System.out.println("char value, cv: " + cv);
}
}
输出:
Values of Wrapper objects (printing as objects)
Byte object byteobj: 1
Integer object intobj: 10
Float object floatobj: 18.6
Double object doubleobj: 250.5
Character object charobj: a
Unwrapped values (printing as data types)
byte value, bv: 1
int value, iv: 10
float value, fv: 18.6
double value, dv: 250.5
char value, cv: a
相关文章:
Java中Autoboxed Integer对象的比较