Python中的中间编码问题
Python是一种非常动态和通用的编程语言,几乎在每个领域都有使用。从软件开发到机器学习,它涵盖了所有内容。本文将重点介绍一些有趣的编码问题,这些问题可以用来进一步提高我们的技能,同时,在解决这个特别策划的问题列表中获得乐趣。尽管本文将重点介绍如何使用Python解决这些问题,但您可以随意使用他们选择的任何其他语言。所以让我们直接进入它!
无限猴子定理
该定理指出,一只猴子在打字机键盘上随机敲击无限时间的键几乎肯定会键入给定的文本,例如威廉·莎士比亚的全集。好吧,假设我们用Python函数替换猴子。 Python函数只生成一个句子需要多长时间?我们将使用的句子是:“极客的计算机科学门户”。
我们将模拟这种情况的方法是编写一个函数,通过从字母表中的 26 个字母加空格中选择随机字母来生成一个 35 个字符长的字符串。我们将编写另一个函数,通过将随机生成的字符串与目标进行比较,对每个生成的字符串进行评分。第三个函数将重复调用 generate 和 score,然后如果 100% 的字母是正确的,我们就完成了。如果字母不正确,那么我们将生成一个全新的字符串。为了更容易理解,我们的程序应该跟踪迄今为止生成的最佳字符串。
例子:
Python3
import random
# function to generate
# a random string
def generateOne(strlen):
# string with all the alphabets
# and a space
alphabet = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz "
res =""
for i in range(strlen):
res+= alphabet[random.randrange(27)]
return res
# function to determine the
# score of the generated string
def score(goal, testString):
numSame = 0
for i in range(len(goal)):
if goal[i] == testString[i]:
numSame+= 1
return numSame / len(goal)
# main function to call the previous
# two functions until the goal is achieved
def main():
goalString = "a computer science portal for geeks"
newString = generateOne(35)
best = 0
newScore = score(goalString, newString)
while newScore<1:
if newScore>best:
print(newString)
best = newScore
newString = generateOne(35)
newScore = score(goalString, newString)
# Driver code
main()Python3
def test_1(string =""):
# initializing the substring
substring = ""
testList = []
initial = 0
for char in string:
for i in range(initial, len(string)):
substring+= string[i]
# checking conditions
if substring.count(string[i])>1:
testList.append(substring[:-1])
initial+= 1
substring = ""
break
maxi =""
for word in testList:
if len(word)>len(maxi):
maxi = word
if len(maxi)<3:
return "-1"
else:
return maxi
# Driver code
print(test_1("character"))
print(test_1("standfan"))
print(test_1("class"))Python3
import random
# generates a four-digit code
def gen_code():
set_code = []
for i in range(4):
val = random.randint(0, 9)
set_code.append(val)
return set_code
# asks for input from the user
def input_code():
code = input("Enter your four digit guess code: ")
return code
# plays the game
def mastermind():
genCode = gen_code()
i = 0
while i < 10:
result = ""
inputCode = [int(c) for c in input_code()]
if len(inputCode) != 4:
print("Enter only 4 digit number")
continue
if inputCode == genCode:
print("You guessed it !", genCode)
break
for element in inputCode:
if element in genCode:
if inputCode.index(element) == genCode.index(element):
result+="R"
else:
result+="Y"
else:
result+="B"
print(result)
i += 1
else:
print("You ran out of trys !", genCode)
# Driver Code
mastermind()Python3
opposite = {'NORTH': 'SOUTH',
'EAST': 'WEST',
'SOUTH': 'NORTH',
'WEST': 'EAST'}
# Function to find the reduced
# direction
def dirReduc(givenDirections):
finalDirections = []
for d in range(0, len(givenDirections)):
if finalDirections:
if finalDirections[-1] == opposite[givenDirections[d]]:
finalDirections.pop()
else:
finalDirections.append(givenDirections[d])
else:
finalDirections.append(givenDirections[d])
return finalDirections
# Driver Code
print(dirReduc(["NORTH", "SOUTH", "SOUTH", "EAST", "WEST", "NORTH", "WEST"]))Python3
# function to compare the arrays
def comp(array1, array2):
# checking if any array is None
if array1 is None or array2 is None:
return False
# checking if any of the array
# is a square of the other
if (sorted(array1) == sorted([i ** 2 for i in array2])) or (sorted(array2) == sorted([i ** 2 for i in array1])):
return True
return False
# Driver Code
comp([1,2,3,4], [1,4,9,16])输出:
pxwvkdfwpbzneycy rifcrnczxqtsfowgjm
wfgytnakffjty ggfy trylljfhurazyxow
docujzolvswarzqszridmejyluhwviujlkj
qbtvqanrbwsximmnlhjgkaacufhskiooxm
w jnlhvvinzrlimtesllsroqqqf wwteela
mjcevludro yoigewqudxjsad bxrl qnlv
f pomksbzrjizegcjwyoqftjz wwx ges在这里,我们编写了三个函数。一个将使用字母和空格的 26 个字符生成一个随机字符串。然后,第二个函数将通过将生成的字符串的每个字母与目标字符串进行比较来对生成的字符串进行评分。第三个函数会重复调用前两个函数,直到任务完成。它还将通过比较它们的分数来记录迄今为止生成的最佳字符串。得分最高的将是最好的。最后,我们在 IDE 中运行该程序并查看它是否正常工作。
子串困境
这是一个非常有趣的程序,因为它会生成一些非常有趣的输出。对于想要更清楚地理解“字符串”类型的初学者来说,这也是一个健康的练习题。让我们来看看这个问题。
给定一个字符串,根据以下条件找到一个子字符串:
- 子字符串必须是给定字符串中所有可能的子字符串中最长的一个。
- 子字符串中不能有任何重复字符。
- 如果满足上述两个条件的子串不止一个,则打印最先出现的子串。
- 如果没有满足上述所有条件的子字符串,则打印 -1。
虽然可以有很多方法来解决这个问题,但我们将看看最基本的一种。
例子:
Python3
def test_1(string =""):
# initializing the substring
substring = ""
testList = []
initial = 0
for char in string:
for i in range(initial, len(string)):
substring+= string[i]
# checking conditions
if substring.count(string[i])>1:
testList.append(substring[:-1])
initial+= 1
substring = ""
break
maxi =""
for word in testList:
if len(word)>len(maxi):
maxi = word
if len(maxi)<3:
return "-1"
else:
return maxi
# Driver code
print(test_1("character"))
print(test_1("standfan"))
print(test_1("class"))
在这里,我们编写一个函数来执行整个任务。首先,它将初始化名为 substring 和 testList 的变量,以分别存储子字符串和可能的输出列表。然后它将遍历提供的整个字符串,并在每次找到重复项并将该单词附加到 testList 时中断。最后,返回可能输出中最长的单词。
输出:
racte
standf
clas 策划者
经典游戏“Mastermind”的低级实现。我们需要编写一个程序来生成一个四位数的随机码,并且用户需要在 10 次或更短的时间内猜出这个代码。如果猜出的四位代码中的任何一个数字是错误的,计算机应该打印出“B”。如果数字正确但位置错误,计算机应打印“Y”。如果数字和位置都正确,计算机应打印“R”。例子:
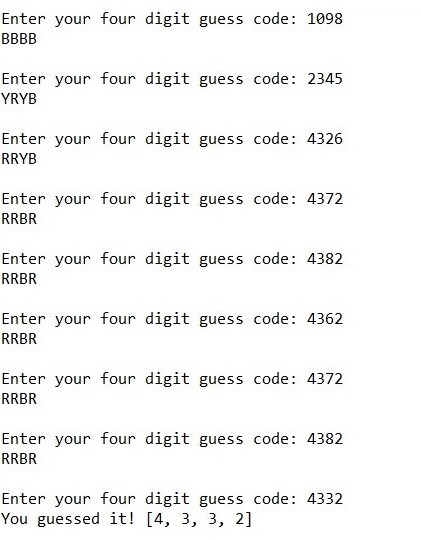
例子:
Python3
import random
# generates a four-digit code
def gen_code():
set_code = []
for i in range(4):
val = random.randint(0, 9)
set_code.append(val)
return set_code
# asks for input from the user
def input_code():
code = input("Enter your four digit guess code: ")
return code
# plays the game
def mastermind():
genCode = gen_code()
i = 0
while i < 10:
result = ""
inputCode = [int(c) for c in input_code()]
if len(inputCode) != 4:
print("Enter only 4 digit number")
continue
if inputCode == genCode:
print("You guessed it !", genCode)
break
for element in inputCode:
if element in genCode:
if inputCode.index(element) == genCode.index(element):
result+="R"
else:
result+="Y"
else:
result+="B"
print(result)
i += 1
else:
print("You ran out of trys !", genCode)
# Driver Code
mastermind()
首先,我们使用 Python 的 random 模块编写一个函数来生成一个随机的四位数代码。接下来,我们定义一个要求用户输入的函数。最后,我们编写一个函数,将生成的代码与猜测的代码进行比较并给出适当的结果。
方向灾难
一个非常简单的问题,有许多不同的解决方案,但主要目的是以最有效的方式解决它。一个人被指示从 A 点到 B 点。方向是:“南”、“北”、“西”、“东”。显然“NORTH”和“SOUTH”是相反的,“WEST”和“EAST”也是。往一个方向走,然后从相反的方向回来是浪费时间和精力。因此,我们需要通过编写一个程序来帮助这个人,该程序将消除无用的步骤并且只包含必要的指导。
例如:方向[“NORTH”、“SOUTH”、“SOUTH”、“EAST”、“WEST”、“NORTH”、“WEST”]应简化为[“WEST”]。这是因为去“北”然后立即“南”意味着回到同一个地方。所以我们取消它们,我们有[“SOUTH”,“EAST”,“WEST”,“NORTH”,“WEST”]。接下来,我们走“SOUTH”,走“EAST”,然后立即走“WEST”,这又意味着回到同一点。因此我们取消“EAST”和“WEST”来给我们[“SOUTH”,“NORTH”,“WEST”]。很明显,“SOUTH”和“NORTH”是相反的,因此取消了,最后我们留下了[“WEST”]。
例子:
Python3
opposite = {'NORTH': 'SOUTH',
'EAST': 'WEST',
'SOUTH': 'NORTH',
'WEST': 'EAST'}
# Function to find the reduced
# direction
def dirReduc(givenDirections):
finalDirections = []
for d in range(0, len(givenDirections)):
if finalDirections:
if finalDirections[-1] == opposite[givenDirections[d]]:
finalDirections.pop()
else:
finalDirections.append(givenDirections[d])
else:
finalDirections.append(givenDirections[d])
return finalDirections
# Driver Code
print(dirReduc(["NORTH", "SOUTH", "SOUTH", "EAST", "WEST", "NORTH", "WEST"]))
在上面的解决方案中,我们创建了一个相反的字典来帮助我们确定一个给定的方向是否与另一个相反。接下来,我们初始化一个名为 finalDirections 的变量,这将是我们的输出。如果 givenDirections 中的方向与 finalDirections 中的最后一个元素相反,我们将其从 finalDirections 中弹出,否则我们将其附加到 finalDirections。
输出:
['WEST'] 比较数组
这个问题有助于理解Python中数组(列表)的关键概念。如果两个数组包含相同的元素且顺序相同,则称它们是相同的。但是,在这个问题中,我们将比较两个数组,看看它们是否相同,但略有不同。在这里,如果一个数组的元素是其他数组元素的平方并且无论顺序如何,两个数组都是相同的。考虑两个数组a和b 。
a = [121, 144, 19, 161, 19, 144, 19, 11]
b = [121, 14641, 20736, 361, 25921, 361, 20736, 361]
这里b可以写成:
b = [11*11, 121*121, 144*144, 19*19, 161*161, 19*19, 144*144, 19*19]
这是 a 的每个元素的平方。因此,它们是相同的。如果a或b为 None,我们的程序应该写为 False
例子:
Python3
# function to compare the arrays
def comp(array1, array2):
# checking if any array is None
if array1 is None or array2 is None:
return False
# checking if any of the array
# is a square of the other
if (sorted(array1) == sorted([i ** 2 for i in array2])) or (sorted(array2) == sorted([i ** 2 for i in array1])):
return True
return False
# Driver Code
comp([1,2,3,4], [1,4,9,16])
输出:
True