在Python中使用 argparse 进行命令行选项和参数解析
命令行参数是在程序调用期间与调用语句一起传递的那些值。通常, Python使用sys.argv数组来处理这些参数,但在这里我们描述了如何通过使用argparse模块使其更加资源化和用户友好。
解析模块
Python中的argparse模块有助于在命令行环境中创建程序,这种方式不仅易于编码,而且可以改善交互。 argparse模块还自动生成帮助和使用消息,并在用户给程序无效参数时发出错误。
使用 Argparse 的步骤
- 创建解析器:导入 argparse 模块是处理该概念的第一种方法。导入它后,您必须创建一个解析器或 ArgumentParser 对象,该对象将存储必须从Python命令行传递的所有必要信息。
Syntax: class argparse.ArgumentParser(prog=None, usage=None, description=None, epilog=None, parents=[], formatter_class=argparse.HelpFormatter, prefix_chars=’-‘, fromfile_prefix_chars=None, argument_default=None, conflict_handler=’error’, add_help=True, allow_abbrev=True)
Parameters:
- prog– name of the program (default=sys.argv[0])
- usage– string describes the program usage(default: generated from arguments added to the parser)
- description– text to display before the argument help(default: none)
- epilog– text to display after the argument help (default: none)
- parents– list of ArgumentParser objects whose arguments should also be included
- formatter_class– class for customizing the help output
- prefix_chars– set of characters that prefix optional arguments (default: ‘-‘)
- fromfile_prefix_chars– set of characters that prefix files from which additional arguments should be read (default: None)
- argument_default– global default value for arguments (default: None)
- conflict_handler– strategy for resolving conflicting optionals (usually unnecessary)
- add_help– Add a -h/–help option to the parser (default: True)
- allow_abbrev– Allows long options to be abbreviated if the abbreviation is unambiguous. (default: True)
- 添加参数:下一步是用有关程序参数的信息填充 ArgumentParser。这意味着调用
add_argument()方法。这些信息告诉 ArgumentParser 如何从命令行获取参数并将它们转换为对象。Syntax: ArgumentParser.add_argument(name or flags…[, action][, nargs][, const][, default][, type][, choices][, required][, help][, metavar][, dest])
Parameters:
- name or flags– either a name or list of option string
- action– basic type of action to be taken when this argument is encountered at the command line
- nargs– number of command-line arguments that should be consumed
- const– constant value required by some action and nargs selections
- default– value produced if the arguments are absent from the command line
- type– type to which the command line arguments should be converted.
- choices – A container of the allowable values for the argument
- required – Whether or not the command-line option may be omitted (optionals only)
- help– brief description of what the argument does
- metavar – A name for the argument in usage messages
- dest – The name of the attribute to be added to the object returned by parse_args()
- 解析参数:在通过 parse_args() 解析参数时存储和使用步骤 2 中收集的信息。数据最初以字符串格式存储在 sys.argv 数组中。使用命令行数据调用 parse_args() 首先将它们转换为所需的数据类型,然后调用适当的操作以产生结果。
Syntax: ArgumentParser.parse_args(args=None, namespace=None)
Parameter:
- args – List of strings to parse. The default is taken from sys.argv.
- namespace – An object to take the attributes. The default is a new empty Namespace object
在大多数情况下,这意味着一个简单的命名空间对象将从命令行中解析出来的属性构建:
Namespace(accumulate=, integers=[ 2, 8, -7, 41 ])
这些是处理 argparse 需要熟悉的基本概念。以下是一些支持此应用程序的示例。
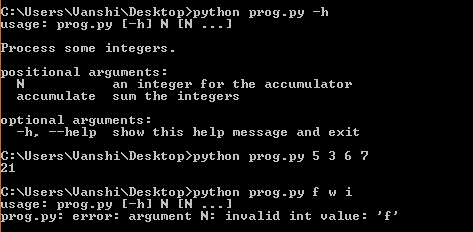
示例 1:使用 argparse 查找命令行参数的总和
import argparse
# Initialize the Parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description ='Process some integers.')
# Adding Arguments
parser.add_argument('integers', metavar ='N',
type = int, nargs ='+',
help ='an integer for the accumulator')
parser.add_argument(dest ='accumulate',
action ='store_const',
const = sum,
help ='sum the integers')
args = parser.parse_args()
print(args.accumulate(args.integers))
输出:
示例 2:按升序排列整数输入的程序
import argparse
# Initializing Parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description ='sort some integers.')
# Adding Argument
parser.add_argument('integers',
metavar ='N',
type = int,
nargs ='+',
help ='an integer for the accumulator')
parser.add_argument(dest ='accumulate',
action ='store_const',
const = sorted,
help ='arranges the integers in ascending order')
args = parser.parse_args()
print(args.accumulate(args.integers))
输出: 
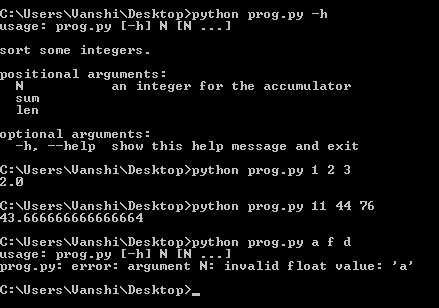
示例 3:求输入的命令行数值参数的平均值
import argparse
# Initializing Parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description ='sort some integers.')
# Adding Argument
parser.add_argument('integers',
metavar ='N',
type = float,
nargs ='+',
help ='an integer for the accumulator')
parser.add_argument('sum',
action ='store_const',
const = sum)
parser.add_argument('len',
action ='store_const',
const = len)
args = parser.parse_args()
add = args.sum(args.integers)
length = args.len(args.integers)
average = add / length
print(average)
输出: