将Python字典序列化为 XML
XML是一种设计用于传输数据的标记语言。它是在牢记自我描述的同时制作的。 XML 的语法与 HTML 相似,只是 XML 中的标签不是预先定义的。这允许将数据存储在自定义标签之间,其中标签包含有关数据的详细信息,并且数据存储在开始标签和结束标签之间。
注意:您可以在此处阅读有关 XML 的更多信息:XML |基础知识和 XML |句法
目前,有两个主要模块允许将Python字典序列化为 XML。他们是
- dict2xml
- 字典
使用 dict2xml
要快速将Python字典转换为 XML,您可以使用 dict2xml。安装它使用:
$ pip install dict2xml现在假设您在Python中有一个名为data的字典,您希望将其转换为 XML
Python3
# Converting Python Dictionary to XML
from dict2xml import dict2xml
data = {'a': 2,
'b': {
'c': 'as',
'f': True},
'd': 7,
}
xml = dict2xml(data)
print(xml)Python3
# Converting Python Dictionary to XML
# with a root elemtnt
from dict2xml import dict2xml
data = {'a': 2,
'b': {
'c': 'as',
'f': True},
'd': 7,
}
xml = dict2xml(data, wrap ='root', indent =" ")
print(xml)Python3
# Using dicttoxml for converting Python
# Dictionary to XML
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
# Data to be parsed
data = {'a': 2,
'b': {
'c': 'as',
'f': True},
'd': 7,
}
xml = dicttoxml(data)
print(xml)Python3
# Pretty printing XML after parsing
# it from dictionary
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
# Data to be parsed
data = {'a': 2,
'b': {
'c': 'as',
'f': True},
'd': 7,
}
xml = dicttoxml(data)
dom = parseString(xml)
print(dom.toprettyxml())Python3
# Removing Type Attribute from parsed XML
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# attr_type = False is used
# to remove type attributes
xml = dicttoxml(data, attr_type = False)
print(parseString(xml).toprettyxml())Python3
# Converting Python Dictionary to
# XML and saving to a file
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# Variable name of Dictionary is data
xml = dicttoxml(data)
# Obtain decode string by decode()
# function
xml_decode = xml.decode()
xmlfile = open("dict.xml", "w")
xmlfile.write(xml_decode)
xmlfile.close()Python3
# Defining custom names for lists
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# Dictionary to be converted
obj = {'mylist': [u'foo', u'bar', u'baz'],
'mydict': {
'foo': u'bar',
'baz': 1},
'ok': True}
# custom function for defining
# item names
my_item_func = lambda x: 'list_item'
xml = dicttoxml(obj, item_func = my_item_func)
# Pretty formating XML
xml_format = parseString(xml).toprettyxml()
print(xml_format)Python3
# Using parent name in dictionary
# as tag name in xml
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# Dictionary to be converted
data = {
'month':['Jan', 'Feb',
'Mar', 'Apr',
'May', 'Jun',
'Jul', 'Aug',
'Sep', 'Oct',
'Nov', 'Dec']
}
# Here x is the parent, you can chose
# to do some processing or use a part
# of the parent name for tag name
my_item_func = lambda x: x+'s'
xml = dicttoxml(data, item_func = my_item_func)
print(parseString(xml).toprettyxml())输出:
2
as
True
7 环绕根元素和自定义缩进
假设您想将答案包装在根元素周围并添加 3 个空格的缩进。
Python3
# Converting Python Dictionary to XML
# with a root elemtnt
from dict2xml import dict2xml
data = {'a': 2,
'b': {
'c': 'as',
'f': True},
'd': 7,
}
xml = dict2xml(data, wrap ='root', indent =" ")
print(xml)
输出:
2
as
True
7
字典
Dict2xml 很好,但它没有很多选项来指定我希望如何格式化我的 XML 或在标签中添加属性。 dicttoxml 可用于这些目的。它也适用于类字典和可迭代对象。通过终端或命令提示符安装它,输入:
$ pip install dicttoxml 或者
$ easy_install dicttoxml Python3
# Using dicttoxml for converting Python
# Dictionary to XML
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
# Data to be parsed
data = {'a': 2,
'b': {
'c': 'as',
'f': True},
'd': 7,
}
xml = dicttoxml(data)
print(xml)
输出:
漂亮地格式化输出
让我们漂亮地格式化文本,以便我们可以清楚地阅读它。 Python已经为此提供了一个内置包!
Python3
# Pretty printing XML after parsing
# it from dictionary
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
# Data to be parsed
data = {'a': 2,
'b': {
'c': 'as',
'f': True},
'd': 7,
}
xml = dicttoxml(data)
dom = parseString(xml)
print(dom.toprettyxml())
输出:
2
as
True
7
删除类型属性
您可能会注意到标签现在包含诸如 type=”int”/”dict”/”str” 之类的属性,可以使用attr_type=False将其关闭
Python3
# Removing Type Attribute from parsed XML
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# attr_type = False is used
# to remove type attributes
xml = dicttoxml(data, attr_type = False)
print(parseString(xml).toprettyxml())
输出:
2
as
True
7
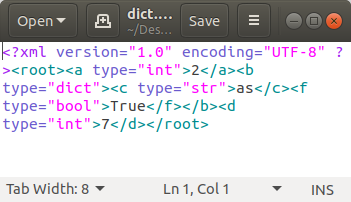
将 XML 保存到文件
有时您可能需要将 XML 保存到文件中,可以按以下方式完成
Python3
# Converting Python Dictionary to
# XML and saving to a file
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# Variable name of Dictionary is data
xml = dicttoxml(data)
# Obtain decode string by decode()
# function
xml_decode = xml.decode()
xmlfile = open("dict.xml", "w")
xmlfile.write(xml_decode)
xmlfile.close()
输出:
定义自定义项目名称
如果您不希望将列表中的项目元素称为“项目”,则可以使用将父元素名称(即列表名称)作为参数的函数来指定元素名称。
Python3
# Defining custom names for lists
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# Dictionary to be converted
obj = {'mylist': [u'foo', u'bar', u'baz'],
'mydict': {
'foo': u'bar',
'baz': 1},
'ok': True}
# custom function for defining
# item names
my_item_func = lambda x: 'list_item'
xml = dicttoxml(obj, item_func = my_item_func)
# Pretty formating XML
xml_format = parseString(xml).toprettyxml()
print(xml_format)
输出:
foo
bar
baz
bar
1
True
将父元素名称作为参数的好处是您可以编写函数来对其进行处理。假设您有一个包含一些特定项目列表的对象:
Python3
# Using parent name in dictionary
# as tag name in xml
from dicttoxml import dicttoxml
from xml.dom.minidom import parseString
# Dictionary to be converted
data = {
'month':['Jan', 'Feb',
'Mar', 'Apr',
'May', 'Jun',
'Jul', 'Aug',
'Sep', 'Oct',
'Nov', 'Dec']
}
# Here x is the parent, you can chose
# to do some processing or use a part
# of the parent name for tag name
my_item_func = lambda x: x+'s'
xml = dicttoxml(data, item_func = my_item_func)
print(parseString(xml).toprettyxml())
输出:
Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec