序列化和反序列化 N 叉树
给定一个 N 叉树,其中每个节点最多有 N 个孩子。如何序列化和反序列化?序列化是将树存储在一个文件中,以便以后可以恢复它。必须保持树的结构。反序列化是从文件中读回树。
这个帖子主要是下面帖子的延伸。
序列化和反序列化二叉树
在 N 叉树中,没有指定的左右孩子。 N 叉树由每个节点存储一个数组或子指针列表来表示。
这个想法是为每个节点存储一个“孩子结束”标记。下图显示了序列化,其中 ')' 用作子标记的结尾。
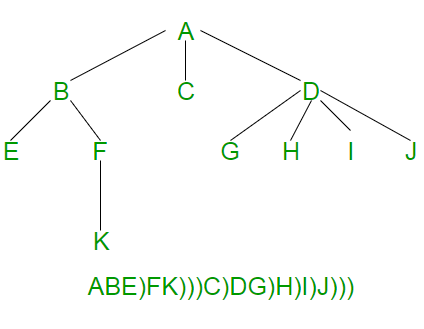
以下是上述想法的 C++ 实现。
C++
// A C++ Program serialize and deserialize an N-ary tree
#include
#define MARKER ')'
#define N 5
using namespace std;
// A node of N-ary tree
struct Node {
char key;
Node *child[N]; // An array of pointers for N children
};
// A utility function to create a new N-ary tree node
Node *newNode(char key)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
temp->child[i] = NULL;
return temp;
}
// This function stores the given N-ary tree in a file pointed by fp
void serialize(Node *root, FILE *fp)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL) return;
// Else, store current node and recur for its children
fprintf(fp, "%c ", root->key);
for (int i = 0; i < N && root->child[i]; i++)
serialize(root->child[i], fp);
// Store marker at the end of children
fprintf(fp, "%c ", MARKER);
}
// This function constructs N-ary tree from a file pointed by 'fp'.
// This function returns 0 to indicate that the next item is a valid
// tree key. Else returns 0
int deSerialize(Node *&root, FILE *fp)
{
// Read next item from file. If there are no more items or next
// item is marker, then return 1 to indicate same
char val;
if ( !fscanf(fp, "%c ", &val) || val == MARKER )
return 1;
// Else create node with this item and recur for children
root = newNode(val);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if (deSerialize(root->child[i], fp))
break;
// Finally return 0 for successful finish
return 0;
}
// A utility function to create a dummy tree shown in above diagram
Node *createDummyTree()
{
Node *root = newNode('A');
root->child[0] = newNode('B');
root->child[1] = newNode('C');
root->child[2] = newNode('D');
root->child[0]->child[0] = newNode('E');
root->child[0]->child[1] = newNode('F');
root->child[2]->child[0] = newNode('G');
root->child[2]->child[1] = newNode('H');
root->child[2]->child[2] = newNode('I');
root->child[2]->child[3] = newNode('J');
root->child[0]->child[1]->child[0] = newNode('K');
return root;
}
// A utility function to traverse the constructed N-ary tree
void traverse(Node *root)
{
if (root)
{
printf("%c ", root->key);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
traverse(root->child[i]);
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create an N-ary tree shown in above diagram
Node *root = createDummyTree();
// Let us open a file and serialize the tree into the file
FILE *fp = fopen("tree.txt", "w");
if (fp == NULL)
{
puts("Could not open file");
return 0;
}
serialize(root, fp);
fclose(fp);
// Let us deserialize the stored tree into root1
Node *root1 = NULL;
fp = fopen("tree.txt", "r");
deSerialize(root1, fp);
printf("Constructed N-Ary Tree from file is \n");
traverse(root1);
return 0;
} 输出:
Constructed N-Ary Tree from file is
A B E F K C D G H I J