Java中的向量类
Vector 类实现了一个可增长的对象数组。向量属于遗留类,但现在它与集合完全兼容。它在Java.util包中,实现了List接口,所以我们可以使用List接口的所有方法,如下所示:
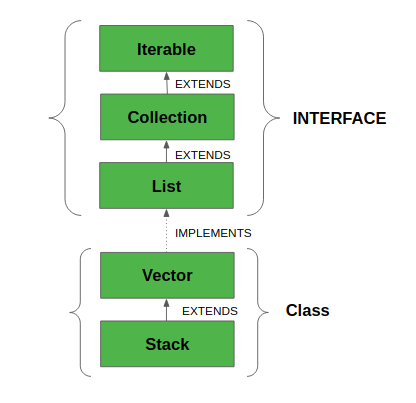
- Vector 实现了一个动态数组,这意味着它可以根据需要增长或缩小。像数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引访问的组件。
- 它们与 ArrayList 非常相似,但 Vector 是同步的,并且有一些集合框架不包含的遗留方法。
- 它还像 ArrayList 一样维护插入顺序。尽管如此,它很少在非线程环境中使用,因为它是同步的,因此,它在添加、搜索、删除和更新其元素时表现不佳。
- Vector 类返回的迭代器是快速失败的。在并发修改的情况下,它会失败并抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
句法:
public class Vector extends AbstractList implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable 这里, E是元素的类型。
- 它扩展了 AbstractList 并实现了 List 接口。
- 它实现了 Serializable、Cloneable、Iterable
、Collection 、List 、RandomAccess 接口。 - 直接已知的子类是 Stack。
关于向量容量增量的要点如下:
如果指定了增量,Vector 将在每个分配周期中根据增量进行扩展。尽管如此,如果未指定增量,则向量的容量在每个分配周期中都会翻倍。 Vector 定义了三个受保护的数据成员:
- int capacityIncreament:包含增量值。
- int elementCount:当前存储在其中的向量中的元素数。
- Object elementData[]:保存向量的数组存储在其中。
Vectors声明中的常见错误如下 如下:
- 如果定义的向量的 InitialSize 为负,Vector 将引发IllegalArgumentException 。
- 如果指定的集合为空,则抛出NullPointerException 。
构造函数
1. Vector():创建一个初始容量为10的默认向量。
Vector v = new Vector(); 2. Vector(int size):创建一个初始容量由大小指定的向量。
Vector v = new Vector(int size); 3. Vector(int size, int incr):创建一个vector,其初始容量由size指定,增量由incr指定。它指定每次向上调整向量大小时要分配的元素数。
Vector v = new Vector(int size, int incr); 4. Vector(Collection c):创建一个包含集合c的元素的向量。
Vector v = new Vector(Collection c); 向量类中的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector. |
| add(int index, E element) | Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this Vector. |
addAll(Collection extends E> c) | Appends all of the elements in the specified Collection to the end of this Vector, in the order that they are returned by the specified Collection’s Iterator. |
addAll(int index, Collection c) | Insert all of the elements in the specified Collection into this Vector at the specified position. |
| addElement(E obj) | Adds the specified component to the end of this vector, increasing its size by one. |
| capacity() | Returns the current capacity of this vector. |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this Vector. |
| clone() | Returns a clone of this vector. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this vector contains the specified element. |
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this Vector contains all of the elements in the specified Collection. |
| copyInto(Object[] anArray) | Copies the components of this vector into the specified array. |
| elementAt(int index) | Returns the component at the specified index. |
| elements() | Returns an enumeration of the components of this vector. |
| ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) | Increases the capacity of this vector, if necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of components specified by the minimum capacity argument. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified Object with this Vector for equality. |
| firstElement() | Returns the first component (the item at index 0) of this vector. |
forEach(Consumer super E> action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| get(int index) | Returns the element at the specified position in this Vector. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this Vector. |
| indexOf(Object o) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element. |
| indexOf(Object o, int index) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in this vector, searching forwards from the index, or returns -1 if the element is not found. |
| insertElementAt(E obj, int index) | Inserts the specified object as a component in this vector at the specified index. |
| isEmpty() | Tests if this vector has no components. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in a proper sequence. |
| lastElement() | Returns the last component of the vector. |
| lastIndexOf(Object o) | Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element. |
| lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) | Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in this vector, searching backward from the index, or returns -1 if the element is not found. |
| listIterator() | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence). |
| listIterator(int index) | Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. |
| remove(int index) | Removes the element at the specified position in this Vector. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this Vector. If the Vector does not contain the element, it is unchanged. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | Removes from this Vector all of its elements contained in the specified Collection. |
| removeAllElements() | Removes all components from this vector and sets its size to zero. |
| removeElement(Object obj) | Removes the first (lowest-indexed) occurrence of the argument from this vector. |
| removeElementAt(int index) | Deletes the component at the specified index. |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| replaceAll(UnaryOperator | Replaces each element of this list with the result of applying the operator to that element. |
| retainAll(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this Vector contained in the specified Collection. |
| set(int index, E element) | Replaces the element at the specified position in this Vector with the specified element. |
| setElementAt(E obj, int index) | Sets the component at the specified index of this vector to be the specified object. |
| setSize(int newSize) | Sets the size of this vector. |
| size() | Returns the number of components in this vector. |
| sort(Comparator c) | Sorts this list according to the order induced by the specified Comparator. |
| spliterator() | Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this list. |
| subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | Returns a view of the portion of this List between fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this Vector in the correct order. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this Vector in the correct order; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this Vector, containing the String representation of each element. |
| trimToSize() | Trims the capacity of this vector to be the vector’s current size. |
让我们先讨论和实现如何创建和使用 Vector,然后再使用该类的方法。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of Vector
// Via Creating and Using It
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Size of the Vector
int n = 5;
// Declaring the Vector with
// initial size n
Vector v = new Vector(n);
// Appending new elements at
// the end of the vector
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
v.add(i);
// Printing elements
System.out.println(v);
// Remove element at index 3
v.remove(3);
// Displaying the vector
// after deletion
System.out.println(v);
// iterating over vector elements
// using for loop
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
// Printing elements one by one
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
} Java
// Java Program to Add Elements in Vector Class
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// AddElementsToVector
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
// Case 1
// Creating a default vector
Vector v1 = new Vector();
// Adding custom elements
// using add() method
v1.add(1);
v1.add(2);
v1.add("geeks");
v1.add("forGeeks");
v1.add(3);
// Printing the vector elements to the console
System.out.println("Vector v1 is " + v1);
// Case 2
// Creating generic vector
Vector v2 = new Vector();
// Adding custom elements
// using add() method
v2.add(1);
v2.add(2);
v2.add(3);
// Printing the vector elements to the console
System.out.println("Vector v2 is " + v2);
}
} Java
// Java code to change the
// elements in vector class
import java.util.*;
public class UpdatingVector {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty Vector
Vector vec_tor = new Vector();
// Use add() method to add elements in the vector
vec_tor.add(12);
vec_tor.add(23);
vec_tor.add(22);
vec_tor.add(10);
vec_tor.add(20);
// Displaying the Vector
System.out.println("Vector: " + vec_tor);
// Using set() method to replace 12 with 21
System.out.println("The Object that is replaced is: "
+ vec_tor.set(0, 21));
// Using set() method to replace 20 with 50
System.out.println("The Object that is replaced is: "
+ vec_tor.set(4, 50));
// Displaying the modified vector
System.out.println("The new Vector is:" + vec_tor);
}
} Java
// Java code illustrating the removal
// of elements from vector
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class RemovingElementsFromVector {
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
// create default vector of capacity 10
Vector v = new Vector();
// Add elements using add() method
v.add(1);
v.add(2);
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("forGeeks");
v.add(4);
// removing first occurrence element at 1
v.remove(1);
// checking vector
System.out.println("after removal: " + v);
}
}Java
// Java program to iterate the elements
// in a Vector
import java.util.*;
public class IteratingVector {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create an instance of vector
Vector v = new Vector<>();
// Add elements using add() method
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("Geeks");
v.add(1, "For");
// Using the Get method and the
// for loop
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Using the for each loop
for (String str : v)
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
} [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 2, 3, 5]
1 2 3 5Note:
- If the vector increment is not specified then it’s capacity will be doubled in every increment cycle.
- The capacity of a vector cannot be below the size, it may equal to it.
在Java中对 Vector 类执行各种操作
让我们讨论一下 Vector 类的各种操作,如下所示:
- 添加元素
- 更新元素
- 移除元素
- 迭代元素
操作 1:添加元素
为了将元素添加到 Vector,我们使用 add() 方法。该方法被重载以根据不同的参数执行多个操作。它们如下所列:
- add(Object):此方法用于在 Vector 的末尾添加一个元素。
- add(int index, Object):此方法用于在 Vector 中的特定索引处添加元素。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Add Elements in Vector Class
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// AddElementsToVector
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
// Case 1
// Creating a default vector
Vector v1 = new Vector();
// Adding custom elements
// using add() method
v1.add(1);
v1.add(2);
v1.add("geeks");
v1.add("forGeeks");
v1.add(3);
// Printing the vector elements to the console
System.out.println("Vector v1 is " + v1);
// Case 2
// Creating generic vector
Vector v2 = new Vector();
// Adding custom elements
// using add() method
v2.add(1);
v2.add(2);
v2.add(3);
// Printing the vector elements to the console
System.out.println("Vector v2 is " + v2);
}
}
输出:
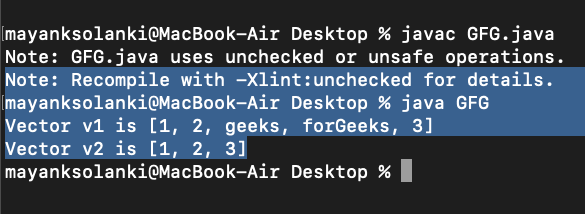
Vector v1 is [1, 2, geeks, forGeeks, 3]
Vector v2 is [1, 2, 3]操作 2:更新元素
添加元素后,如果我们希望更改元素,可以使用 set() 方法完成。由于 Vector 是索引的,因此我们希望更改的元素由元素的索引引用。因此,此方法采用索引和要在该索引处插入的更新元素。
例子
Java
// Java code to change the
// elements in vector class
import java.util.*;
public class UpdatingVector {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty Vector
Vector vec_tor = new Vector();
// Use add() method to add elements in the vector
vec_tor.add(12);
vec_tor.add(23);
vec_tor.add(22);
vec_tor.add(10);
vec_tor.add(20);
// Displaying the Vector
System.out.println("Vector: " + vec_tor);
// Using set() method to replace 12 with 21
System.out.println("The Object that is replaced is: "
+ vec_tor.set(0, 21));
// Using set() method to replace 20 with 50
System.out.println("The Object that is replaced is: "
+ vec_tor.set(4, 50));
// Displaying the modified vector
System.out.println("The new Vector is:" + vec_tor);
}
}
Vector: [12, 23, 22, 10, 20]
The Object that is replaced is: 12
The Object that is replaced is: 20
The new Vector is:[21, 23, 22, 10, 50]操作 3:移除元素
为了从 Vector 中删除元素,我们可以使用 remove() 方法。该方法被重载以根据不同的参数执行多个操作。他们是:
- remove(Object):此方法用于从 Vector 中移除一个对象。如果有多个这样的对象,则删除第一次出现的对象。
- remove(int index):由于 Vector 被索引,因此此方法采用一个整数值,该值仅删除 Vector 中该特定索引处存在的元素。删除元素后,所有元素都向左移动以填充空间并更新对象的索引。
例子
Java
// Java code illustrating the removal
// of elements from vector
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class RemovingElementsFromVector {
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
// create default vector of capacity 10
Vector v = new Vector();
// Add elements using add() method
v.add(1);
v.add(2);
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("forGeeks");
v.add(4);
// removing first occurrence element at 1
v.remove(1);
// checking vector
System.out.println("after removal: " + v);
}
}
输出:
after removal: [1, Geeks, forGeeks, 4]操作 4:迭代向量
有多种方法可以遍历 Vector。最著名的方法是结合使用基本的 for 循环和 get() 方法来获取特定索引处的元素和高级的 for 循环。
例子
Java
// Java program to iterate the elements
// in a Vector
import java.util.*;
public class IteratingVector {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// create an instance of vector
Vector v = new Vector<>();
// Add elements using add() method
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("Geeks");
v.add(1, "For");
// Using the Get method and the
// for loop
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// Using the for each loop
for (String str : v)
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
}
Geeks For Geeks
Geeks For GeeksNote: Do give a read to the ArrayList vs Vector class in Java to grasp it better.