Spring Boot – 多模块项目
当某些事情变得复杂时,有时会出现在应用程序的开发阶段。管理应用程序的服务、存储库、实体等变得非常困难。我们知道 Spring Boot 的开发是出于自动配置、效率、快速开发、减少繁琐工作等原因。为了克服这个或类似的问题,我们可以使用 Spring Boot 将应用程序作为 Multi-Module项目。在多模块项目中,一个应用程序被划分为多个模块,每个模块在应用程序的某些功能中扮演着重要的角色。一个模块可以被认为是一个独立的项目或子项目。
Note: Multi-Module Project is just a set of multiple projects where each project has its own respective function.
多模块项目的优势
- 它提供了一种强大的能力,只需一个命令即可构建所有子模块。
- 我们可以从父模块运行构建命令。
- 在构建应用程序时,构建系统负责构建顺序。
- 应用程序的部署变得非常方便和灵活。
- 此外,可以重复使用来自不同项目的各种模块的代码。
- 最后但并非最不重要的一点是,借助 Multi-Module Project 架构,我们可以从微服务架构中获益。
多模块项目的工作
- 首先,您必须创建一个父模块。
- 父模块充当子模块的容器。
- 此外,您可以使用 Parent 模块来引导应用程序( main() 方法)。
- 或者,您也可以通过实现 main() 方法来引导应用程序并从父模块中删除 main() 方法来使用任何子模块。
- 你的父模块应该有 'pom' 包装而不是 jar 和 war。
- 当您创建子模块时,它们都会列在父模块的 pom.xml 中的“
”标签中。 - 您在父模块的 pom.xml 中登记的所有依赖项将直接由子模块自动继承。
- 因此,您无需在子模块的 pom.xml 中添加依赖项即可使用它们。
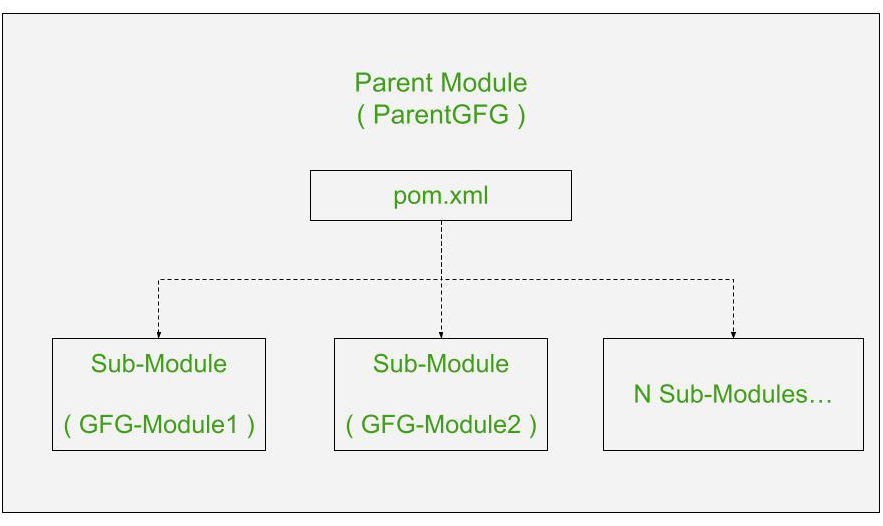
多模块项目的架构
创建多模块项目(STS – Spring Tool Suite)
- 创建一个简单的 Spring Starter 项目(文件->新建-> Spring Starter 项目->下一步-> (选择依赖项) ->下一步->完成)
- 更改或添加 '
pom ' 。 - 添加一个子模块(右键单击父模块->新建->其他-> Maven -> Maven 模块->下一步(选中两个复选框) ->下一步-> jar 或战争->完成)。
- 创建子模块后,父模块将包含子模块的文件夹,同时也会创建已创建的各个子模块的独立项目。
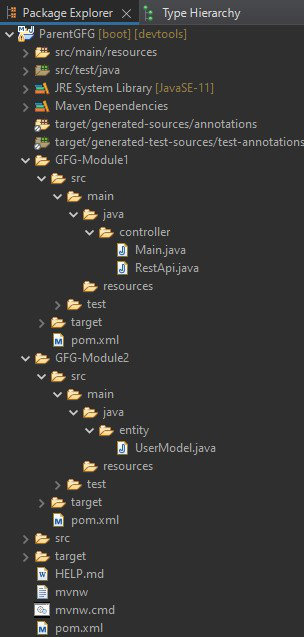
多模块项目 ( Parent-Module ) – Maven
ParentGFG – 父模块
pom.xml (配置)
XML
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.6.3
sia
ParentGFG
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
pom
ParentGFG
Multi Module Project
11
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
runtime
true
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
org.projectlombok
lombok
GFG-Module1
GFG-Module2
XML
4.0.0
sia
ParentGFG
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
GFG-Module1
GFG-Module1
GeeksforGeeks
Java
package controller;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
}Java
package controller;
import entity.UserModel;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/get")
public class RestApi {
@GetMapping public UserModel get()
{
UserModel entity = new UserModel();
entity.setId("1");
entity.setName("Darshan.G.Pawar");
entity.setEmail("geek@geek");
entity.setPincode("422 009");
return entity;
}
}XML
4.0.0
sia
ParentGFG
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
GFG-Module2
GFG-Module2
GeeksforGeeks
Java
package entity;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@Data
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class UserModel {
String id;
String name;
String email;
String pincode;
}Notes:
- After creating Spring Starter Project with a jar or war packaging, make sure that you add or change the ‘packaging’ tag with ‘pom’ -> ‘
pom ’. - When you will create sub-modules, the ‘modules’ tag will automatically get generated with added respective modules.
- You can also remove the ‘src’ folder from Parent Module after implementing the main() method in any of the sub-module, as the Parent Module can also act just like a container.
GFG-Module1(子模块)
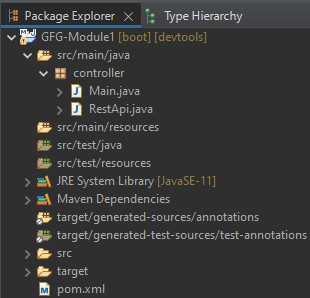
一个独立的 GFG-Module1(子模块)项目 – Maven
pom.xml (配置)
- 声明该子模块将成为其一部分的父模块。
- 该子模块的信息标签也被初始化。
XML
4.0.0
sia
ParentGFG
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
GFG-Module1
GFG-Module1
GeeksforGeeks
主要的。 Java (应用程序的引导)
Java
package controller;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
}
休息API。 Java (应用程序的端点)
- 此类使用自动从父模块的 pom.xml 继承的“Starter Web”依赖项。
- 这个控制器类接受 HTTP 请求。
- 这里,HTTP GET 请求被 get() 方法接受。
- 此方法使用在子模块 (GFG-Module2) 中创建和声明的实体类。
- 要从不同的模块导入类等,您必须将鼠标悬停在红色错误下划线上。
- 单击 -> 'fix project setup' 并选择您在其中创建类的相应子模块。
Java
package controller;
import entity.UserModel;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/get")
public class RestApi {
@GetMapping public UserModel get()
{
UserModel entity = new UserModel();
entity.setId("1");
entity.setName("Darshan.G.Pawar");
entity.setEmail("geek@geek");
entity.setPincode("422 009");
return entity;
}
}
GFG-Module2(子模块)
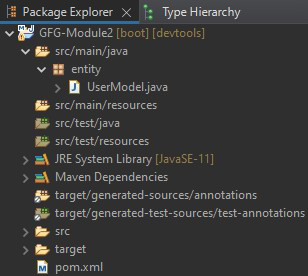
一个独立的 GFG-Module2(子模块)项目 – Maven
pom.xml (配置)
XML
4.0.0
sia
ParentGFG
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
GFG-Module2
GFG-Module2
GeeksforGeeks
用户模型。 Java (用户数据实体类)
- 这个类代表一个用户实体类,已经被RestApi的get()方法使用了。 Java类。
- 此类需要所有实例变量字段的一组重要的 Getter 和 Setter 方法。
- 此类使用从父模块的 pom.xml 自动继承的“Lombok”依赖项。
- 因此,Lombok 库的“ @Data ”注解用于在运行时自动生成 Getter 和 Setter 方法。
- 注释“ @RequiredArgsConstructor ”用于为类的必需(其中约束为“ @NonNull” )或最终字段自动生成构造函数。
- 如果类不包含字段,则“ @RequiredArgsConstructor ”注释充当“ @NoArgsConstructor ”注释,它创建零参数构造函数。
Java
package entity;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@Data
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class UserModel {
String id;
String name;
String email;
String pincode;
}
输出: RestApi。 GFG-Module1的Java
- GFG-Module2(子模块)声明一个实体(数据)对象。
- 此数据用于 GFG-Module1(子模块)的 RESTful API 返回的响应正文中。
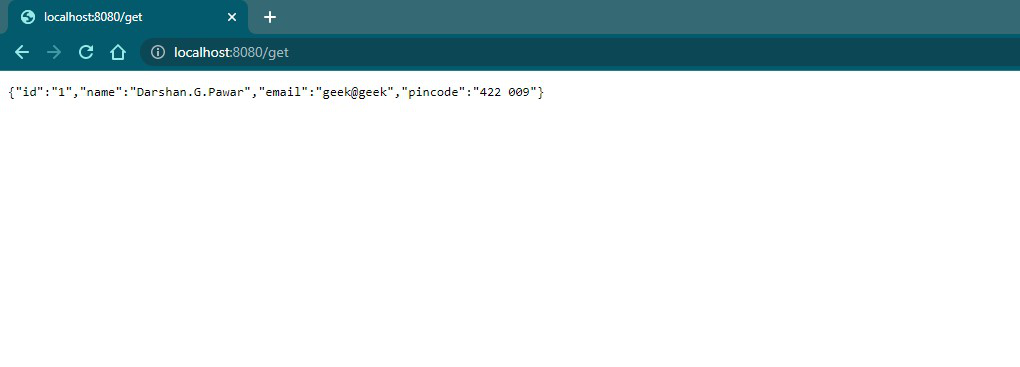
来自 @RestController 的默认 JSON 正文输出(UserModel 对象)
Note: You will have to run the GFG-Module1 as the main() method and the controller class is in this sub-module.