- Spring Boot多模块项目(1)
- Spring Boot – 多模块项目
- 如何创建一个 Spring Boot 项目?(1)
- 如何创建一个 Spring Boot 项目?
- Spring Boot CLI-创建项目(1)
- Spring Boot CLI-创建项目
- spring boot - CSS (1)
- Spring Boot属性(1)
- Spring Boot属性
- Spring 和 Spring Boot 的区别
- Spring 和 Spring Boot 的区别(1)
- spring boot - CSS 代码示例
- Spring和Spring Boot之间的区别(1)
- Spring和Spring Boot之间的区别
- Spring Boot应用程序
- Spring Boot应用程序(1)
- Spring Boot版本
- Spring Boot版本(1)
- Spring Boot教程(1)
- Spring Boot教程
- 什么是 Spring Boot - Java (1)
- Spring Boot 简介(1)
- Spring Boot 简介
- Spring Boot-简介(1)
- Spring Boot-简介
- Spring Cloud与Spring Boot
- Spring Cloud与Spring Boot(1)
- 讨论Spring Boot
- 讨论Spring Boot(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-11 05:11:08 🧑 作者: Mango
Spring Boot多模块项目
多模块项目
包含嵌套Maven项目的Spring Boot项目称为多模块项目。在多模块项目中,父项目充当基础Maven配置的容器。
换句话说,一个多模块项目是由管理一组子模块的父pom构建的。或者,一个多模块项目是由父POM引用一个或多个子模块定义的。
父Maven项目必须包含使项目成为聚合器的包装类型pom。父项目的pom.xml文件包含子项目继承的所有模块,公共依赖项和属性的列表。父pom位于项目的根目录中。子模块是实际的Spring Boot项目,它们从父项目继承maven属性。
当我们运行多模块项目时,所有模块都一起部署在嵌入式Tomcat服务器中。我们也可以部署一个单独的模块。
父POM
父POM定义组ID,工件ID,版本和包装。在以前的Maven项目中,我们已经看到父POM定义了包装罐。但是在多模块项目中,父POM定义了包装pom。包装pom涉及其他Maven项目。
为什么我们需要多模块项目
将项目分为多个模块非常有用且易于维护。我们还可以轻松编辑或删除项目中的模块,而不会影响其他模块。当我们需要单独部署模块时,这很有用。
我们只需要在父pom中指定所有依赖项即可。所有其他模块共享相同的pom,因此我们无需在每个模块中分别指定相同的依赖项。它使代码更易于与大型项目保持一致。
子模块的耳朵,战争和罐子
子模块可以是任何项目,并且可以具有任何包装。我们可以自由地在模块和包之间创建任何类型的依赖关系。
例如,我们正在创建EAR (企业归档), WAR (Web归档)和JAR (Java归档)文件。 JAR文件捆绑到war文件中,而war文件捆绑到EAR文件中。 EAR文件是准备在应用服务器上部署的最终软件包。
EAR文件包含一个或多个WAR文件。每个WAR文件都包含服务项目,该项目对所有WAR文件和JAR中的包装类型具有通用代码。
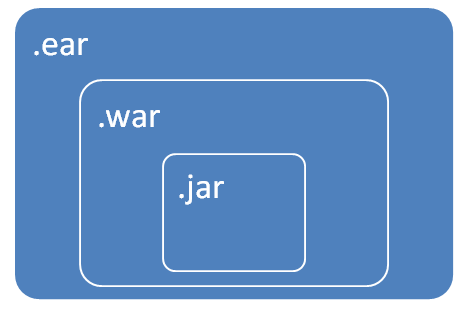
Maven子项目/模块
- 子模块是独立的Maven项目,它们共享父项目的属性。
- 可以使用单个命令来构建所有子项目,因为它位于父项目中。
- 定义项目之间的关系更容易。
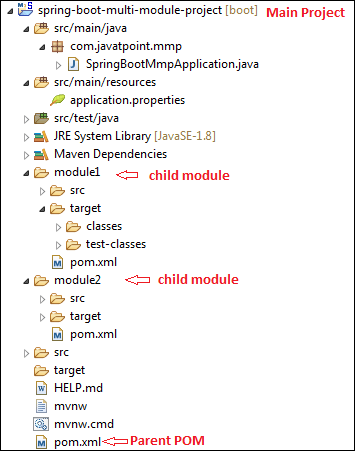
多模块项目目录结构
让我们了解多模块项目目录结构。
在下图中,我们创建了一个名为spring-boot-multi-module-project的项目。它在目录底部包含父pom。之后,我们创建了两个分别名为module1和module2的Maven模块。这两个模块包含自己的pom文件。
让我们打开父POM并查看在项目中创建Maven模块时其配置。
pom.xml
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.2.2.BUILD-SNAPSHOT
com.javatpoint
spring-boot-example
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
spring-boot-multi-module-project
Demo project for Spring Boot
1.8
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.2.1.RELEASE
pom
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework
spring-webmvc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.junit.vintage
junit-vintage-engine
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
spring-milestones
Spring Milestones
https://repo.spring.io/milestone
spring-snapshots
Spring Snapshots
https://repo.spring.io/snapshot
true
spring-milestones
Spring Milestones
https://repo.spring.io/milestone
spring-snapshots
Spring Snapshots
https://repo.spring.io/snapshot
true
module1
module2
上面的pom文件与我们在前面的示例中看到的相同。但是在此pom文件中,需要注意两件事:包装和模块。
创建多模块项目时,需要在父pom文件而不是jar中配置包装pom。
pom
当我们在项目中创建Maven模块时,Spring Boot会自动在module标签内的父pom中配置模块,如下所示。
module1
module2
现在,我们将看到module1的pom文件中包含什么。
pom.xml
4.0.0
com.javatpoint
spring-boot-multi-module-project
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
com.javatpoint
module1
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
module1
http://maven.apache.org
UTF-8
junit
junit
3.8.1
test
在这里,需要注意的一点是,以上pom文件不包含诸如starter-web,web-mvc等通用依赖关系。它继承了父pom的所有通用依赖关系和属性。
Spring Boot多模块项目示例
让我们创建一个多模块应用程序的示例。
- 在以下示例中,我们创建了一个名为spring-boot-multimodule的Maven项目。它是主要应用程序。在主应用程序中,我们创建了五个模块,如下所示:
- 应用
- 模型
- 资料库
- 服务API
- 服务说明
应用模块
应用程序模块是项目的主要模块。它包含应用程序类,在其中定义了运行Spring Boot Application所需的main方法。它还包含应用程序配置属性,Controller,视图和资源。
应用程序模块包括模型模块,作为依赖的服务实现模块,其中包含模型模块,存储库模块和服务API模块。
模型模块
模型模块包含要在项目中使用的实体和视觉对象。
储存库模块
存储库模块包含要在项目中使用的存储库。这取决于模型模块。
服务API模块
服务API模块包含所有项目服务。它还取决于模型模块。
服务实施模块
服务实现模块实现服务。它取决于存储库模块和服务API模块。
POM聚合器(父POM)
父pom包含所有应用程序模块。它还包括一个以上模块所需的所有常见依赖关系和属性。定义的依赖项没有版本,因为该项目已将Spring IO Platform定义为父项。
让我们了解所创建的多模块应用程序的结构。
Spring-boot-multimodule
├── pom.xml
│ └── REDME.adoc
├── application
│ ├── pom.xml
│ └── src
│ └── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── sample
│ │ └── multimodule
│ │ ├── SampleWebJspApplication.java
│ │ └── web
│ │ └── WelcomeController.java
│ └── resources
│ ├── application.properties
│ └── templates
│ └── welcome
│ └── show.html
├── model
│ ├── pom.xml
│ └── src
│ └── main
│ └── java
│ └── sample
│ └── multimodule
│ └── domain
│ └── entity
│ └── Account.java
|
├── repository
│ ├── pom.xml
│ └── src
│ └── main
│ └── java
│ └── sample
│ └── multimodule
│ └── repository
│ └── AccountRepository.java
├── service-api
│ ├── pom.xml
│ └── src
│ └── main
│ └── java
│ └── sample
│ └── multimodule
│ └── service
│ └── api
│ ├── AccountNotFoundException.java
│ └── AccountService.java
└── service-impl
├── pom.xml
└── src
└── main
└── java
└── sample
└── multimodule
└── service
└── impl
└── AccountServiceImpl.java
步骤1:使用名称spring-boot-multimodule创建一个Maven项目。
步骤2:打开pom.xml (父pom)文件,并将打包类型jar更改为pom。
pom.xml(父pom)
4.0.0
io.spring.platform
platform-bom
2.0.1.RELEASE
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
pom
Parent - Pom Aggregator
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
在上面的pom文件中要注意的一件事是,由于我们尚未创建,因此未配置任何Maven模块。现在,我们将如上所述创建一个Maven模块。
步骤3:使用名称应用程序创建Maven模块。
步骤4:打开应用程序模块的pom.xml文件,并确保打包类型为jar。
pom.xml
4.0.0
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
sample.multimodule.application
jar
Project Module - Application
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule.service.impl
${project.version}
org.apache.tomcat.embed
tomcat-embed-jasper
provided
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
步骤5:创建主类。这是要运行的类。
SampleWebJspApplication.java
package sample.multimodule;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityScan;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SampleWebJspApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
SpringApplication.run(SampleWebJspApplication.class, args);
}
}
步骤6:在smaple.multimodule.web包下创建一个名称为WelocameController的Controller类。
WelcomeController.java
package sample.multimodule.web;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import sample.multimodule.domain.entity.Account;
import sample.multimodule.service.api.AccountService;
@Controller
public class WelcomeController
{
@Value("${application.message:Hello World}")
private String message = "Hello World";
@Autowired
protected AccountService accountService;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String welcome(Map model)
{
// Trying to obtain 23 account
Account account = accountService.findOne("23");
if(account == null){
// If there's some problem creating account, return show view with error status
model.put("message", "Error getting account!");
model.put("account", "");
return "welcome/show";
}
// Return show view with 23 account info
String accountInfo = "Your account number is ".concat(account.getNumber());
model.put("message", this.message);
model.put("account", accountInfo);
return "welcome/show";
}
@RequestMapping("foo")
public String foo(Map model) {
throw new RuntimeException("Foo");
}
}
步骤7:在src / main / resource->模板-> welcome文件夹下创建一个名为show.html的HTML文件。
show.html
Spring Boot Multimodule
Message:
Your account:
步骤8:打开application.properties文件,将应用程序消息和thymeleaf缓存配置为false。
application.properties
# Application messages
application.message = Hello User!
dummy.type = type-inside-the-war
# Spring Thymeleaf config
spring.thymeleaf.cache = false
创建上述所有文件之后,应用程序模块目录如下所示:
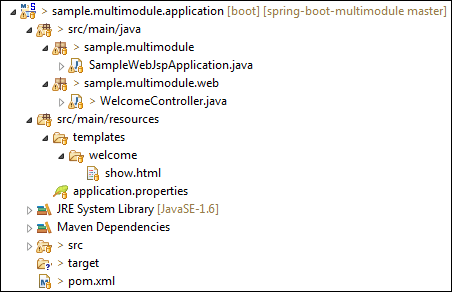
让我们创建第二个模型模块。
步骤9:使用名称模型创建Maven模块。
步骤10:打开模型模块的pom.xml文件,并确保包装类型为jar。
pom.xml
4.0.0
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
sample.multimodule.model
jar
Project Module - Model
Module that contains all Entities and Visual Objects to be used in the project. It doesn't have any dependencies.
步骤11:在包sample.multimodule.domain.entity下创建一个名称为Account的类。
Account.java
package sample.multimodule.domain.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
@Entity
public class Account
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String number;
private String type;
private String creditCardNumber;
/**
* Create an empty account.
*/
public Account() {
}
/**
* Create a new account.
*
* @param number
* the account number
* @param id
* the account id
*/
public Account(Long id, String number) {
this.number = number;
this.id = id;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getCreditCardNumber() {
return creditCardNumber;
}
public void setCreditCardNumber(String creditCardNumber) {
this.creditCardNumber = creditCardNumber;
}
}
创建上述所有文件之后,模型模块目录如下所示:
让我们创建第三个模块,即存储库。
步骤12:使用名称存储库创建Maven模块。
步骤13:打开应用程序模块的pom.xml文件,并确保打包类型为jar。
pom.xml
4.0.0
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
sample.multimodule.repository
jar
Project Module - Repository
Module that contains all repositories to be used in the project. Depends of Model Module.
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule.model
${project.version}
org.hsqldb
hsqldb
runtime
步骤14:在包sample.multimodule.repository下创建一个名称为AccountRepository的类。
AccountRepository.java
package sample.multimodule.repository;
import org.springframework.data.domain.*;
import org.springframework.data.repository.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import sample.multimodule.domain.entity.Account;
@Repository
public interface AccountRepository extends CrudRepository
{
Account findByNumber(String number);
}
创建上述所有文件之后,存储库模块目录如下所示:
让我们创建第四个模块,即service-api。
步骤15:使用名称service-api创建一个Maven模块。
步骤16:打开应用程序service-api的pom.xml文件,并确保打包类型为jar。
pom.xml
4.0.0
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
sample.multimodule.service.api
jar
Project Module - Service API
Module that contains API of all project services. Depends of Model Module.
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule.model
${project.version}
步骤17:创建一个名为sample.multimodule.service.api的包。
步骤18:创建一个名称为AccountNotFoundException的类。如果找不到该帐户,它将处理异常。
AccountNotFoundException.java
package sample.multimodule.service.api;
public class AccountNotFoundException extends RuntimeException
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3891534644498426670L;
public AccountNotFoundException(String accountId)
{
super("No such account with id: " + accountId);
}
}
步骤19:创建一个名称为AccountService的类。它提供与帐户相关的服务,例如查找和创建帐户。
AccountService.java
package sample.multimodule.service.api;
import java.util.List;
import sample.multimodule.domain.entity.Account;
public interface AccountService
{
/**
* Finds the account with the provided account number.
*
* @param number The account number
* @return The account
* @throws AccountNotFoundException If no such account exists.
*/
Account findOne(String number) throws AccountNotFoundException;
/**
* Creates a new account.
* @param number
* @return created account
*/
Account createAccountByNumber(String number);
}
创建上述所有文件之后,service-api模块目录如下所示:
步骤20:使用名称service-impl创建一个Maven模块。
步骤21:打开应用程序service-impl的pom.xml文件,并确保打包类型为jar。
pom.xml
4.0.0
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
sample.multimodule.service.impl
jar
Project Module - Service Implementation
Module that contains services implementation defined on Service API module. Depends of Repository Module and Service API Module.
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule.repository
${project.version}
sample.multimodule
sample.multimodule.service.api
${project.version}
步骤22:在包sample.multimodule.service.impl下创建一个名称为AccountServiceImpl的类。
AccountServiceImpl.java
package sample.multimodule.service.impl;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import sample.multimodule.domain.entity.Account;
import sample.multimodule.repository.AccountRepository;
import sample.multimodule.service.api.AccountService;
import sample.multimodule.service.api.AccountNotFoundException;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService
{
@Value("${dummy.type}")
private String dummyType;
@Autowired
private AccountRepository accountRepository;
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* Dummy method for testing purposes.
*
* @param number The account number. Set 0000 to get an {@link AccountNotFoundException}
*/
@Override
public Account findOne(String number) throws AccountNotFoundException {
if(number.equals("0000")) {
throw new AccountNotFoundException("0000");
}
Account account = accountRepository.findByNumber(number);
if(account == null){
account = createAccountByNumber(number);
}
return account;
}
@Override
public Account createAccountByNumber(String number) {
Account account = new Account();
account.setNumber(number);
return accountRepository.save(account);
}
public String getDummyType() {
return dummyType;
}
public void setDummyType(String dummyType) {
this.dummyType = dummyType;
}
}
创建上述所有文件之后, service-impl模块目录如下所示:
现在打开父pom文件,我们看到我们创建的所有Maven模块都在父pom中进行了配置。
现在确保已创建所有五个模块,如下所示:
创建所有模块后,主项目目录如下所示:
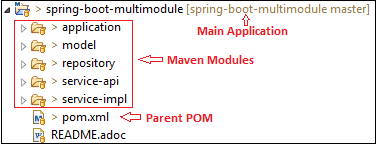
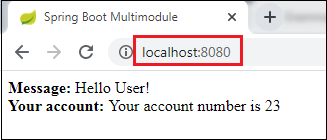
步骤23:现在将SampleWebJspApplication.java文件作为Java Application运行。
步骤24:打开浏览器并调用URL http:// localhost:8080。它返回消息和帐号为23。