删除双向链表中的节点
先决条件:双向链表集1|介绍和插入
编写一个函数来删除双向链表中的给定节点。
原始双向链表
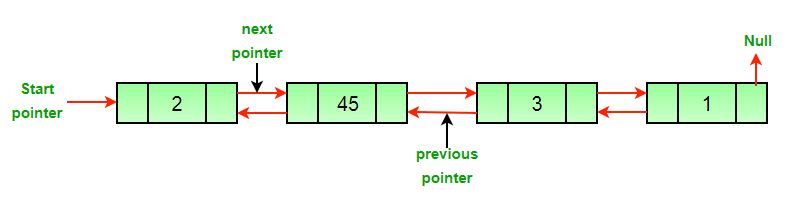
方法:删除双向链表中的节点可以分为三大类:
- 删除头节点后。
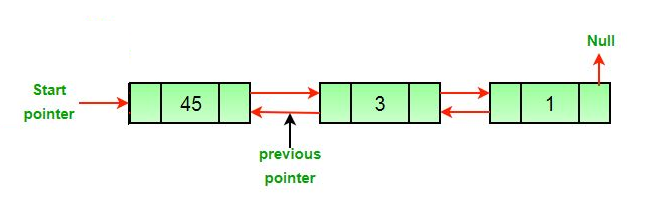
- 删除中间节点后。
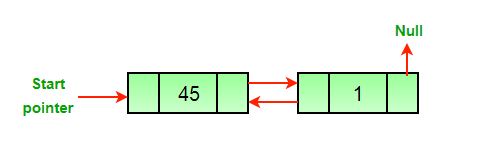
- 删除最后一个节点后。

如果要删除的节点的指针和头指针是已知的,则所有提到的三种情况都可以分两步处理。
- 如果要删除的节点是头节点,则将下一个节点作为头节点。
- 如果一个节点被删除,连接被删除节点的下一个和上一个节点。
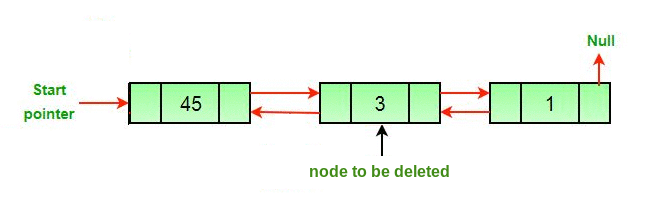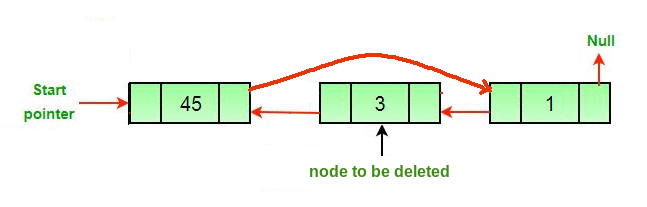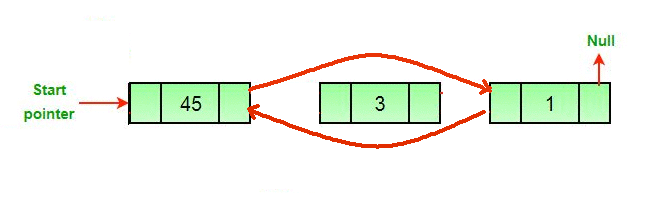
算法
- 让要删除的节点为del 。
- 如果要删除的节点是头节点,则将头指针更改为下一个当前头。
if headnode == del then
headnode = del.nextNode- 接下来的一组以德尔,如果之前的德尔存在。
if del.nextNode != none
del.nextNode.previousNode = del.previousNode - 旁边德尔的套装prev,如果旁边德尔存在。
if del.previousNode != none
del.previousNode.nextNode = del.nextC++
// C++ program to delete a node from
// Doubly Linked List
#include
using namespace std;
/* a node of the doubly linked list */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
};
/* Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
del --> pointer to node to be deleted. */
void deleteNode(Node** head_ref, Node* del)
{
/* base case */
if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL)
return;
/* If node to be deleted is head node */
if (*head_ref == del)
*head_ref = del->next;
/* Change next only if node to be
deleted is NOT the last node */
if (del->next != NULL)
del->next->prev = del->prev;
/* Change prev only if node to be
deleted is NOT the first node */
if (del->prev != NULL)
del->prev->next = del->next;
/* Finally, free the memory occupied by del*/
free(del);
return;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
cout << "Original Linked list ";
printList(head);
/* delete nodes from the doubly linked list */
deleteNode(&head, head); /*delete first node*/
deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete middle node*/
deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete last node*/
/* Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL */
cout << "\nModified Linked list ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
#include
#include
/* a node of the doubly linked list */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
/* Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
del --> pointer to node to be deleted. */
void deleteNode(struct Node** head_ref, struct Node* del)
{
/* base case */
if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL)
return;
/* If node to be deleted is head node */
if (*head_ref == del)
*head_ref = del->next;
/* Change next only if node to be deleted is NOT the last node */
if (del->next != NULL)
del->next->prev = del->prev;
/* Change prev only if node to be deleted is NOT the first node */
if (del->prev != NULL)
del->prev->next = del->next;
/* Finally, free the memory occupied by del*/
free(del);
return;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
printf("\n Original Linked list ");
printList(head);
/* delete nodes from the doubly linked list */
deleteNode(&head, head); /*delete first node*/
deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete middle node*/
deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete last node*/
/* Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL */
printf("\n Modified Linked list ");
printList(head);
getchar();
} Java
// Java program to delete a node from
// Doubly Linked List
// Class for Doubly Linked List
public class DLL {
Node head; // head of list
/* Doubly Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// next and prev is by default initialized
// as null
Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as head
// and previous as NULL
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
head = new_Node;
}
// This function prints contents of linked list
// starting from the given node
public void printlist(Node node)
{
Node last = null;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
// head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
// del --> data of node to be deleted.
void deleteNode(Node del)
{
// Base case
if (head == null || del == null) {
return;
}
// If node to be deleted is head node
if (head == del) {
head = del.next;
}
// Change next only if node to be deleted
// is NOT the last node
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
// Change prev only if node to be deleted
// is NOT the first node
if (del.prev != null) {
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
// Finally, free the memory occupied by del
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the empty list
DLL dll = new DLL();
// Insert 2. So linked list becomes 2->NULL
dll.push(2);
// Insert 4. So linked list becomes 4->2->NULL
dll.push(4);
// Insert 8. So linked list becomes 8->4->2->NULL
dll.push(8);
// Insert 10. So linked list becomes 10->8->4->2->NULL
dll.push(10);
System.out.print("Created DLL is: ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
// Deleting first node
dll.deleteNode(dll.head);
// List after deleting first node
// 8->4->2
System.out.print("\nList after deleting first node: ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
// Deleting middle node from 8->4->2
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next);
System.out.print("\nList after Deleting middle node: ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
}
}Python
# Program to delete a node in a doubly-linked list
# for Garbage collection
import gc
# A node of the doublly linked list
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
# Constructor for empty Doubly Linked List
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
# head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
# dele --> pointer to node to be deleted
def deleteNode(self, dele):
# Base Case
if self.head is None or dele is None:
return
# If node to be deleted is head node
if self.head == dele:
self.head = dele.next
# Change next only if node to be deleted is NOT
# the last node
if dele.next is not None:
dele.next.prev = dele.prev
# Change prev only if node to be deleted is NOT
# the first node
if dele.prev is not None:
dele.prev.next = dele.next
# Finally, free the memory occupied by dele
# Call python garbage collector
gc.collect()
# Given a reference to the head of a list and an
# integer, inserts a new node on the front of list
def push(self, new_data):
# 1. Allocates node
# 2. Put the data in it
new_node = Node(new_data)
# 3. Make next of new node as head and
# previous as None (already None)
new_node.next = self.head
# 4. change prev of head node to new_node
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
# 5. move the head to point to the new node
self.head = new_node
def printList(self, node):
while(node is not None):
print node.data,
node = node.next
# Driver program to test the above functions
# Start with empty list
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
# Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2
dll.push(2);
dll.push(4);
dll.push(8);
dll.push(10);
print "\n Original Linked List",
dll.printList(dll.head)
# delete nodes from doubly linked list
dll.deleteNode(dll.head)
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next)
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next)
# Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL
print "\n Modified Linked List",
dll.printList(dll.head)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to delete a node from
// Doubly Linked List
using System;
// Class for Doubly Linked List
public class DLL
{
Node head; // head of list
/* Doubly Linked list Node*/
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// next and prev is by default
// initialized as null
public Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as head
// and previous as NULL
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
head = new_Node;
}
// This function prints contents of linked list
// starting from the given node
public void printlist(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
// head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
// del --> data of node to be deleted.
void deleteNode(Node del)
{
// Base case
if (head == null || del == null)
{
return;
}
// If node to be deleted is head node
if (head == del)
{
head = del.next;
}
// Change next only if node to be deleted
// is NOT the last node
if (del.next != null)
{
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
// Change prev only if node to be deleted
// is NOT the first node
if (del.prev != null)
{
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
// Finally, free the memory occupied by del
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Start with the empty list
DLL dll = new DLL();
// Insert 2. So linked list becomes 2->NULL
dll.push(2);
// Insert 4. So linked list becomes 4->2->NULL
dll.push(4);
// Insert 8. So linked list becomes 8->4->2->NULL
dll.push(8);
// Insert 10. So linked list becomes 10->8->4->2->NULL
dll.push(10);
Console.Write("Created DLL is: ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
// Deleting first node
dll.deleteNode(dll.head);
// List after deleting first node
// 8->4->2
Console.Write("\nList after deleting first node: ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
// Deleting middle node from 8->4->2
dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next);
Console.Write("\nList after Deleting middle node: ");
dll.printlist(dll.head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Javascript
输出:
Original Linked list 10 8 4 2
Modified Linked list 8复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(1)。
由于不需要遍历链表,因此时间复杂度是恒定的。 - 空间复杂度: O(1)。
由于不需要额外的空间,所以空间复杂度是恒定的。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。