Java中的地图接口
map 接口存在于Java.util 包中,表示键和值之间的映射。 Map 接口不是 Collection 接口的子类型。因此,它的行为与其他集合类型略有不同。地图包含唯一键。
极客们,头脑风暴者应该是为什么以及何时使用地图?
映射非常适合用于键值关联映射,例如字典。这些映射用于通过键执行查找,或者当有人想要通过键检索和更新元素时。一些常见的场景如下:
- 错误代码及其描述的映射。
- 邮政编码和城市地图。
- 经理和员工的地图。每个经理(键)都与他管理的员工(值)列表相关联。
- 班级和学生的地图。每个班级(键)都与学生列表(值)相关联。
创建地图对象
由于 Map 是一个接口,因此无法创建类型为 map 的对象。我们总是需要一个扩展这个映射的类来创建一个对象。而且,在Java 1.5 引入Generics 之后,可以限制Map 中可以存储的对象类型。
语法:定义类型安全的映射
Map hm = new HashMap();
// Obj is the type of the object to be stored in Map地图界面的特征
- Map 不能包含重复的键,每个键最多可以映射到一个值。一些实现允许空键和空值,如 HashMap 和 LinkedHashMap,但有些不喜欢 TreeMap。
- 地图的顺序取决于具体的实现。例如,TreeMap 和 LinkedHashMap 具有可预测的顺序,而 HashMap 则没有。
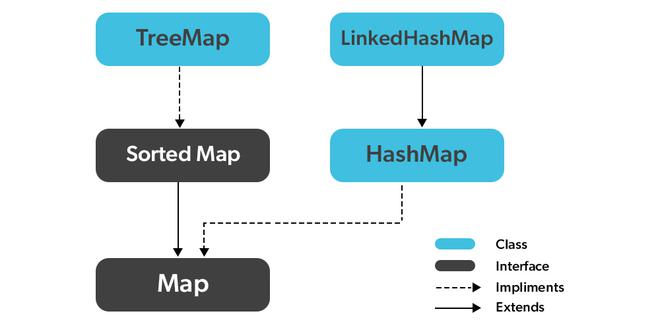
- 在Java中实现 Map 有两个接口。它们是 Map 和 SortedMap,以及三个类:HashMap、TreeMap 和 LinkedHashMap。
地图接口中的方法
| Method | Action Performed |
|---|---|
| clear() | This method is used to clear and remove all of the elements or mappings from a specified Map collection. |
| containsKey(Object) | This method is used to check whether a particular key is being mapped into the Map or not. It takes the key element as a parameter and returns True if that element is mapped in the map. |
| containsValue(Object) | This method is used to check whether a particular value is being mapped by a single or more than one key in the Map. It takes the value as a parameter and returns True if that value is mapped by any of the key in the map. |
| entrySet() | This method is used to create a set out of the same elements contained in the map. It basically returns a set view of the map or we can create a new set and store the map elements into them. |
| equals(Object) | This method is used to check for equality between two maps. It verifies whether the elements of one map passed as a parameter is equal to the elements of this map or not. |
| get(Object) | This method is used to retrieve or fetch the value mapped by a particular key mentioned in the parameter. It returns NULL when the map contains no such mapping for the key. |
| hashCode() | This method is used to generate a hashCode for the given map containing keys and values. |
| isEmpty() | This method is used to check if a map is having any entry for key and value pairs. If no mapping exists, then this returns true. |
| keySet() | This method is used to return a Set view of the keys contained in this map. The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are reflected in the set, and vice-versa. |
| put(Object, Object) | This method is used to associate the specified value with the specified key in this map. |
| putAll(Map) | This method is used to copy all of the mappings from the specified map to this map. |
| remove(Object) | This method is used to remove the mapping for a key from this map if it is present in the map. |
| size() | This method is used to return the number of key/value pairs available in the map. |
| values() | This method is used to create a collection out of the values of the map. It basically returns a Collection view of the values in the HashMap. |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or defaultValue if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value. |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null) associates it with the given value and returns null, else returns the curassociaterent value. |
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate
// Working of Map interface
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an empty HashMap
Map hm
= new HashMap();
// Inserting pairs in above Map
// using put() method
hm.put("a", new Integer(100));
hm.put("b", new Integer(200));
hm.put("c", new Integer(300));
hm.put("d", new Integer(400));
// Traversing through Map using for-each loop
for (Map.Entry me :
hm.entrySet()) {
// Printing keys
System.out.print(me.getKey() + ":");
System.out.println(me.getValue());
}
}
} Java
// Java Program to illustrate the Hashmap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashMap
Map map = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting entries in the Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
} Java
// Java Program to Illustrate the LinkedHashmap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty LinkedHashMap
Map map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Inserting pair entries in above Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
} Java
// Java Program to Illustrate TreeMap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty TreeMap
Map map = new TreeMap<>();
// Inserting custom elements in the Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map using for each loop
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Default Initialization of a
// Map
Map hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm2
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(1, "Geeks");
hm1.put(2, "For");
hm1.put(3, "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm2.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println(hm1);
System.out.println(hm2);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm1
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial Map " + hm1);
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
System.out.println("Updated Map " + hm1);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm1
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(4), "For");
// Initial Map
System.out.println(hm1);
hm1.remove(new Integer(4));
// Final Map
System.out.println(hm1);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm1
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
for (Map.Entry mapElement : hm1.entrySet()) {
int key
= (int)mapElement.getKey();
// Finding the value
String value
= (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : "
+ value);
}
}
} a:100
b:200
c:300
d:400实现 Map 接口的类在下面的媒体中描述,稍后描述如下:

第一类:HashMap
HashMap 是自Java 1.2 以来 Java 集合的一部分。它提供了Java Map 接口的基本实现。它将数据存储在(键,值)对中。要访问一个值,必须知道它的键。此类使用一种称为散列的技术。散列是一种将大字符串转换为代表相同字符串的小字符串的技术。较短的值有助于索引和更快的搜索。让我们看看如何使用此类创建地图对象。
例子
Java
// Java Program to illustrate the Hashmap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashMap
Map map = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting entries in the Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
vaibhav 20
vishal 10
sachin 30第 2 类:LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap 就像 HashMap 一样,具有维护插入其中的元素顺序的附加功能。 HashMap 提供了快速插入、搜索和删除的优势,但它从未维护 LinkedHashMap 提供的插入轨道和插入顺序,其中元素可以按插入顺序访问。让我们看看如何使用此类创建地图对象。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate the LinkedHashmap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty LinkedHashMap
Map map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// Inserting pair entries in above Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
vishal 10
sachin 30
vaibhav 20第 3 类:树图
Java中的 TreeMap 用于实现 Map 接口和 NavigableMap 以及抽象类。地图根据其键的自然顺序排序,或者由地图创建时提供的比较器排序,具体取决于使用的构造函数。这被证明是排序和存储键值对的一种有效方式。树图维护的存储顺序必须与 equals 一致,就像任何其他排序图一样,与显式比较器无关。让我们看看如何使用此类创建地图对象。
例子
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate TreeMap Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty TreeMap
Map map = new TreeMap<>();
// Inserting custom elements in the Map
// using put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterating over Map using for each loop
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
// Printing key-value pairs
System.out.println(e.getKey() + " "
+ e.getValue());
}
}
sachin 30
vaibhav 20
vishal 10使用Map 接口和HashMap 类执行各种操作
由于 Map 是一个接口,它只能与实现该接口的类一起使用。现在,让我们看看如何使用广泛使用的 HashMap 类对 Map 执行一些常用操作。而且,在Java 1.5 中引入泛型之后,可以限制可以存储在映射中的对象类型。
操作 1:添加元素
为了向地图添加元素,我们可以使用 put() 方法。但是,插入顺序不会保留在 hashmap 中。在内部,对于每个元素,都会生成一个单独的散列,并根据该散列对元素进行索引,以提高效率。
例子
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Default Initialization of a
// Map
Map hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm2
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(1, "Geeks");
hm1.put(2, "For");
hm1.put(3, "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm2.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm2.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println(hm1);
System.out.println(hm2);
}
}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}操作 2:更改元素
添加元素后,如果我们希望更改元素,可以通过使用 put() 方法再次添加元素来完成。由于地图中的元素是使用键索引的,因此可以通过简单地插入我们希望更改的键的更新值来更改键的值。
例子
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm1
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial Map " + hm1);
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
System.out.println("Updated Map " + hm1);
}
}
Initial Map {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
Updated Map {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}操作 3:移除元素
为了从 Map 中删除元素,我们可以使用 remove() 方法。此方法获取键值并从该映射中删除该键的映射(如果它存在于映射中)。
例子
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm1
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(4), "For");
// Initial Map
System.out.println(hm1);
hm1.remove(new Integer(4));
// Final Map
System.out.println(hm1);
}
}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}操作 4:遍历地图
有多种方法可以遍历 Map。最著名的方法是使用 for-each 循环并获取密钥。键的值是通过使用 getValue() 方法找到的。
例子
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// the working of Map interface
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a Map
// using Generics
Map hm1
= new HashMap();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(new Integer(1), "Geeks");
hm1.put(new Integer(2), "For");
hm1.put(new Integer(3), "Geeks");
for (Map.Entry mapElement : hm1.entrySet()) {
int key
= (int)mapElement.getKey();
// Finding the value
String value
= (String)mapElement.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " : "
+ value);
}
}
}
1 : Geeks
2 : For
3 : Geeks