给定2D矩阵,找到总和为0的最大矩形子矩阵。例如,考虑以下N x M输入矩阵
例子:
Input : 1, 2, 3
-3, -2, -1
1, 7, 5
Output : 1, 2, 3
-3, -2, -1
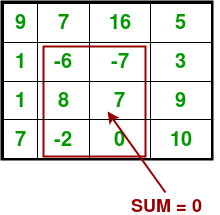
Input : 9, 7, 16, 5
1, -6, -7, 3
1, 8, 7, 9
7, -2, 0, 10
Output :-6, -7
8, 7
-2, 0
这个问题的幼稚解决方案是检查给定2D数组中的每个可能的矩形。此解决方案需要4个嵌套循环,并且此解决方案的时间复杂度为O(n ^ 4)。
该解决方案基于2D矩阵中的最大和矩形。这个想法是将问题减少到一维数组。我们可以使用哈希在O(n)时间内找到一维数组中子数组的最大长度。我们一一固定左列和右列,并为每个左列和右列对找到最大有0个连续行的子数组。我们基本上为每个固定的左右列对找到顶部和底部的行号(总和为零)。要找到顶部和底部的行号,请从左到右计算每行中的元素总和,并将这些总和存储在一个名为temp []的数组中。因此,temp [i]表示第i行中从左到右的元素总和。如果我们找到最大的子数组,其temp的总和为0,否。的元素数大于以前的数字。元素,然后更新final row_up,final row_down,final col_left,final col_right的值。
// A C++ program to find Largest rectangular
// sub-matrix whose sum is 0
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
// This function basically finds largest 0
// sum aubarray in temp[0..n-1]. If 0 sum
// does't exist, then it returns false. Else
// it returns true and sets starting and
// ending indexes as starti and endj.
bool sumZero(int temp[], int* starti,
int* endj, int n)
{
// Map to store the previous sums
map presum;
int sum = 0; // Initialize sum of elements
// Initialize length of sub-array with sum 0
int max_length = 0;
// Traverse through the given array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Add current element to sum
sum += temp[i];
if (temp[i] == 0 && max_length == 0)
{
*starti = i;
*endj = i;
max_length = 1;
}
if (sum == 0)
{
if (max_length < i + 1)
{
*starti = 0;
*endj = i;
}
max_length = i + 1;
}
// Look for this sum in Hash table
if (presum.find(sum) != presum.end())
{
// store previous max_length so
// that we can check max_length
// is updated or not
int old = max_length;
// If this sum is seen before,
// then update max_len
max_length = max(max_length, i - presum[sum]);
if (old < max_length)
{
// If max_length is updated then
// enter and update start and end
// point of array
*endj = i;
*starti = presum[sum] + 1;
}
}
else
// Else insert this sum with
// index in hash table
presum[sum] = i;
}
// Return true if max_length is non-zero
return (max_length != 0);
}
// The main function that finds Largest rectangle
// sub-matrix in a[][] whose sum is 0.
void sumZeroMatrix(int a[][MAX], int row, int col)
{
int temp[row];
// Variables to store the final output
int fup = 0, fdown = 0, fleft = 0, fright = 0;
int sum;
int up, down;
int maxl = INT_MIN;
// Set the left column
for (int left = 0; left < col; left++)
{
// Initialize all elements of temp as 0
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp));
// Set the right column for the left column
// set by outer loop
for (int right = left; right < col; right++)
{
// Calculate sum between current left
// and right for every row 'i'
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
temp[i] += a[i][right];
// Find largest subarray with 0 sum in
// temp[]. The sumZero() function also
// sets values of start and finish. So
// 'sum' is sum of rectangle between (start,
// left) and (finish, right) which is
// boundary columns strictly as left and right.
bool sum = sumZero(temp, &up, &down, row);
int ele = (down - up + 1) * (right - left + 1);
// Compare no. of elements with previous
// no. of elements in sub-Matrix.
// If new sub-matrix has more elements
// then update maxl and final boundaries
// like fup, fdown, fleft, fright
if (sum && ele > maxl)
{
fup = up;
fdown = down;
fleft = left;
fright = right;
maxl = ele;
}
}
}
// If there is no change in boundaries
// than check if a[0][0] is 0
// If it not zero then print
// that no such zero-sum sub-matrix exists
if (fup == 0 && fdown == 0 && fleft == 0 &&
fright == 0 && a[0][0] != 0) {
cout << "No zero-sum sub-matrix exists";
return;
}
// Print final values
for (int j = fup; j <= fdown; j++)
{
for (int i = fleft; i <= fright; i++)
cout << a[j][i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int a[][MAX] = { { 9, 7, 16, 5 }, { 1, -6, -7, 3 },
{ 1, 8, 7, 9 }, { 7, -2, 0, 10 } };
int row = 4, col = 4;
sumZeroMatrix(a, row, col);
return 0;
}
输出:
-6, -7
8, 7
-2, 0