给定两个数字X和N ,任务是找到X的最后一位升为N阶乘的最后一位,即![]() 。
。
例子:
Input: X = 5, N = 2
Output: 5
Explanation:
Since, 2! mod 10 = 2
therefore 52 = 25 and the last digit of 25 is 5.
Input: X = 10, N = 4
Output: 0
Explanation:
Since, 4! mod 10 = 24 mod 10 = 4
therefore 104 = 10000 and the last digit of 10000 is 0.
方法:解决此问题的最有效方法是在N的最后一位的帮助下找到所需的最后一位的任何模式! X的最后一位升至Y
下面是上述方程的各种观察结果:
- 如果N = 0或N = 1 ,则最后一位是1或
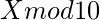 分别。
分别。 - 从5开始!是120 ,因此对于N≥5 , (N!mod 10)的值将为零。
- 现在我们剩下数字2、3、4。为此,我们有:
for N = 2,
N! mod 10 = 2! mod 10 = 2for N = 3,
N! mod 10 = 3! mod 10 = 6for N = 4,
N! mod 10 = 4! mod 10 = 24 mod 10 = 4Now for X2, X4, and X6
we will check that after which nth power of Xn the value of last digit repeats,
i.e, after which nth power of last digit of Xn the value of last digit repeats. - 下表是任意数字中从0到9的最后一位的幂次重复的表格:
Number Cyclicity 0 1 1 1 2 4 3 4 4 2 5 1 6 1 7 4 8 4 9 2
以下是基于上述观察的步骤:
- 如果X不是10的倍数,则除以的评估值
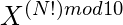 由X的最后一位数字的循环性决定。如果remainder(例如r )为0,则执行以下操作:
由X的最后一位数字的循环性决定。如果remainder(例如r )为0,则执行以下操作:
- 如果X的最后一位是2、4、6或8,那么答案将是6 。
- 如果X的最后一位是1、3、7或9,则答案将是1 。
- 如果X的最后一位是5,则答案将是5 。
- 否则,如果remainder(例如r )为非零值,则答案为
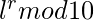 ,其中“ l”是X的最后一位。
,其中“ l”是X的最后一位。 - 否则,如果X为10的倍数,则答案始终为0 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find a^b using
// binary exponentiation
long power(long a, long b, long c)
{
// Initialise result
long result = 1;
while (b > 0)
{
// If b is odd then,
// multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) == 1)
{
result = (result * a) % c;
}
// b must be even now
// Change b to b/2
b /= 2;
// Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c;
}
return result;
}
// Function to find the last digit
// of the given equation
long calculate(long X, long N)
{
int a[10];
// To store cyclicity
int cyclicity[11];
// Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1;
cyclicity[2] = 4;
cyclicity[3] = 4;
cyclicity[4] = 2;
cyclicity[5] = 1;
cyclicity[6] = 1;
cyclicity[7] = 4;
cyclicity[8] = 4;
cyclicity[9] = 2;
cyclicity[10] = 1;
// Observation 1
if (N == 0 || N == 1)
{
return (X % 10);
}
// Observation 3
else if (N == 2 || N == 3 || N == 4)
{
long temp = (long)1e18;
// To store the last digits
// of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2;
a[3] = 6;
a[4] = 4;
// Find the last digit of X
long v = X % 10;
// Step 1
if (v != 0)
{
int u = cyclicity[(int)v];
// Divide a[N] by cyclicity
// of v
int r = a[(int)N] % u;
// If remainder is 0
if (r == 0)
{
// Step 1.1
if (v == 2 || v == 4 ||
v == 6 || v == 8)
{
return 6;
}
// Step 1.2
else if (v == 5)
{
return 5;
}
// Step 1.3
else if (v == 1 || v == 3 ||
v == 7 || v == 9)
{
return 1;
}
}
// If r is non-zero,
// then return (l^r) % 10
else
{
return (power(v, r, temp) % 10);
}
}
// Else return 0
else
{
return 0;
}
}
// Else return 1
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Numbers
int X = 18;
int N = 4;
// Function Call
long result = calculate(X, N);
// Print the result
cout << result;
}
// This code is contributed by spp____ Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class TestClass {
// Function to find a^b using
// binary exponentiation
public static long power(long a,
long b,
long c)
{
// Initialise result
long result = 1;
while (b > 0) {
// If b is odd then,
// multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) = = 1) {
result = (result * a) % c;
}
// b must be even now
// Change b to b/2
b / = 2;
// Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c;
}
return result;
}
// Function to find the last digit
// of the given equation
public static long calculate(long X,
long N)
{
int a[] = new int[10];
// To store cyclicity
int cyclicity[] = new int[11];
// Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1;
cyclicity[2] = 4;
cyclicity[3] = 4;
cyclicity[4] = 2;
cyclicity[5] = 1;
cyclicity[6] = 1;
cyclicity[7] = 4;
cyclicity[8] = 4;
cyclicity[9] = 2;
cyclicity[10] = 1;
// Observation 1
if (N = = 0 || N = = 1) {
return (X % 10);
}
// Observation 3
else if (N = = 2
|| N
= = 3
|| N
= = 4) {
long temp = (long)1e18;
// To store the last digits
// of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2;
a[3] = 6;
a[4] = 4;
// Find the last digit of X
long v = X % 10;
// Step 1
if (v ! = 0) {
int u = cyclicity[(int)v];
// Divide a[N] by cyclicity
// of v
int r = a[(int)N] % u;
// If remainder is 0
if (r = = 0) {
// Step 1.1
if (v = = 2
|| v
= = 4
|| v
= = 6
|| v
= = 8) {
return 6;
}
// Step 1.2
else if (v = = 5) {
return 5;
}
// Step 1.3
else if (
v = = 1
|| v
= = 3
|| v
= = 7
|| v
= = 9) {
return 1;
}
}
// If r is non-zero,
// then return (l^r) % 10
else {
return (power(v,
r,
temp)
% 10);
}
}
// Else return 0
else {
return 0;
}
}
// Else return 1
return 1;
}
// Driver's Code
public static void main(String args[])
throws Exception
{
// Given Numbers
int X = 18;
int N = 4;
// Function Call
long result = calculate(X, N);
// Print the result
System.out.println(result);
}
}Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to find a^b using
# binary exponentiation
def power(a, b, c):
# Initialise result
result = 1
while (b > 0):
# If b is odd then,
# multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) == 1):
result = (result * a) % c
# b must be even now
# Change b to b/2
b //= 2
# Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c
return result
# Function to find the last digit
# of the given equation
def calculate(X, N):
a = 10 * [0]
# To store cyclicity
cyclicity = 11 * [0]
# Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1
cyclicity[2] = 4
cyclicity[3] = 4
cyclicity[4] = 2
cyclicity[5] = 1
cyclicity[6] = 1
cyclicity[7] = 4
cyclicity[8] = 4
cyclicity[9] = 2
cyclicity[10] = 1
# Observation 1
if (N == 0 or N == 1):
return (X % 10)
# Observation 3
elif (N == 2 or N == 3 or N == 4):
temp = 1e18;
# To store the last digits
# of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2
a[3] = 6
a[4] = 4
# Find the last digit of X
v = X % 10
# Step 1
if (v != 0):
u = cyclicity[v]
# Divide a[N] by cyclicity
# of v
r = a[N] % u
# If remainder is 0
if (r == 0):
# Step 1.1
if (v == 2 or v == 4 or
v == 6 or v == 8):
return 6
# Step 1.2
elif (v == 5):
return 5
# Step 1.3
elif (v == 1 or v == 3 or
v == 7 or v == 9):
return 1
# If r is non-zero,
# then return (l^r) % 10
else:
return (power(v, r, temp) % 10)
# Else return 0
else:
return 0
# Else return 1
return 1
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Given numbers
X = 18
N = 4
# Function call
result = calculate(X, N)
# Print the result
print(result)
# This code is contributed by chitranayalC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to find a^b using
// binary exponentiation
static long power(long a, long b, long c)
{
// Initialise result
long result = 1;
while (b > 0)
{
// If b is odd then,
// multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) == 1)
{
result = (result * a) % c;
}
// b must be even now
// Change b to b/2
b /= 2;
// Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c;
}
return result;
}
// Function to find the last digit
// of the given equation
public static long calculate(long X,
long N)
{
int[] a = new int[10];
// To store cyclicity
int[] cyclicity = new int[11];
// Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1;
cyclicity[2] = 4;
cyclicity[3] = 4;
cyclicity[4] = 2;
cyclicity[5] = 1;
cyclicity[6] = 1;
cyclicity[7] = 4;
cyclicity[8] = 4;
cyclicity[9] = 2;
cyclicity[10] = 1;
// Observation 1
if (N == 0 || N == 1)
{
return (X % 10);
}
// Observation 3
else if (N == 2 || N == 3 || N == 4)
{
long temp = (long)1e18;
// To store the last digits
// of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2;
a[3] = 6;
a[4] = 4;
// Find the last digit of X
long v = X % 10;
// Step 1
if (v != 0)
{
int u = cyclicity[(int)v];
// Divide a[N] by cyclicity
// of v
int r = a[(int)N] % u;
// If remainder is 0
if (r == 0)
{
// Step 1.1
if (v == 2 || v == 4 ||
v == 6 || v == 8)
{
return 6;
}
// Step 1.2
else if (v == 5)
{
return 5;
}
// Step 1.3
else if ( v == 1 || v == 3 ||
v == 7 || v == 9)
{
return 1;
}
}
// If r is non-zero,
// then return (l^r) % 10
else
{
return (power(v, r, temp) % 10);
}
}
// Else return 0
else
{
return 0;
}
}
// Else return 1
return 1;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// Given numbers
int X = 18;
int N = 4;
// Function call
long result = calculate(X, N);
// Print the result
Console.Write(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07输出:
6
时间复杂度: O(1)