在上一篇文章Android Jetpack中的View Binding中,已经讨论了为什么在Android项目中获得ViewBinding功能会带来很多好处。但是,当涉及到带有片段的ViewBinding时,情况就会发生变化。因为Fragment的生命周期不同,而Activity的生命周期也不同,所以这里的内容也与上述文章中讨论的相同,片段布局的命名约定更改为Pascal大小写,而片段布局的属性更改为驼峰大小写。例如, fragment1.xml-> Fragment1Binding和片段布局下的edit_text (id)更改为eEditText (驼峰式),因此在本文中,我们将使用Fragments讨论ViewBinding。下面提供了一个示例视频,以使您对我们在本文中将要做的事情有个大概的了解。请注意,我们将使用Kotlin语言实施此项目。
分步实施
步骤1:创建一个新的空活动项目
- 使用Android Studio创建一个空的Activity Android Studio项目。参考Android |如何在Android Studio中创建/启动新项目?
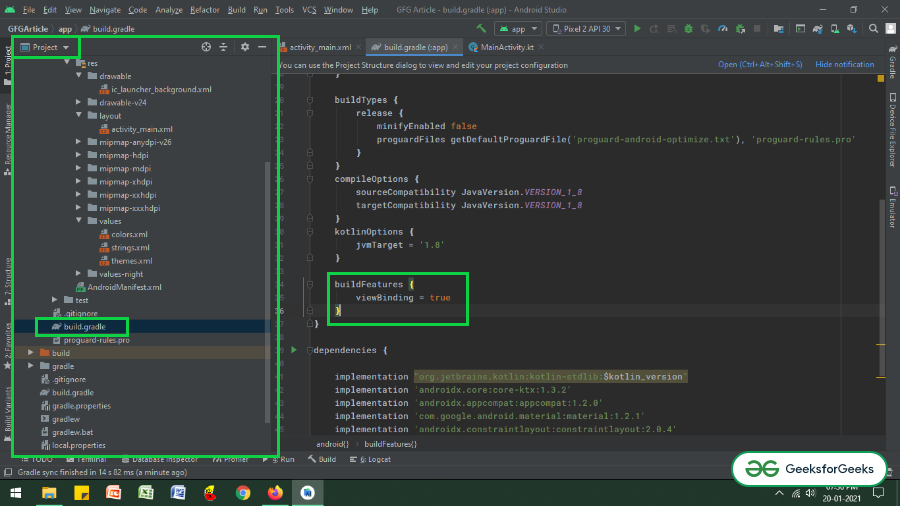
步骤2:启用ViewBinding功能
- 通过在应用程序级别的build.gradle文件中调用以下代码段来启用ViewBinding功能,然后单击右上角出现的“立即同步”按钮。
buildFeatures {
viewBinding = true
}
- 如果无法找到应用程序级build.gradle文件,则请参考下图。调用上述构建功能。
步骤3:使用activity_main.xml文件
- 活动的主要布局包含两个按钮,用于切换片段1和片段2,以及一个Framelayout,用于将片段保存在CardView中。还有一个“提交”按钮,用于检查何时按下时提交了其片段的数据。
- 要实现相同的功能,请在activity_main.xml文件中调用以下代码。
XML
XML
XML
Kotlin
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
// Enter your package name here
import com.adityamshidlyali.gfgarticle.databinding.Fragment1Binding
class ExampleFragment1 : Fragment() {
// assign the _binding variable initially to null and
// also when the view is destroyed again it has to be set to null
private var _binding: Fragment1Binding? = null
// with the backing property of the kotlin we extract
// the non null value of the _binding
private val binding get() = _binding!!
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View {
// inflate the layout and bind to the _binding
_binding = Fragment1Binding.inflate(inflater, container, false)
// retrieve the entered data by the user
binding.doneButton1.setOnClickListener {
val str: String = binding.editText1.text.toString()
if (str.isNotEmpty()) {
Toast.makeText(activity, str, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Please Enter Data", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
// handle the button from the host activity using findViewById method
val submitButton: Button = activity!!.findViewById(R.id.submit_button)
submitButton.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Host Activity Element Clicked from Fragment 1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return binding.root
}
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
_binding = null
}
}Kotlin
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
// Enter your package name here
import com.adityamshidlyali.gfgarticle.databinding.Fragment2Binding
class ExampleFragment2 : Fragment() {
// assign the _binding variable initially to null and
// also when the view is destroyed again it has to be
// set to null
private var _binding: Fragment2Binding? = null
// with the backing property of the kotlin
// we extract
// the non null value of the _binding
private val binding get() = _binding!!
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View {
// inflate the layout and bind to the _binding
_binding = Fragment2Binding.inflate(inflater, container, false)
// retrieve the entered data by the user
binding.doneButton2.setOnClickListener {
val str: String = binding.editText2.text.toString()
if (str.isNotEmpty()) {
Toast.makeText(activity, str, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Please Enter Data", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
// handle the button from the host activity using findViewById method
val submitButton: Button = activity!!.findViewById(R.id.submit_button)
submitButton.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Host Activity Element Clicked from Fragment 2", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return binding.root
}
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
_binding = null
}
}Kotlin
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
import com.adityamshidlyali.gfgarticle.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// create binding instance for the activity_main.xml
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
// when app is initially opened the Fragment 1 should be visible
supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction().apply {
replace(binding.fragmentHolder.id, ExampleFragment1())
addToBackStack(null)
commit()
}
// handle the fragment 2 button to toggle the fragment 2
binding.fragment1B.setOnClickListener {
changeFragment(ExampleFragment1())
}
// handle the fragment 2 button to toggle the fragment 2
binding.fragment2B.setOnClickListener {
changeFragment(ExampleFragment1())
}
}
// function to change the fragment which is used to reduce the lines of code
private fun changeFragment(fragmentToChange: Fragment): Unit {
supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction().apply {
replace(binding.fragmentHolder.id, fragmentToChange)
addToBackStack(null)
commit()
}
}
}输出界面:

步骤4:创建两个片段
- 创建两个片段,其中包括表示片段编号编辑文本的文本视图和一个按钮。要实现每个片段的UI,您可以参考以下代码。
- 片段1:
XML格式
- 片段2:
XML格式
步骤5:使用Fragments.kt文件
- 首先,可为空的绑定变量最初被分配为null,并且当片段的视图被破坏时,必须再次将其设置为null(在本例中为_binding )。
- 为了避免对可为空的绑定对象进行null检查,通过使用kotlin的backing属性,我们制作了绑定变量的另一个副本(在本例中为binding )。
- 但是,如果该片段想从主机活动访问视图,则可以使用findViewById()方法来完成。
- 在每个片段的.kt文件中调用以下代码。添加了注释以便更好地理解。
- 片段1:
科特林
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
// Enter your package name here
import com.adityamshidlyali.gfgarticle.databinding.Fragment1Binding
class ExampleFragment1 : Fragment() {
// assign the _binding variable initially to null and
// also when the view is destroyed again it has to be set to null
private var _binding: Fragment1Binding? = null
// with the backing property of the kotlin we extract
// the non null value of the _binding
private val binding get() = _binding!!
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View {
// inflate the layout and bind to the _binding
_binding = Fragment1Binding.inflate(inflater, container, false)
// retrieve the entered data by the user
binding.doneButton1.setOnClickListener {
val str: String = binding.editText1.text.toString()
if (str.isNotEmpty()) {
Toast.makeText(activity, str, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Please Enter Data", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
// handle the button from the host activity using findViewById method
val submitButton: Button = activity!!.findViewById(R.id.submit_button)
submitButton.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Host Activity Element Clicked from Fragment 1", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return binding.root
}
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
_binding = null
}
}
- 片段2:
科特林
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater
import android.view.View
import android.view.ViewGroup
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
// Enter your package name here
import com.adityamshidlyali.gfgarticle.databinding.Fragment2Binding
class ExampleFragment2 : Fragment() {
// assign the _binding variable initially to null and
// also when the view is destroyed again it has to be
// set to null
private var _binding: Fragment2Binding? = null
// with the backing property of the kotlin
// we extract
// the non null value of the _binding
private val binding get() = _binding!!
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View {
// inflate the layout and bind to the _binding
_binding = Fragment2Binding.inflate(inflater, container, false)
// retrieve the entered data by the user
binding.doneButton2.setOnClickListener {
val str: String = binding.editText2.text.toString()
if (str.isNotEmpty()) {
Toast.makeText(activity, str, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Please Enter Data", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
// handle the button from the host activity using findViewById method
val submitButton: Button = activity!!.findViewById(R.id.submit_button)
submitButton.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(activity, "Host Activity Element Clicked from Fragment 2", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return binding.root
}
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
_binding = null
}
}
步骤6:使用MainActivity.kt文件
- 在MainActivity.kt文件中,仅实现了片段的事务功能。请参阅以下代码及其输出,以更好地理解。
科特林
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.fragment.app.Fragment
import com.adityamshidlyali.gfgarticle.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// create binding instance for the activity_main.xml
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
// when app is initially opened the Fragment 1 should be visible
supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction().apply {
replace(binding.fragmentHolder.id, ExampleFragment1())
addToBackStack(null)
commit()
}
// handle the fragment 2 button to toggle the fragment 2
binding.fragment1B.setOnClickListener {
changeFragment(ExampleFragment1())
}
// handle the fragment 2 button to toggle the fragment 2
binding.fragment2B.setOnClickListener {
changeFragment(ExampleFragment1())
}
}
// function to change the fragment which is used to reduce the lines of code
private fun changeFragment(fragmentToChange: Fragment): Unit {
supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction().apply {
replace(binding.fragmentHolder.id, fragmentToChange)
addToBackStack(null)
commit()
}
}
}
输出:
想要一个节奏更快,更具竞争性的环境来学习Android的基础知识吗?
单击此处前往由我们的专家精心策划的指南,以使您立即做好行业准备!