- Java collection中的排序
- Java collection中的排序(1)
- Python collection模块
- Python collection模块(1)
- 库和框架(1)
- 库和框架
- Java中的 Collection contains() 方法和示例(1)
- Java中的 Collection contains() 方法和示例
- Python框架
- Python框架(1)
- Java-集合框架(1)
- Java-集合框架(1)
- Java-集合框架
- Java-集合框架
- Java8 Collection类(1)
- Java8 Collection类
- HTML-框架(1)
- HTML-框架
- laravel collection max - PHP (1)
- 单元测试框架-框架
- 框架 CSS (1)
- laravel collection min - PHP (1)
- 如何在框架 tkinter 内创建框架?(1)
- 如何在框架 tkinter 内创建框架?
- 在Java中将 Iterable 转换为 Collection(1)
- 在Java中将 Iterable 转换为 Collection
- laravel collection max - PHP 代码示例
- laravel collection unique (1)
- MongoDB-Drop Collection(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-11 06:11:29 🧑 作者: Mango
Java中的集合
Java中的Collection是一个框架,提供了用于存储和操作对象组的体系结构。
Java Collections可以完成您对数据执行的所有操作,例如搜索,排序,插入,操作和删除。
Java Collection表示单个对象单元。 Java Collection框架提供了许多接口(Set,List,Queue,Deque)和类(ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList,PriorityQueue,HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet)。
Java中的集合是什么
集合表示对象的单个单元,即一个组。
Java中的框架是什么
- 它提供了现成的架构。
- 它代表一组类和接口。
- 它是可选的。
什么是收藏框架
Collection框架表示用于存储和处理一组对象的统一体系结构。它具有:
- 接口及其实现,即类
- 算法
收集框架层次结构
让我们看看Collection框架的层次结构。 java.util包包含Collection框架的所有类和接口。
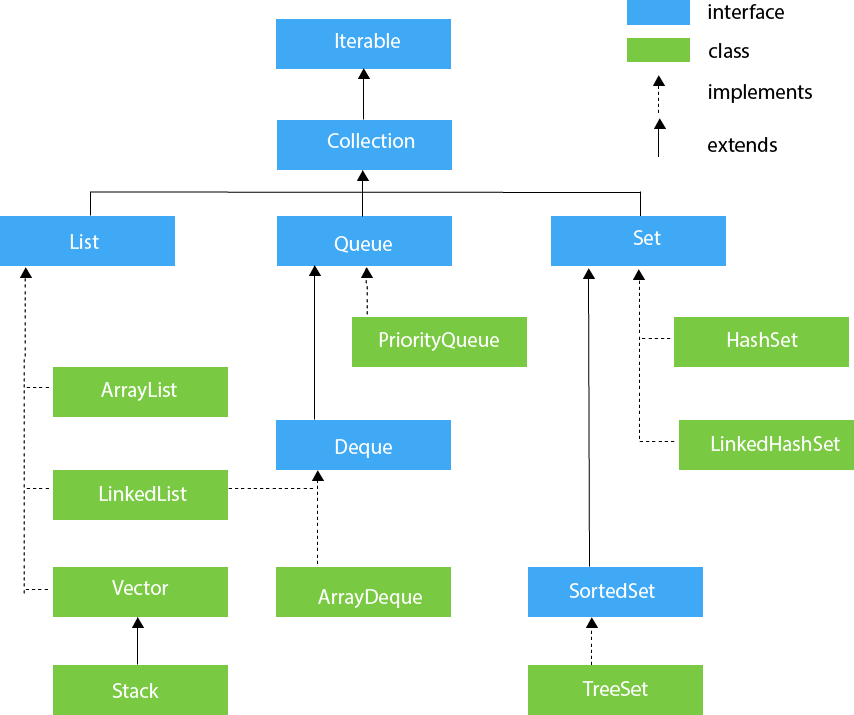
收集方法界面
在Collection接口中声明了许多方法。它们如下:
| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | public boolean add(E e) | It is used to insert an element in this collection. |
| 2 | public boolean addAll(Collection c) | It is used to insert the specified collection elements in the invoking collection. |
| 3 | public boolean remove(Object element) | It is used to delete an element from the collection. |
| 4 | public boolean removeAll(Collection c) | It is used to delete all the elements of the specified collection from the invoking collection. |
| 5 | default boolean removeIf(Predicate filter) | It is used to delete all the elements of the collection that satisfy the specified predicate. |
| 6 | public boolean retainAll(Collection c) | It is used to delete all the elements of invoking collection except the specified collection. |
| 7 | public int size() | It returns the total number of elements in the collection. |
| 8 | public void clear() | It removes the total number of elements from the collection. |
| 9 | public boolean contains(Object element) | It is used to search an element. |
| 10 | public boolean containsAll(Collection c) | It is used to search the specified collection in the collection. |
| 11 | public Iterator iterator() | It returns an iterator. |
| 12 | public Object[] toArray() | It converts collection into array. |
| 13 | public |
It converts collection into array. Here, the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| 14 | public boolean isEmpty() | It checks if collection is empty. |
| 15 | default Stream |
It returns a possibly parallel Stream with the collection as its source. |
| 16 | default Stream |
It returns a sequential Stream with the collection as its source. |
| 17 | default Spliterator |
It generates a Spliterator over the specified elements in the collection. |
| 18 | public boolean equals(Object element) | It matches two collections. |
| 19 | public int hashCode() | It returns the hash code number of the collection. |
迭代器接口
迭代器接口仅提供了向前迭代元素的功能。
迭代器接口的方法
Iterator接口中只有三种方法。他们是:
| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | public boolean hasNext() | It returns true if the iterator has more elements otherwise it returns false. |
| 2 | public Object next() | It returns the element and moves the cursor pointer to the next element. |
| 3 | public void remove() | It removes the last elements returned by the iterator. It is less used. |
可迭代的接口
Iterable接口是所有集合类的根接口。 Collection接口扩展了Iterable接口,因此Collection接口的所有子类也实现了Iterable接口。
它仅包含一种抽象方法。即
Iterator iterator()
它返回类型T的元素上的迭代器。
采集界面
Collection接口是由收集框架中的所有类实现的接口。它声明每个集合将具有的方法。换句话说,我们可以说Collection接口构建了收集框架所依赖的基础。
Collection接口的一些方法是Boolean add(对象obj),Boolean addAll(Collection c),void clear()等,它们由Collection接口的所有子类实现。
列表界面
List接口是Collection接口的子接口。它禁止使用列表类型的数据结构,我们可以在其中存储对象的有序集合。它可以有重复的值。
List接口由ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector和Stack类实现。
要实例化List接口,我们必须使用:
List list1= new ArrayList();
List list2 = new LinkedList();
List list3 = new Vector();
List list4 = new Stack();
List界面中有多种方法可用于插入,删除和访问列表中的元素。
下面给出了实现List接口的类。
数组列表
ArrayList类实现List接口。它使用动态数组来存储不同数据类型的重复元素。 ArrayList类保持插入顺序,并且是不同步的。可以随机访问ArrayList类中存储的元素。考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
class TestJavaCollection1{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Ravi");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Vijay");
list.add("Ravi");
list.add("Ajay");
//Traversing list through Iterator
Iterator itr=list.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
链表
LinkedList实现Collection接口。它在内部使用双向链表来存储元素。它可以存储重复的元素。它保持插入顺序,并且不同步。在LinkedList中,由于不需要进行移位,因此操作很快。
考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection2{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList al=new LinkedList();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Ajay");
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
向量
Vector使用动态数组来存储数据元素。它类似于ArrayList。但是,它是同步的,并且包含不属于Collection框架的许多方法。
考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection3{
public static void main(String args[]){
Vector v=new Vector();
v.add("Ayush");
v.add("Amit");
v.add("Ashish");
v.add("Garima");
Iterator itr=v.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Ayush
Amit
Ashish
Garima
叠放
堆栈是Vector的子类。它实现了后进先出的数据结构,即堆栈。堆栈包含Vector类的所有方法,还提供定义其属性的方法,例如boolean push(),boolean peek(),boolean push(object o)。
考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection4{
public static void main(String args[]){
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push("Ayush");
stack.push("Garvit");
stack.push("Amit");
stack.push("Ashish");
stack.push("Garima");
stack.pop();
Iterator itr=stack.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Ayush
Garvit
Amit
Ashish
队列接口
队列接口保持先进先出顺序。可以将其定义为用于保存将要处理的元素的有序列表。有许多类(例如PriorityQueue,Deque和ArrayDeque)实现了Queue接口。
队列接口可以实例化为:
Queue q1 = new PriorityQueue();
Queue q2 = new ArrayDeque();
有多种实现Queue接口的类,下面提供了其中的一些类。
PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue类实现Queue接口。它包含要按其优先级处理的元素或对象。 PriorityQueue不允许将空值存储在队列中。
考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection5{
public static void main(String args[]){
PriorityQueue queue=new PriorityQueue();
queue.add("Amit Sharma");
queue.add("Vijay Raj");
queue.add("JaiShankar");
queue.add("Raj");
System.out.println("head:"+queue.element());
System.out.println("head:"+queue.peek());
System.out.println("iterating the queue elements:");
Iterator itr=queue.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
queue.remove();
queue.poll();
System.out.println("after removing two elements:");
Iterator itr2=queue.iterator();
while(itr2.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr2.next());
}
}
}
输出:
head:Amit Sharma
head:Amit Sharma
iterating the queue elements:
Amit Sharma
Raj
JaiShankar
Vijay Raj
after removing two elements:
Raj
Vijay Raj
双端队列接口
Deque接口扩展了Queue接口。在Deque中,我们可以从两侧移除和添加元素。 Deque代表双端队列,它使我们能够在两端执行操作。
双端队列可以实例化为:
Deque d = new ArrayDeque();
ArrayDeque
ArrayDeque类实现Deque接口。它有助于我们使用双端队列。与队列不同,我们可以从两端添加或删除元素。
ArrayDeque比ArrayList和Stack更快,并且没有容量限制。
考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection6{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creating Deque and adding elements
Deque deque = new ArrayDeque();
deque.add("Gautam");
deque.add("Karan");
deque.add("Ajay");
//Traversing elements
for (String str : deque) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
输出:
Gautam
Karan
Ajay
设置界面
Java中的Set Interface存在于java.util软件包中。它扩展了Collection接口。它代表无序的元素集,不允许我们存储重复的项目。我们最多可以在Set中存储一个空值。 Set由HashSet,LinkedHashSet和TreeSet实现。
Set可以实例化为:
Set s1 = new HashSet();
Set s2 = new LinkedHashSet();
Set s3 = new TreeSet();
哈希集
HashSet类实现Set接口。它表示使用哈希表进行存储的集合。散列用于将元素存储在HashSet中。它包含唯一项。
考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection7{
public static void main(String args[]){
//Creating HashSet and adding elements
HashSet set=new HashSet();
set.add("Ravi");
set.add("Vijay");
set.add("Ravi");
set.add("Ajay");
//Traversing elements
Iterator itr=set.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
链接哈希集
LinkedHashSet类表示Set接口的LinkedList实现。它扩展了HashSet类并实现Set接口。像HashSet一样,它也包含唯一元素。它保持插入顺序并允许空元素。
考虑以下示例。
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection8{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedHashSet set=new LinkedHashSet();
set.add("Ravi");
set.add("Vijay");
set.add("Ravi");
set.add("Ajay");
Iterator itr=set.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Ravi
Vijay
Ajay
SortedSet接口
SortedSet是Set接口的替代方法,它提供其元素的总体排序。 SortedSet的元素以升序(升序)排列。 SortedSet提供了其他禁止元素自然排序的方法。
SortedSet可以实例化为:
SortedSet set = new TreeSet();
树集
Java TreeSet类实现了Set接口,该接口使用树进行存储。与HashSet一样,TreeSet也包含唯一元素。但是,TreeSet的访问和检索时间非常快。 TreeSet中的元素以升序存储。
考虑以下示例:
import java.util.*;
public class TestJavaCollection9{
public static void main(String args[]){
//Creating and adding elements
TreeSet set=new TreeSet();
set.add("Ravi");
set.add("Vijay");
set.add("Ravi");
set.add("Ajay");
//traversing elements
Iterator itr=set.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Ajay
Ravi
Vijay