- arraylist 到 java (1)
- Java ArrayList类(1)
- Java ArrayList(1)
- Java ArrayList类
- Java中ArrayList的ArrayList
- Java中ArrayList的ArrayList(1)
- java arraylist - Java (1)
- arraylist - Java 代码示例
- arraylist 到 java 代码示例
- java代码示例中的arraylist
- java arraylist - Java 代码示例
- java中的arraylist方法(1)
- Java中的ArrayList数组(1)
- Java中的ArrayList数组
- arraylist 到数组 java (1)
- C#中的ArrayList(1)
- C#| ArrayList类
- C#| ArrayList类(1)
- c# arraylist - C# (1)
- C#中的ArrayList
- java arraylist 到数组 - Java (1)
- java arraylist 到字符串 - Java (1)
- java中的arraylist删除值(1)
- arraylist 设置 java 8 - Java (1)
- java代码示例中的arraylist方法
- arraylist 到数组 java 代码示例
- java arraylist 到数组 - Java 代码示例
- 什么是arraylist - Java (1)
- java arraylist 到字符串 - Java 代码示例
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-12 05:51:08 🧑 作者: Mango
Java ArrayList
Java ArrayList类使用动态数组来存储元素。它就像一个数组,但是没有大小限制。我们可以随时添加或删除元素。因此,它比传统阵列灵活得多。在java.util包中可以找到它。就像C++中的Vector。
Java中的ArrayList也可以具有重复的元素。它实现了List接口,因此我们可以在这里使用List接口的所有方法。 ArrayList在内部维护插入顺序。
它继承了AbstractList类并实现List接口。
关于Java ArrayList类的要点是:
- Java ArrayList类可以包含重复的元素。
- Java ArrayList类维护插入顺序。
- Java ArrayList类不同步。
- Java ArrayList允许随机访问,因为数组基于索引工作。
- 在ArrayList中,操作要比Java中的LinkedList慢一点,因为如果从数组列表中删除任何元素,则需要进行很多转换。
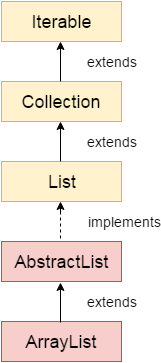
ArrayList类的层次结构
如上图所示,Java ArrayList类扩展了实现List接口的AbstractList类。 List接口按层次结构扩展了Collection和Iterable接口。
ArrayList类声明
我们来看一下java.util.ArrayList类的声明。
public class ArrayList extends AbstractList implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
ArrayList的构造方法
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | It is used to build an empty array list. |
| ArrayList(Collection c) | It is used to build an array list that is initialized with the elements of the collection c. |
| ArrayList(int capacity) | It is used to build an array list that has the specified initial capacity. |
ArrayList的方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| void add(int index, E element) | It is used to insert the specified element at the specified position in a list. |
| boolean add(E e) | It is used to append the specified element at the end of a list. |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | It is used to append all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) | It is used to append all the elements in the specified collection, starting at the specified position of the list. |
| void clear() | It is used to remove all of the elements from this list. |
| void ensureCapacity(int requiredCapacity) | It is used to enhance the capacity of an ArrayList instance. |
| E get(int index) | It is used to fetch the element from the particular position of the list. |
| boolean isEmpty() | It returns true if the list is empty, otherwise false. |
| Iterator() | |
| listIterator() | |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in this list of the last occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain this element. |
| Object[] toArray() | It is used to return an array containing all of the elements in this list in the correct order. |
| It is used to return an array containing all of the elements in this list in the correct order. | |
| Object clone() | It is used to return a shallow copy of an ArrayList. |
| boolean contains(Object o) | It returns true if the list contains the specified element |
| int indexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in this list of the first occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the List does not contain this element. |
| E remove(int index) | It is used to remove the element present at the specified position in the list. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | It is used to remove the first occurrence of the specified element. |
| boolean removeAll(Collection c) | It is used to remove all the elements from the list. |
| boolean removeIf(Predicate filter) | It is used to remove all the elements from the list that satisfies the given predicate. |
| protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | It is used to remove all the elements lies within the given range. |
| void replaceAll(UnaryOperator |
It is used to replace all the elements from the list with the specified element. |
| void retainAll(Collection c) | It is used to retain all the elements in the list that are present in the specified collection. |
| Eset(int index, E element) | It is used to replace the specified element in the list, present at the specified position. |
| void sort(Comparator c) | It is used to sort the elements of the list on the basis of specified comparator. |
| Spliterator |
It is used to create spliterator over the elements in a list. |
| List |
It is used to fetch all the elements lies within the given range. |
| int size() | It is used to return the number of elements present in the list. |
| void trimToSize() | It is used to trim the capacity of this ArrayList instance to be the list’s current size. |
Java非通用Vs。通用集合
Java收集框架在JDK 1.5之前是非通用的。从1.5开始,它是通用的。
Java新的通用集合允许您在集合中仅包含一种类型的对象。现在它是类型安全的,因此在运行时不需要类型转换。
让我们看看创建Java集合的旧的非通用示例。
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();//creating old non-generic arraylist
让我们看看创建Java集合的新的通用示例。
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();//creating new generic arraylist
在通用集合中,我们在花括号中指定类型。现在,ArrayList被强制具有唯一指定类型的对象。如果尝试添加其他类型的对象,则会产生编译时错误。
有关Java泛型的更多信息,请单击此处Java泛型教程。
Java ArrayList示例
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListExample1{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Mango");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Grapes");
//Printing the arraylist object
System.out.println(list);
}
}
输出:
[Mango, Apple, Banana, Grapes]
使用迭代器迭代ArrayList
让我们看一个使用Iterator接口遍历ArrayList元素的示例。
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListExample2{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Mango");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Grapes");
//Traversing list through Iterator
Iterator itr=list.iterator();//getting the Iterator
while(itr.hasNext()){//check if iterator has the elements
System.out.println(itr.next());//printing the element and move to next
}
}
}
输出:
Mango
Apple
Banana
Grapes
使用For-each循环迭代ArrayList
让我们看一个使用for-each循环遍历ArrayList元素的示例
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListExample3{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Mango");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Grapes");
//Traversing list through for-each loop
for(String fruit:list)
System.out.println(fruit);
}
}
输出:
Mango
Apple
Banana
Grapes
获取并设置ArrayList
get()方法返回指定索引处的元素,而set()方法更改该元素。
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListExample4{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("Mango");
al.add("Apple");
al.add("Banana");
al.add("Grapes");
//accessing the element
System.out.println("Returning element: "+al.get(1));//it will return the 2nd element, because index starts from 0
//changing the element
al.set(1,"Dates");
//Traversing list
for(String fruit:al)
System.out.println(fruit);
}
}
输出:
Returning element: Apple
Mango
Dates
Banana
Grapes
如何对ArrayList进行排序
java.util包提供了一个实用程序类Collections,它具有静态方法sort()。使用Collections.sort()方法,我们可以轻松地对ArrayList进行排序。
import java.util.*;
class SortArrayList{
public static void main(String args[]){
//Creating a list of fruits
List list1=new ArrayList();
list1.add("Mango");
list1.add("Apple");
list1.add("Banana");
list1.add("Grapes");
//Sorting the list
Collections.sort(list1);
//Traversing list through the for-each loop
for(String fruit:list1)
System.out.println(fruit);
System.out.println("Sorting numbers...");
//Creating a list of numbers
List list2=new ArrayList();
list2.add(21);
list2.add(11);
list2.add(51);
list2.add(1);
//Sorting the list
Collections.sort(list2);
//Traversing list through the for-each loop
for(Integer number:list2)
System.out.println(number);
}
}
输出:
Apple
Banana
Grapes
Mango
Sorting numbers...
1
11
21
51
在Java中迭代集合元素的方法
有多种遍历集合元素的方法:
- 通过Iterator接口。
- 通过for-each循环。
- 通过ListIterator接口。
- 通过for循环。
- 通过forEach()方法。
- 通过forEachRemaining()方法。
通过剩余方式迭代Collection
让我们看一个通过其他方式遍历ArrayList元素的示例
import java.util.*;
class ArrayList4{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Ravi");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Vijay");
list.add("Ravi");
list.add("Ajay");
System.out.println("Traversing list through List Iterator:");
//Here, element iterates in reverse order
ListIterator list1=list.listIterator(list.size());
while(list1.hasPrevious())
{
String str=list1.previous();
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("Traversing list through for loop:");
for(int i=0;i{ //Here, we are using lambda expression
System.out.println(a);
});
System.out.println("Traversing list through forEachRemaining() method:");
Iterator itr=list.iterator();
itr.forEachRemaining(a-> //Here, we are using lambda expression
{
System.out.println(a);
});
}
}
输出:
Traversing list through List Iterator:
Ajay
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Traversing list through for loop:
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
Traversing list through forEach() method:
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
Traversing list through forEachRemaining() method:
Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
Java ArrayList中的用户定义的类对象
让我们看一个将学生类对象存储在数组列表中的示例。
class Student{
int rollno;
String name;
int age;
Student(int rollno,String name,int age){
this.rollno=rollno;
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
}
import java.util.*;
class ArrayList5{
public static void main(String args[]){
//Creating user-defined class objects
Student s1=new Student(101,"Sonoo",23);
Student s2=new Student(102,"Ravi",21);
Student s2=new Student(103,"Hanumat",25);
//creating arraylist
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add(s1);//adding Student class object
al.add(s2);
al.add(s3);
//Getting Iterator
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
//traversing elements of ArrayList object
while(itr.hasNext()){
Student st=(Student)itr.next();
System.out.println(st.rollno+" "+st.name+" "+st.age);
}
}
}
输出:
101 Sonoo 23
102 Ravi 21
103 Hanumat 25
Java ArrayList序列化和反序列化示例
让我们看一个序列化ArrayList对象然后反序列化它的示例。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ArrayList6 {
public static void main(String [] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ajay");
try
{
//Serialization
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("file");
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(al);
fos.close();
oos.close();
//Deserialization
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("file");
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis);
ArrayList list=(ArrayList)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(list);
}catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
输出:
[Ravi, Vijay, Ajay]
Java ArrayList示例添加元素
在这里,我们看到了添加元素的不同方法。
import java.util.*;
class ArrayList7{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
System.out.println("Initial list of elements: "+al);
//Adding elements to the end of the list
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ajay");
System.out.println("After invoking add(E e) method: "+al);
//Adding an element at the specific position
al.add(1, "Gaurav");
System.out.println("After invoking add(int index, E element) method: "+al);
ArrayList al2=new ArrayList();
al2.add("Sonoo");
al2.add("Hanumat");
//Adding second list elements to the first list
al.addAll(al2);
System.out.println("After invoking addAll(Collection c) method: "+al);
ArrayList al3=new ArrayList();
al3.add("John");
al3.add("Rahul");
//Adding second list elements to the first list at specific position
al.addAll(1, al3);
System.out.println("After invoking addAll(int index, Collection c) method: "+al);
}
}
输出:
Initial list of elements: []
After invoking add(E e) method: [Ravi, Vijay, Ajay]
After invoking add(int index, E element) method: [Ravi, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay]
After invoking addAll(Collection c) method:
[Ravi, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat]
After invoking addAll(int index, Collection c) method:
[Ravi, John, Rahul, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat]
Java ArrayList示例删除元素
在这里,我们看到了删除元素的不同方法。
import java.util.*;
class ArrayList8 {
public static void main(String [] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ajay");
al.add("Anuj");
al.add("Gaurav");
System.out.println("An initial list of elements: "+al);
//Removing specific element from arraylist
al.remove("Vijay");
System.out.println("After invoking remove(object) method: "+al);
//Removing element on the basis of specific position
al.remove(0);
System.out.println("After invoking remove(index) method: "+al);
//Creating another arraylist
ArrayList al2=new ArrayList();
al2.add("Ravi");
al2.add("Hanumat");
//Adding new elements to arraylist
al.addAll(al2);
System.out.println("Updated list : "+al);
//Removing all the new elements from arraylist
al.removeAll(al2);
System.out.println("After invoking removeAll() method: "+al);
//Removing elements on the basis of specified condition
al.removeIf(str -> str.contains("Ajay")); //Here, we are using Lambda expression
System.out.println("After invoking removeIf() method: "+al);
//Removing all the elements available in the list
al.clear();
System.out.println("After invoking clear() method: "+al);
}
}
输出:
An initial list of elements: [Ravi, Vijay, Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav]
After invoking remove(object) method: [Ravi, Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav]
After invoking remove(index) method: [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav]
Updated list : [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav, Ravi, Hanumat]
After invoking removeAll() method: [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav]
After invoking removeIf() method: [Anuj, Gaurav]
After invoking clear() method: []
保留所有Java方法的ArrayList示例
import java.util.*;
class ArrayList9{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ajay");
ArrayList al2=new ArrayList();
al2.add("Ravi");
al2.add("Hanumat");
al.retainAll(al2);
System.out.println("iterating the elements after retaining the elements of al2");
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
iterating the elements after retaining the elements of al2
Ravi
Java ArrayList示例isEmpty()方法
import java.util.*;
class ArrayList10{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
System.out.println("Is ArrayList Empty: "+al.isEmpty());
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ajay");
System.out.println("After Insertion");
System.out.println("Is ArrayList Empty: "+al.isEmpty());
}
}
输出:
Is ArrayList Empty: true
After Insertion
Is ArrayList Empty: false
Java ArrayList示例:书籍
让我们看一个ArrayList示例,其中我们将书添加到列表并打印所有书。
import java.util.*;
class Book {
int id;
String name,author,publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
public class ArrayListExample20 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creating list of Books
List list=new ArrayList();
//Creating Books
Book b1=new Book(101,"Let us C","Yashwant Kanetkar","BPB",8);
Book b2=new Book(102,"Data Communications and Networking","Forouzan","Mc Graw Hill",4);
Book b3=new Book(103,"Operating System","Galvin","Wiley",6);
//Adding Books to list
list.add(b1);
list.add(b2);
list.add(b3);
//Traversing list
for(Book b:list){
System.out.println(b.id+" "+b.name+" "+b.author+" "+b.publisher+" "+b.quantity);
}
}
}
输出:
101 Let us C Yashwant Kanetkar BPB 8
102 Data Communications and Networking Forouzan Mc Graw Hill 4
103 Operating System Galvin Wiley 6