数组是一种数据结构,用于在连续位置存储具有相似数据类型的变量。阵列的主要优点是随机访问和缓存友好性。数组主要有三种类型:
- 一维(1D)阵列
- 二维(2D)阵列
- 多维数组
一维数组:
- 它是类似数据类型的变量的列表。
- 它允许随机访问,并且可以在它们的索引的帮助下访问所有元素。
- 数组的大小是固定的。
- 对于动态大小的数组,可以在C++中使用vector。
- 一维数组的表示形式:
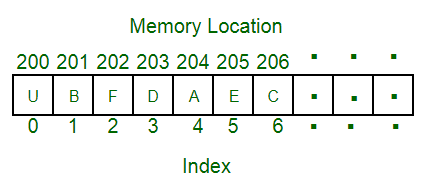
二维数组:
- 它是具有相同数据类型的变量的列表的列表。
- 它还允许随机访问,并且可以在它们的索引的帮助下访问所有元素。
- 它也可以看作是一维数组的集合。它也被称为矩阵。
- 它的尺寸可以从2增加到3和4,依此类推。
- 它们都被称为多维数组。
- 最常见的多维数组是2D数组。
- 二维数组的表示形式:
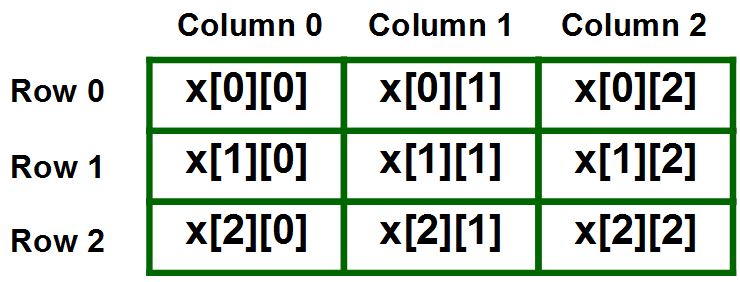
差异表:
| Basis | One Dimension Array | Two Dimension Array |
| Definition | Store a single list of the element of a similar data type. | Store a ‘list of lists’ of the element of a similar data type. |
| Representation | Represent multiple data items as a list. | Represent multiple data items as a table consisting of rows and columns. |
| Declaration |
The declaration varies for different programing language:
|
The declaration varies for different programing language:
|
| Dimension | One | Two |
| Size(bytes) | size of(datatype of the variable of the array) * size of the array | size of(datatype of the variable of the array)* the number of rows* the number of columns. |
| Address calculation. | Address of a[index] is equal to (base Address+ Size of each element of array * index). |
Address of a[i[[j] can be calculated in two ways row-major and column-major
|
数组的应用:
- 2D数组用于实现矩阵。
- 数组可用于实现各种数据结构,例如堆,堆栈,队列等。
- 它们允许随机访问。
- 它们是缓存友好的。