📌 相关文章
- Java LinkedList类(1)
- Java LinkedList
- C#| LinkedList类
- C#LinkedList(1)
- C#LinkedList
- C#| LinkedList类(1)
- 在Java中反转 LinkedList(1)
- 在Java中反转 LinkedList
- Java中的LinkedList set()方法
- Java中的LinkedList set()方法(1)
- java linkedlist print - Java (1)
- 如何在Java中获取 LinkedList 的子列表?
- 如何在Java中获取 LinkedList 的子列表?(1)
- arraylist 到linkedlist java (1)
- Java的ArrayList 与 LinkedList(1)
- Java的ArrayList 与 LinkedList
- Java中的LinkedList get()方法
- Java中的LinkedList get()方法(1)
- java linkedlist print - Java 代码示例
- 如何在Java中迭代 LinkedList?(1)
- 如何在Java中迭代 LinkedList?
- Java.util.LinkedList类(1)
- Java.util.LinkedList类
- arraylist 到linkedlist java 代码示例
- 将字符串数组转换为 LinkedList java 代码示例
- Java中的LinkedList remove()方法
- Java中的LinkedList remove()方法(1)
- 如何在Java对LinkedList进行排序?
- 如何在Java对 LinkedList 进行排序?(1)
📜 Java LinkedList类
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-12 09:37:51 🧑 作者: Mango
Java LinkedList类
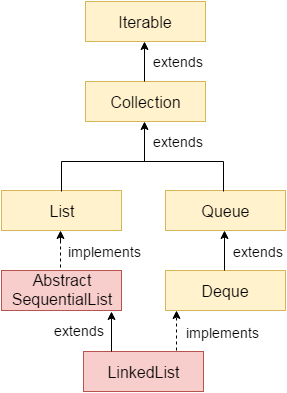
Java LinkedList类使用双链表来存储元素。它提供了一个链表数据结构。它继承了AbstractList类并实现List和Deque接口。
关于Java LinkedList的要点是:
- Java LinkedList类可以包含重复的元素。
- Java LinkedList类维护插入顺序。
- Java LinkedList类不同步。
- 在Java LinkedList类中,由于不需要进行任何转换,因此处理速度很快。
- Java LinkedList类可以用作列表,堆栈或队列。
LinkedList类的层次结构
如上图所示,Java LinkedList类扩展了AbstractSequentialList类并实现了List和Deque接口。
双链表
如果是双向链表,则可以从两侧添加或删除元素。

LinkedList类声明
我们来看一下java.util.LinkedList类的声明。
public class LinkedList extends AbstractSequentialList implements List, Deque, Cloneable, Serializable
Java LinkedList的构造方法
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| LinkedList() | It is used to construct an empty list. |
| LinkedList(Collection c) | It is used to construct a list containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order, they are returned by the collection’s iterator. |
Java LinkedList的方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | It is used to append the specified element to the end of a list. |
| void add(int index, E element) | It is used to insert the specified element at the specified position index in a list. |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | It is used to append all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | It is used to append all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection’s iterator. |
| boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) | It is used to append all the elements in the specified collection, starting at the specified position of the list. |
| void addFirst(E e) | It is used to insert the given element at the beginning of a list. |
| void addLast(E e) | It is used to append the given element to the end of a list. |
| void clear() | It is used to remove all the elements from a list. |
| Object clone() | It is used to return a shallow copy of an ArrayList. |
| boolean contains(Object o) | It is used to return true if a list contains a specified element. |
| Iterator |
It is used to return an iterator over the elements in a deque in reverse sequential order. |
| E element() | It is used to retrieve the first element of a list. |
| E get(int index) | It is used to return the element at the specified position in a list. |
| E getFirst() | It is used to return the first element in a list. |
| E getLast() | It is used to return the last element in a list. |
| int indexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in a list of the first occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | It is used to return the index in a list of the last occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if the list does not contain any element. |
| ListIterator |
It is used to return a list-iterator of the elements in proper sequence, starting at the specified position in the list. |
| boolean offer(E e) | It adds the specified element as the last element of a list. |
| boolean offerFirst(E e) | It inserts the specified element at the front of a list. |
| boolean offerLast(E e) | It inserts the specified element at the end of a list. |
| E peek() | It retrieves the first element of a list |
| E peekFirst() | It retrieves the first element of a list or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E peekLast() | It retrieves the last element of a list or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E poll() | It retrieves and removes the first element of a list. |
| E pollFirst() | It retrieves and removes the first element of a list, or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E pollLast() | It retrieves and removes the last element of a list, or returns null if a list is empty. |
| E pop() | It pops an element from the stack represented by a list. |
| void push(E e) | It pushes an element onto the stack represented by a list. |
| E remove() | It is used to retrieve and removes the first element of a list. |
| E remove(int index) | It is used to remove the element at the specified position in a list. |
| boolean remove(Object o) | It is used to remove the first occurrence of the specified element in a list. |
| E removeFirst() | It removes and returns the first element from a list. |
| boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) | It is used to remove the first occurrence of the specified element in a list (when traversing the list from head to tail). |
| E removeLast() | It removes and returns the last element from a list. |
| boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) | It removes the last occurrence of the specified element in a list (when traversing the list from head to tail). |
| E set(int index, E element) | It replaces the element at the specified position in a list with the specified element. |
| Object[] toArray() | It is used to return an array containing all the elements in a list in proper sequence (from first to the last element). |
| It returns an array containing all the elements in the proper sequence (from first to the last element); the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. | |
| int size() | It is used to return the number of elements in a list. |
Java LinkedList示例
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList1{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList al=new LinkedList();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Ajay");
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
Output: Ravi
Vijay
Ravi
Ajay
Java LinkedList示例添加元素
在这里,我们看到了添加元素的不同方法。
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList2{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList ll=new LinkedList();
System.out.println("Initial list of elements: "+ll);
ll.add("Ravi");
ll.add("Vijay");
ll.add("Ajay");
System.out.println("After invoking add(E e) method: "+ll);
//Adding an element at the specific position
ll.add(1, "Gaurav");
System.out.println("After invoking add(int index, E element) method: "+ll);
LinkedList ll2=new LinkedList();
ll2.add("Sonoo");
ll2.add("Hanumat");
//Adding second list elements to the first list
ll.addAll(ll2);
System.out.println("After invoking addAll(Collection c) method: "+ll);
LinkedList ll3=new LinkedList();
ll3.add("John");
ll3.add("Rahul");
//Adding second list elements to the first list at specific position
ll.addAll(1, ll3);
System.out.println("After invoking addAll(int index, Collection c) method: "+ll);
//Adding an element at the first position
ll.addFirst("Lokesh");
System.out.println("After invoking addFirst(E e) method: "+ll);
//Adding an element at the last position
ll.addLast("Harsh");
System.out.println("After invoking addLast(E e) method: "+ll);
}
}
Initial list of elements: []
After invoking add(E e) method: [Ravi, Vijay, Ajay]
After invoking add(int index, E element) method: [Ravi, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay]
After invoking addAll(Collection c) method:
[Ravi, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat]
After invoking addAll(int index, Collection c) method:
[Ravi, John, Rahul, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat]
After invoking addFirst(E e) method:
[Lokesh, Ravi, John, Rahul, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat]
After invoking addLast(E e) method:
[Lokesh, Ravi, John, Rahul, Gaurav, Vijay, Ajay, Sonoo, Hanumat, Harsh]
Java LinkedList示例删除元素
在这里,我们看到了删除元素的不同方法。
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList3 {
public static void main(String [] args)
{
LinkedList ll=new LinkedList();
ll.add("Ravi");
ll.add("Vijay");
ll.add("Ajay");
ll.add("Anuj");
ll.add("Gaurav");
ll.add("Harsh");
ll.add("Virat");
ll.add("Gaurav");
ll.add("Harsh");
ll.add("Amit");
System.out.println("Initial list of elements: "+ll);
//Removing specific element from arraylist
ll.remove("Vijay");
System.out.println("After invoking remove(object) method: "+ll);
//Removing element on the basis of specific position
ll.remove(0);
System.out.println("After invoking remove(index) method: "+ll);
LinkedList ll2=new LinkedList();
ll2.add("Ravi");
ll2.add("Hanumat");
// Adding new elements to arraylist
ll.addAll(ll2);
System.out.println("Updated list : "+ll);
//Removing all the new elements from arraylist
ll.removeAll(ll2);
System.out.println("After invoking removeAll() method: "+ll);
//Removing first element from the list
ll.removeFirst();
System.out.println("After invoking removeFirst() method: "+ll);
//Removing first element from the list
ll.removeLast();
System.out.println("After invoking removeLast() method: "+ll);
//Removing first occurrence of element from the list
ll.removeFirstOccurrence("Gaurav");
System.out.println("After invoking removeFirstOccurrence() method: "+ll);
//Removing last occurrence of element from the list
ll.removeLastOccurrence("Harsh");
System.out.println("After invoking removeLastOccurrence() method: "+ll);
//Removing all the elements available in the list
ll.clear();
System.out.println("After invoking clear() method: "+ll);
}
}
Initial list of elements: [Ravi, Vijay, Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav, Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh, Amit]
After invoking remove(object) method: [Ravi, Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav, Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh, Amit]
After invoking remove(index) method: [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav, Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh, Amit]
Updated list : [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav, Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh, Amit, Ravi, Hanumat]
After invoking removeAll() method: [Ajay, Anuj, Gaurav, Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh, Amit]
After invoking removeFirst() method: [Gaurav, Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh, Amit]
After invoking removeLast() method: [Gaurav, Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh]
After invoking removeFirstOccurrence() method: [Harsh, Virat, Gaurav, Harsh]
After invoking removeLastOccurrence() method: [Harsh, Virat, Gaurav]
After invoking clear() method: []
Java LinkedList示例,以反转元素列表
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedList4{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList ll=new LinkedList();
ll.add("Ravi");
ll.add("Vijay");
ll.add("Ajay");
//Traversing the list of elements in reverse order
Iterator i=ll.descendingIterator();
while(i.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
}
Output: Ajay
Vijay
Ravi
Java LinkedList示例:书籍
import java.util.*;
class Book {
int id;
String name,author,publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
public class LinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creating list of Books
List list=new LinkedList();
//Creating Books
Book b1=new Book(101,"Let us C","Yashwant Kanetkar","BPB",8);
Book b2=new Book(102,"Data Communications & Networking","Forouzan","Mc Graw Hill",4);
Book b3=new Book(103,"Operating System","Galvin","Wiley",6);
//Adding Books to list
list.add(b1);
list.add(b2);
list.add(b3);
//Traversing list
for(Book b:list){
System.out.println(b.id+" "+b.name+" "+b.author+" "+b.publisher+" "+b.quantity);
}
}
}
输出:
101 Let us C Yashwant Kanetkar BPB 8
102 Data Communications & Networking Forouzan Mc Graw Hill 4
103 Operating System Galvin Wiley 6