📌 相关文章
- Java中ArrayList转Vector
- Java中ArrayList转Vector(1)
- java中的arraylist vs vector(1)
- java代码示例中的arraylist vs vector
- Java中将 Vector 转换为 ArrayList(1)
- Java中将 Vector 转换为 ArrayList
- ArrayList vs Vector (1)
- 将 Vector 的元素复制到Java ArrayList(1)
- 将 Vector 的元素复制到Java ArrayList
- 将 ArrayList 的元素复制到 Vector 的Java程序
- 将 ArrayList 的元素复制到 Vector 的Java程序(1)
- ArrayList vs Vector - 任何代码示例
- Java ArrayList
- Java ArrayList类
- arraylist 到 java (1)
- arraylist - Java (1)
- Java ArrayList类(1)
- Java ArrayList(1)
- C++ Vector(1)
- C++ Vector
- Java中ArrayList的ArrayList
- Java中ArrayList的ArrayList(1)
- java arraylist - Java (1)
- java代码示例中的arraylist
- arraylist - Java 代码示例
- arraylist 到 java 代码示例
- java arraylist - Java 代码示例
- java中的arraylist方法(1)
- ArrayList和LinkedList之间的区别(1)
📜 Java ArrayList和Vector之间的区别
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-13 00:43:04 🧑 作者: Mango
ArrayList和Vector之间的区别
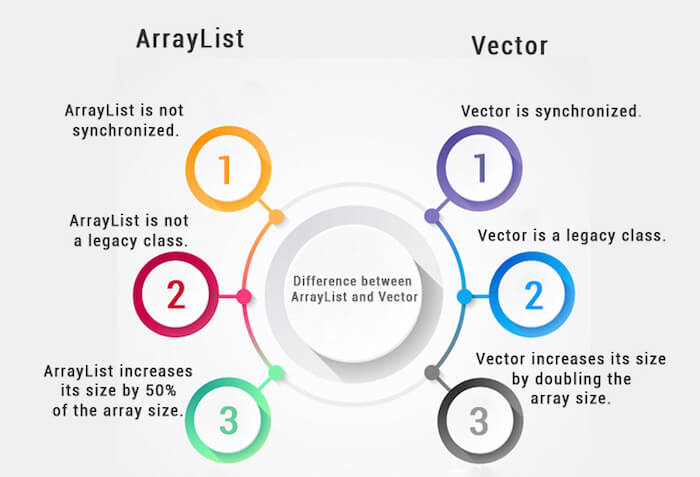
ArrayList和Vector都实现List接口并维护插入顺序。
但是,下面给出的ArrayList和Vector类之间有很多区别。
| ArrayList | Vector |
|---|---|
| 1) ArrayList is not synchronized. | Vector is synchronized. |
| 2) ArrayList increments 50% of current array size if the number of elements exceeds from its capacity. | Vector increments 100% means doubles the array size if the total number of elements exceeds than its capacity. |
| 3) ArrayList is not a legacy class. It is introduced in JDK 1.2. | Vector is a legacy class. |
| 4) ArrayList is fast because it is non-synchronized. | Vector is slow because it is synchronized, i.e., in a multithreading environment, it holds the other threads in runnable or non-runnable state until current thread releases the lock of the object. |
| 5) ArrayList uses the Iterator interface to traverse the elements. | A Vector can use the Iterator interface or Enumeration interface to traverse the elements. |
Java ArrayList的示例
让我们看一个简单的示例,其中我们使用ArrayList来存储和遍历元素。
import java.util.*;
class TestArrayList21{
public static void main(String args[]){
List al=new ArrayList();//creating arraylist
al.add("Sonoo");//adding object in arraylist
al.add("Michael");
al.add("James");
al.add("Andy");
//traversing elements using Iterator
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}
输出:
Sonoo
Michael
James
Andy
Java Vector的示例
让我们看一个使用Enumeration接口的Java Vector类的简单示例。
import java.util.*;
class TestVector1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Vector v=new Vector();//creating vector
v.add("umesh");//method of Collection
v.addElement("irfan");//method of Vector
v.addElement("kumar");
//traversing elements using Enumeration
Enumeration e=v.elements();
while(e.hasMoreElements()){
System.out.println(e.nextElement());
}
}
}
输出:
umesh
irfan
kumar