在 R 编程中循环对象
先决条件:R 编程中的数据结构
“for”循环的最大问题之一是它的内存消耗和执行重复任务的速度慢。在处理大型数据集并对其进行迭代时,不建议使用 for 循环。 R 提供了许多用于循环操作的向量的替代方法,这些方法在以交互方式在命令行上工作时非常有用。在本文中,我们处理apply()函数及其变体:
-
apply() lapply() sapply() tapply() mapply() -
apply() lapply() sapply() tapply() mapply() -
apply() lapply() sapply() tapply() mapply() -
apply() lapply() sapply() tapply() mapply() -
apply() lapply() sapply() tapply() mapply()
让我们看看每个函数的作用。
| Looping Function | Operation |
|---|---|
apply() | Applies a function over the margins of an array or matrix |
lapply() | Apply a function over a list or a vector |
sapply() | Same as lapply() but with simplified results |
tapply() | Apply a function over a ragged array |
mapply() | Multivariate version of lapply() |
-
apply():此函数在给定数组的边距上应用给定函数。apply(array, margins, function, …)
array = list of elements
margins = dimension of the array along which the function needs to be applied
function = the operation which you want to perform例子:
# R program to illustrate # apply() function # Creating a matrix A = matrix(1:9, 3, 3) print(A) # Applying apply() over row of matrix # Here margin 1 is for row r = apply(A, 1, sum) print(r) # Applying apply() over column of matrix # Here margin 2 is for column c = apply(A, 2, sum) print(c)输出:
[, 1] [, 2] [, 3] [1, ] 1 4 7 [2, ] 2 5 8 [3, ] 3 6 9 [1] 12 15 18 [1] 6 15 24 -
lapply():此函数用于在列表上应用函数。它总是返回一个与输入列表长度相同的列表。lapply(list, function, …)
list = Created list
function = the operation which you want to perform例子:
# R program to illustrate # lapply() function # Creating a matrix A = matrix(1:9, 3, 3) # Creating another matrix B = matrix(10:18, 3, 3) # Creating a list myList = list(A, B) # applying lapply() determinant = lapply(myList, det) print(determinant)输出:
[[1]] [1] 0 [[2]] [1] 5.329071e-15 -
sapply():如果可能,此函数用于简化lapply()的结果。与lapply()不同,结果并不总是一个列表。输出以下列方式变化:-- 如果输出是包含长度为 1 的元素的列表,则返回一个向量。
- 如果输出是一个列表,其中所有元素都是相同长度 (>1) 的向量,则返回一个矩阵。
- 如果输出包含无法简化的元素或不同类型的元素,则返回一个列表。
sapply(list, function, …)
list = Created list
function = the operation which you want to perform例子:
# R program to illustrate # sapply() function # Creating a list A = list(a = 1:5, b = 6:10) # applying sapply() means = sapply(A, mean) print(means)输出:
a b 3 8返回一个向量,因为输出有一个长度为 1 的列表。
-
tapply():此函数用于将函数应用于由因子组合给出的向量子集。tapply(vector, factor, function, …)
vector = Created vector
factor = Created factor
function = the operation which you want to perform例子:
# R program to illustrate # tapply() function # Creating a factor Id = c(1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3) # Creating a vector val = c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) # applying tapply() result = tapply(val, Id, sum) print(result)输出:
1 2 3 10 18 17上面的代码是如何工作的?
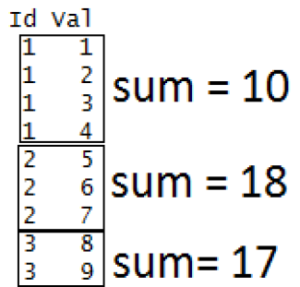
-
mapply():它是lapply()的多变量版本。此函数可以同时应用于多个列表。mapply(function, list1, list2, …)
function = the operation which you want to perform
list1, list2 = 创建的列表
例子:
# R program to illustrate # mapply() function # Creating a list A = list(c(1, 2, 3, 4)) # Creating another list B = list(c(2, 5, 1, 6)) # Applying mapply() result = mapply(sum, A, B) print(result)输出:
[1] 24