给定一棵二叉树,任务是打印从根节点到叶节点的最长路径。如果有多个答案,请打印其中任何一个。
例子:
Input:
4
/ \
3 6
/ \
5 7
Output:
4 -> 6 -> 7
Explanation:
Longest paths from root to leaf
are (4 -> 6 -> 5)
and (4 -> 6 -> 7).
Print any of them.
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
\
6
Output:
1 -> 2 -> 5 -> 6
天真的方法:想法是生成从根节点到所有叶节点的所有可能路径,跟踪最大长度的路径,最后打印最长的路径。
时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
高效方法:想法是使用递归有效地解决此问题。主要思想是从左子树和右子树递归获得最长的路径,然后将当前节点添加到具有更大长度的节点,这将是从当前节点到叶的最长路径。从根节点开始,对每个递归调用的节点执行以下步骤。
- 如果根节点为null,则不存在路径,返回空向量。
- 通过递归遍历root- > right ,可以得到向量rightvect中来自right子树的最长路径。
- 类似地,通过递归遍历root- > left ,可以得到矢量leftvect中来自左子树的最长路径。
- 比较rightvect和leftvect的长度,并将当前节点附加到两者中的较长者,然后返回该向量。
通过执行上述步骤,在树遍历结束时获得的向量是可能的最长路径。反向打印矢量,作为从根到叶的最长路径。
查看此图以了解如何使用来自左子树和右子树的节点的最长路径来获取来自当前节点的最长路径:
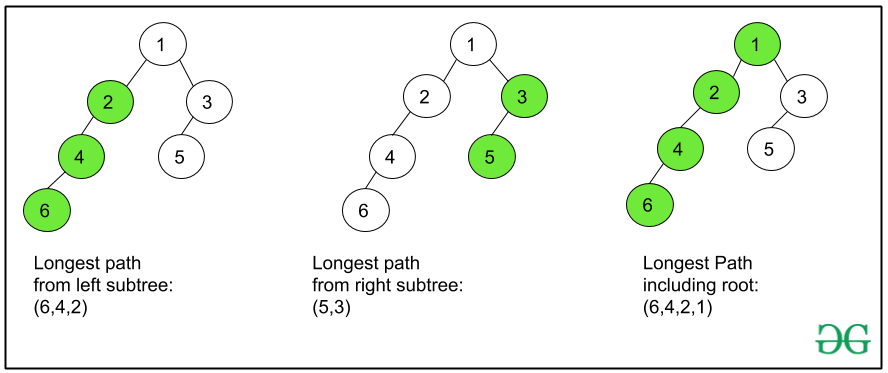
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ Program to print Longest Path
// from root to leaf in a Binary tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Tree node Structure
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Function to find and return the
// longest path
vector longestPath(Node* root)
{
// If root is null means there
// is no binary tree so
// return a empty vector
if (root == NULL) {
vector temp
= {};
return temp;
}
// Recursive call on root->right
vector rightvect
= longestPath(root->right);
// Recursive call on root->left
vector leftvect
= longestPath(root->left);
// Compare the size of the two vectors
// and insert current node accordingly
if (leftvect.size() > rightvect.size())
leftvect.push_back(root->data);
else
rightvect.push_back(root->data);
// Return the appropriate vector
return (leftvect.size() > rightvect.size()
? leftvect
: rightvect);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->left->right->right = newNode(6);
vector output = longestPath(root);
int n = output.size();
cout << output[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << " -> " << output[i];
}
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print Longest Path
// from root to leaf in a Binary tree
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class GFG{
// Binary tree node
static class Node
{
Node left;
Node right;
int data;
};
// Function to create a new
// Binary node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to find and return the
// longest path
public static ArrayList longestPath(Node root)
{
// If root is null means there
// is no binary tree so
// return a empty vector
if(root == null)
{
ArrayList output = new ArrayList<>();
return output;
}
// Recursive call on root.right
ArrayList right = longestPath(root.right);
// Recursive call on root.left
ArrayList left = longestPath(root.left);
// Compare the size of the two ArrayList
// and insert current node accordingly
if(right.size() < left.size())
{
left.add(root.data);
}
else
{
right.add(root.data);
}
// Return the appropriate ArrayList
return (left.size() >
right.size() ? left :right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.left.right.right = newNode(6);
ArrayList output = longestPath(root);
int n = output.size();
System.out.print(output.get(n - 1));
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
System.out.print(" -> " + output.get(i));
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by HamreetSingh Python3
# Python3 program to print longest path
# from root to leaf in a Binary tree
# Tree node Structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to find and return the
# longest path
def longestPath(root):
# If root is null means there
# is no binary tree so
# return a empty vector
if (root == None):
return []
# Recursive call on root.right
rightvect = longestPath(root.right)
# Recursive call on root.left
leftvect = longestPath(root.left)
# Compare the size of the two vectors
# and insert current node accordingly
if (len(leftvect) > len(rightvect)):
leftvect.append(root.data)
else:
rightvect.append(root.data)
# Return the appropriate vector
if len(leftvect) > len(rightvect):
return leftvect
return rightvect
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.left.right.right = Node(6)
output = longestPath(root)
n = len(output)
print(output[n - 1], end = "")
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
print(" ->", output[i], end = "")
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program to print
// longest Path from
// root to leaf in a
// Binary tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Binary tree node
class Node
{
public Node left;
public Node right;
public int data;
};
// Function to create a new
// Binary node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to find and
// return the longest path
static List longestPath(Node root)
{
// If root is null means there
// is no binary tree so
// return a empty vector
if(root == null)
{
List output = new List();
return output;
}
// Recursive call on root.right
List right = longestPath(root.right);
// Recursive call on root.left
List left = longestPath(root.left);
// Compare the size of the two List
// and insert current node accordingly
if(right.Count < left.Count)
{
left.Add(root.data);
}
else
{
right.Add(root.data);
}
// Return the appropriate List
return (left.Count >
right.Count ?
left :right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.left.right.right = newNode(6);
List output = longestPath(root);
int n = output.Count;
Console.Write(output[n - 1]);
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
Console.Write(" -> " + output[i]);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar 输出
1 -> 2 -> 5 -> 6
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。