N Queen是在N×N棋盘上放置N个国际象棋皇后的问题,这样就不会有两个女王互相攻击。例如,以下是4 Queen问题的解决方案。
N Queen是在N×N棋盘上放置N个国际象棋皇后的问题,这样就不会有两个女王互相攻击。例如,以下是4 Queen问题的两种解决方案。
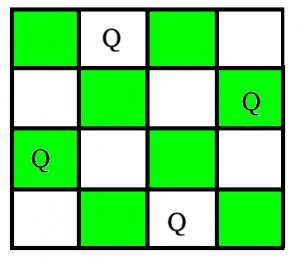
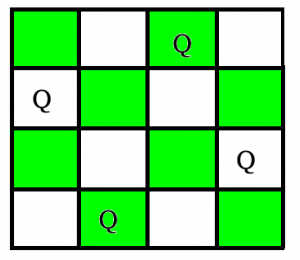
在上一篇文章中,我们讨论了仅打印一种可能的解决方案的方法,因此,在本篇文章中,现在的任务是在N-Queen问题中打印所有解决方案。每个解决方案包含N个皇后位置的不同板配置,其中解决方案是[1,2,3..n]的升序排列,此处第i个位置的数字表示第i个-列皇后是放在该编号所在的行中。对于上面的示例,解决方案写为[[2 4 1 3] [3 1 4 2]]。这里讨论的解决方案是相同方法的扩展。
回溯算法
想法是将皇后区从最左边的列开始一个一列地放置在不同的列中。将皇后放置在列中时,我们检查是否与已放置的皇后发生冲突。在当前列中,如果找到没有冲突的行,则将该行和列标记为解决方案的一部分。如果由于冲突而找不到这样的行,那么我们将回溯并返回false。
1) Start in the leftmost column
2) If all queens are placed
return true
3) Try all rows in the current column. Do following
for every tried row.
a) If the queen can be placed safely in this row
then mark this [row, column] as part of the
solution and recursively check if placing
queen here leads to a solution.
b) If placing queen in [row, column] leads to a
solution then return true.
c) If placing queen doesn't lead to a solution
then unmark this [row, column] (Backtrack)
and go to step (a) to try other rows.
3) If all rows have been tried and nothing worked,
return false to trigger backtracking.在代码中突出显示的上述算法只有很小的修改。
C++
/* C/C++ program to solve N Queen Problem using
backtracking */
#include
using namespace std;
vector > result;
/* A utility function to check if a queen can
be placed on board[row][col]. Note that this
function is called when "col" queens are
already placed in columns from 0 to col -1.
So we need to check only left side for
attacking queens */
bool isSafe(vector > board,
int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
int N = board.size();
/* Check this row on left side */
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i])
return false;
/* Check upper diagonal on left side */
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false;
/* Check lower diagonal on left side */
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false;
return true;
}
/* A recursive utility function to solve N
Queen problem */
bool solveNQUtil(vector >& board, int col)
{
/* base case: If all queens are placed
then return true */
int N = board.size();
if (col == N) {
vector v;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 1)
v.push_back(j + 1);
}
}
result.push_back(v);
return true;
}
/* Consider this column and try placing
this queen in all rows one by one */
bool res = false;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
/* Check if queen can be placed on
board[i][col] */
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
/* Place this queen in board[i][col] */
board[i][col] = 1;
// Make result true if any placement
// is possible
res = solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) || res;
/* If placing queen in board[i][col]
doesn't lead to a solution, then
remove queen from board[i][col] */
board[i][col] = 0; // BACKTRACK
}
}
/* If queen can not be place in any row in
this column col then return false */
return res;
}
/* This function solves the N Queen problem using
Backtracking. It mainly uses solveNQUtil() to
solve the problem. It returns false if queens
cannot be placed, otherwise return true and
prints placement of queens in the form of 1s.
Please note that there may be more than one
solutions, this function prints one of the
feasible solutions.*/
vector > nQueen(int n)
{
result.clear();
vector > board(n, vector(n, 0));
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false) {
return {};
}
sort(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
vector > v = nQueen(n);
for (auto ar : v) {
cout << "[";
for (auto it : ar)
cout << it << " ";
cout << "]";
}
return 0;
} Java
/* Java program to solve N Queen
Problem using backtracking */
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
static List > result
= new ArrayList >();
/* A utility function to check if a queen can
be placed on board[row][col]. Note that this
function is called when "col" queens are
already placed in columns from 0 to col -1.
So we need to check only left side for
attacking queens */
static boolean isSafe(int board[][], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
int N = board.length;
/* Check this row on left side */
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i] == 1)
return false;
/* Check upper diagonal on left side */
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j] == 1)
return false;
/* Check lower diagonal on left side */
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j] == 1)
return false;
return true;
}
/* A recursive utility function
to solve N Queen problem */
static boolean solveNQUtil(int board[][], int col)
{
/* base case: If all queens are placed
then return true */
int N = board.length;
if (col == N) {
List v = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 1)
v.add(j + 1);
}
}
result.add(v);
return true;
}
/* Consider this column and try placing
this queen in all rows one by one */
boolean res = false;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
/* Check if queen can be placed on
board[i][col] */
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
/* Place this queen in board[i][col] */
board[i][col] = 1;
// Make result true if any placement
// is possible
res = solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) || res;
/* If placing queen in board[i][col]
doesn't lead to a solution, then
remove queen from board[i][col] */
board[i][col] = 0; // BACKTRACK
}
}
/* If queen can not be place in any row in
this column col then return false */
return res;
}
/* This function solves the N Queen problem using
Backtracking. It mainly uses solveNQUtil() to
solve the problem. It returns false if queens
cannot be placed, otherwise return true and
prints placement of queens in the form of 1s.
Please note that there may be more than one
solutions, this function prints one of the
feasible solutions.*/
static List > nQueen(int n)
{
result.clear();
int board[][] = new int[n][n];
solveNQUtil(board, 0);
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
List > res = nQueen(n);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
// This code has been contributed
// by 29AjayKumar Python3
''' Python3 program to solve N Queen Problem using
backtracking '''
result = []
# A utility function to print solution
''' A utility function to check if a queen can
be placed on board[row][col]. Note that this
function is called when "col" queens are
already placed in columns from 0 to col -1.
So we need to check only left side for
attacking queens '''
def isSafe(board, row, col):
# Check this row on left side
for i in range(col):
if (board[row][i]):
return False
# Check upper diagonal on left side
i = row
j = col
while i >= 0 and j >= 0:
if(board[i][j]):
return False
i -= 1
j -= 1
# Check lower diagonal on left side
i = row
j = col
while j >= 0 and i < 4:
if(board[i][j]):
return False
i = i + 1
j = j - 1
return True
''' A recursive utility function to solve N
Queen problem '''
def solveNQUtil(board, col):
''' base case: If all queens are placed
then return true '''
if (col == 4):
v = []
for i in board:
for j in range(len(i)):
if i[j] == 1:
v.append(j+1)
result.append(v)
return True
''' Consider this column and try placing
this queen in all rows one by one '''
res = False
for i in range(4):
''' Check if queen can be placed on
board[i][col] '''
if (isSafe(board, i, col)):
# Place this queen in board[i][col]
board[i][col] = 1
# Make result true if any placement
# is possible
res = solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) or res
''' If placing queen in board[i][col]
doesn't lead to a solution, then
remove queen from board[i][col] '''
board[i][col] = 0 # BACKTRACK
''' If queen can not be place in any row in
this column col then return false '''
return res
''' This function solves the N Queen problem using
Backtracking. It mainly uses solveNQUtil() to
solve the problem. It returns false if queens
cannot be placed, otherwise return true and
prints placement of queens in the form of 1s.
Please note that there may be more than one
solutions, this function prints one of the
feasible solutions.'''
def solveNQ(n):
result.clear()
board = [[0 for j in range(n)]
for i in range(n)]
solveNQUtil(board, 0)
result.sort()
return result
# Driver Code
n = 4
res = solveNQ(n)
print(res)
# This code is contributed by YatinGuptaC#
/* C# program to solve N Queen
Problem using backtracking */
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
static List > result = new List >();
/* A utility function to check if a queen can
be placed on board[row,col]. Note that this
function is called when "col" queens are
already placed in columns from 0 to col -1.
So we need to check only left side for
attacking queens */
static bool isSafe(int[, ] board, int row, int col,
int N)
{
int i, j;
/* Check this row on left side */
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row, i] == 1)
return false;
/* Check upper diagonal on left side */
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i, j] == 1)
return false;
/* Check lower diagonal on left side */
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i, j] == 1)
return false;
return true;
}
/* A recursive utility function
to solve N Queen problem */
static bool solveNQUtil(int[, ] board, int col, int N)
{
/* base case: If all queens are placed
then return true */
if (col == N) {
List v = new List();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (board[i, j] == 1)
v.Add(j + 1);
}
result.Add(v);
return true;
}
/* Consider this column and try placing
this queen in all rows one by one */
bool res = false;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
/* Check if queen can be placed on
board[i,col] */
if (isSafe(board, i, col, N)) {
/* Place this queen in board[i,col] */
board[i, col] = 1;
// Make result true if any placement
// is possible
res = solveNQUtil(board, col + 1, N) || res;
/* If placing queen in board[i,col]
doesn't lead to a solution, then
remove queen from board[i,col] */
board[i, col] = 0; // BACKTRACK
}
}
/* If queen can not be place in any row in
this column col then return false */
return res;
}
/* This function solves the N Queen problem using
Backtracking. It mainly uses solveNQUtil() to
solve the problem. It returns false if queens
cannot be placed, otherwise return true and
prints placement of queens in the form of 1s.
Please note that there may be more than one
solutions, this function prints one of the
feasible solutions.*/
static List > solveNQ(int n)
{
result.Clear();
int[, ] board = new int[n, n];
solveNQUtil(board, 0, n);
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 4;
List > res = solveNQ(n);
for (int i = 0; i < res.Count; i++) {
Console.Write("[");
for (int j = 0; j < res[i].Count; j++) {
Console.Write(res[i][j]+ " ");
}
Console.Write("]");
}
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */ C++
// CPP program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector > result;
// Program to solve N Quuens problem
void solveBoard(vector >& board, int row,
int rowmask, int ldmask, int rdmask,
int& ways)
{
int n = board.size();
// All_rows_filled is a bit mask having all N bits set
int all_rows_filled = (1 << n) - 1;
// If rowmask will have all bits set, means queen has
// been placed successfully in all rows and board is
// diplayed
if (rowmask == all_rows_filled) {
vector v;
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.size(); j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
v.push_back(j + 1);
}
}
result.push_back(v);
return;
}
// We extract a bit mask(safe) by rowmask,
// ldmask and rdmask. all set bits of 'safe'
// indicates the safe column index for queen
// placement of this iteration for row index(row).
int safe
= all_rows_filled & (~(rowmask | ldmask | rdmask));
while (safe) {
// Extracts the right-most set bit
// (safe column index) where queen
// can be placed for this row
int p = safe & (-safe);
int col = (int)log2(p);
board[row][col] = 'Q';
// This is very important:
// we need to update rowmask, ldmask and rdmask
// for next row as safe index for queen placement
// will be decided by these three bit masks.
// We have all three rowmask, ldmask and
// rdmask as 0 in beginning. Suppose, we are placing
// queen at 1st column index at 0th row. rowmask,
// ldmask and rdmask will change for next row as
// below:
// rowmask's 1st bit will be set by OR operation
// rowmask = 00000000000000000000000000000010
// ldmask will change by setting 1st
// bit by OR operation and left shifting
// by 1 as it has to block the next column
// of next row because that will fall on left
// diagonal. ldmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000100
// rdmask will change by setting 1st bit
// by OR operation and right shifting by 1
// as it has to block the previous column
// of next row because that will fall on right
// diagonal. rdmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000001
// these bit masks will keep updated in each
// iteration for next row
solveBoard(board, row + 1, rowmask | p,
(ldmask | p) << 1, (rdmask | p) >> 1,
ways);
// Reset right-most set bit to 0 so,
// next iteration will continue by placing the queen
// at another safe column index of this row
safe = safe & (safe - 1);
// Backtracking, replace 'Q' by ' '
board[row][col] = ' ';
}
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Board size
int n = 4;
int ways = 0;
vector > board;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vector tmp;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
tmp.push_back(' ');
}
board.push_back(tmp);
}
int rowmask = 0, ldmask = 0, rdmask = 0;
int row = 0;
// Function Call
result.clear();
solveBoard(board, row, rowmask, ldmask, rdmask, ways);
sort(result.begin(),result.end());
for (auto ar : result) {
cout << "[";
for (auto it : ar)
cout << it << " ";
cout << "]";
}
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Nikhil Vinay Java
// Java Program for aove approach
import java.util.*;
public class NQueenSolution {
static List > result
= new ArrayList >();
// Program to solve N-Queens Problem
public void solveBoard(char[][] board, int row,
int rowmask, int ldmask,
int rdmask)
{
int n = board.length;
// All_rows_filled is a bit mask
// having all N bits set
int all_rows_filled = (1 << n) - 1;
// If rowmask will have all bits set,
// means queen has been placed successfully
// in all rows and board is diplayed
if (rowmask == all_rows_filled) {
List v = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
v.add(j + 1);
}
}
result.add(v);
return;
}
// We extract a bit mask(safe) by rowmask,
// ldmask and rdmask. all set bits of 'safe'
// indicates the safe column index for queen
// placement of this iteration for row index(row).
int safe = all_rows_filled
& (~(rowmask | ldmask | rdmask));
while (safe > 0) {
// Extracts the right-most set bit
// (safe column index) where queen
// can be placed for this row
int p = safe & (-safe);
int col = (int)(Math.log(p) / Math.log(2));
board[row][col] = 'Q';
// This is very important:
// we need to update rowmask, ldmask and rdmask
// for next row as safe index for queen
// placement will be decided by these three bit
// masks.
// We have all three rowmask, ldmask and
// rdmask as 0 in beginning. Suppose, we are
// placing queen at 1st column index at 0th row.
// rowmask, ldmask and rdmask will change for
// next row as below:
// rowmask's 1st bit will be set by OR operation
// rowmask = 00000000000000000000000000000010
// ldmask will change by setting 1st
// bit by OR operation and left shifting
// by 1 as it has to block the next column
// of next row because that will fall on left
// diagonal. ldmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000100
// rdmask will change by setting 1st bit
// by OR operation and right shifting by 1
// as it has to block the previous column
// of next row because that will fall on right
// diagonal. rdmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000001
// these bit masks will keep updated in each
// iteration for next row
solveBoard(board, row + 1, rowmask | p,
(ldmask | p) << 1,
(rdmask | p) >> 1);
// Reset right-most set bit to 0 so,
// next iteration will continue by placing the
// queen at another safe column index of this
// row
safe = safe & (safe - 1);
// Backtracking, replace 'Q' by ' '
board[row][col] = ' ';
}
}
// Program to print board
public void printBoard(char[][] board)
{
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
System.out.print("|");
for (int j = 0; j < board[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(board[i][j] + "|");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Board size
int n = 4;
char board[][] = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
int rowmask = 0, ldmask = 0, rdmask = 0;
int row = 0;
NQueenSolution solution = new NQueenSolution();
// Function Call
result.clear();
solution.solveBoard(board, row, rowmask, ldmask,
rdmask);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Nikhil Vinay Python3
# Python program for above approach
import math
result = []
# Program to solve N-Queens Problem
def solveBoard(board, row, rowmask,
ldmask, rdmask):
n = len(board)
# All_rows_filled is a bit mask
# having all N bits set
all_rows_filled = (1 << n) - 1
# If rowmask will have all bits set, means
# queen has been placed successfully
# in all rows and board is diplayed
if (rowmask == all_rows_filled):
v = []
for i in board:
for j in range(len(i)):
if i[j] == 'Q':
v.append(j+1)
result.append(v)
# We extract a bit mask(safe) by rowmask,
# ldmask and rdmask. all set bits of 'safe'
# indicates the safe column index for queen
# placement of this iteration for row index(row).
safe = all_rows_filled & (~(rowmask |
ldmask | rdmask))
while (safe > 0):
# Extracts the right-most set bit
# (safe column index) where queen
# can be placed for this row
p = safe & (-safe)
col = (int)(math.log(p)/math.log(2))
board[row][col] = 'Q'
# This is very important:
# we need to update rowmask, ldmask and rdmask
# for next row as safe index for queen placement
# will be decided by these three bit masks.
# We have all three rowmask, ldmask and
# rdmask as 0 in beginning. Suppose, we are placing
# queen at 1st column index at 0th row. rowmask, ldmask
# and rdmask will change for next row as below:
# rowmask's 1st bit will be set by OR operation
# rowmask = 00000000000000000000000000000010
# ldmask will change by setting 1st
# bit by OR operation and left shifting
# by 1 as it has to block the next column
# of next row because that will fall on left diagonal.
# ldmask = 00000000000000000000000000000100
# rdmask will change by setting 1st bit
# by OR operation and right shifting by 1
# as it has to block the previous column
# of next row because that will fall on right diagonal.
# rdmask = 00000000000000000000000000000001
# these bit masks will keep updated in each
# iteration for next row
solveBoard(board, row+1, rowmask | p,
(ldmask | p) << 1, (rdmask | p) >> 1)
# Reset right-most set bit to 0 so, next
# iteration will continue by placing the queen
# at another safe column index of this row
safe = safe & (safe-1)
# Backtracking, replace 'Q' by ' '
board[row][col] = ' '
# Program to print board
def printBoard(board):
for row in board:
print("|" + "|".join(row) + "|")
# Driver Code
def main():
n = 4 # board size
board = []
for i in range(n):
row = []
for j in range(n):
row.append(' ')
board.append(row)
rowmask = 0
ldmask = 0
rdmask = 0
row = 0
# Function Call
result.clear()
solveBoard(board, row, rowmask, ldmask, rdmask)
result.sort()
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Vinay[2 4 1 3 ][3 1 4 2 ]使用位屏蔽的高效回溯方法
算法:
在每一行和每一列中始终只有一个皇后,因此回溯的想法是从每一行的最左列开始放置皇后,然后找到可以放置皇后而不会与先前放置的皇后发生冲突的列。从第一行到最后一行重复此过程。放置皇后后,将对其进行跟踪,就好像它没有与放置在前一行中的皇后发生碰撞(行,列和对角线)。一旦发现不能将女王/王后放置在行中的特定列索引上,算法将回溯并更改放置在前一行中的女王/王后的位置,然后向前移动以将女王/王后放置在下一行中。
- 从三位向量开始,该向量用于跟踪在每次迭代中按行,列和对角线排列的皇后放置的安全位置。
- 三位向量将包含以下信息:
- rowmask:此位向量的设置的位索引(i)将指示,不能将女王/王后放置在下一行的第i列。
- ldmask:设置此位向量的位索引(i)将指示,不能将女王/王后放置在下一行的第i列。它代表下一行的不安全列索引,该索引位于上一行中的女王/王后的左对角线之下。
- rdmask:设置此位向量的位索引(i)将指示,不能将女王/王后放置在下一行的第i列。它代表下一行的不安全列索引落在上一行中的女王/王后的对角线处。
- 有一个二维(NxN)矩阵(板),该矩阵的开头的所有索引处都带有”字符,并且逐行用’Q’填充。一旦所有行都用“ Q”填充,当前解决方案将被推入结果列表。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// CPP program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
vector > result;
// Program to solve N Quuens problem
void solveBoard(vector >& board, int row,
int rowmask, int ldmask, int rdmask,
int& ways)
{
int n = board.size();
// All_rows_filled is a bit mask having all N bits set
int all_rows_filled = (1 << n) - 1;
// If rowmask will have all bits set, means queen has
// been placed successfully in all rows and board is
// diplayed
if (rowmask == all_rows_filled) {
vector v;
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.size(); j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
v.push_back(j + 1);
}
}
result.push_back(v);
return;
}
// We extract a bit mask(safe) by rowmask,
// ldmask and rdmask. all set bits of 'safe'
// indicates the safe column index for queen
// placement of this iteration for row index(row).
int safe
= all_rows_filled & (~(rowmask | ldmask | rdmask));
while (safe) {
// Extracts the right-most set bit
// (safe column index) where queen
// can be placed for this row
int p = safe & (-safe);
int col = (int)log2(p);
board[row][col] = 'Q';
// This is very important:
// we need to update rowmask, ldmask and rdmask
// for next row as safe index for queen placement
// will be decided by these three bit masks.
// We have all three rowmask, ldmask and
// rdmask as 0 in beginning. Suppose, we are placing
// queen at 1st column index at 0th row. rowmask,
// ldmask and rdmask will change for next row as
// below:
// rowmask's 1st bit will be set by OR operation
// rowmask = 00000000000000000000000000000010
// ldmask will change by setting 1st
// bit by OR operation and left shifting
// by 1 as it has to block the next column
// of next row because that will fall on left
// diagonal. ldmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000100
// rdmask will change by setting 1st bit
// by OR operation and right shifting by 1
// as it has to block the previous column
// of next row because that will fall on right
// diagonal. rdmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000001
// these bit masks will keep updated in each
// iteration for next row
solveBoard(board, row + 1, rowmask | p,
(ldmask | p) << 1, (rdmask | p) >> 1,
ways);
// Reset right-most set bit to 0 so,
// next iteration will continue by placing the queen
// at another safe column index of this row
safe = safe & (safe - 1);
// Backtracking, replace 'Q' by ' '
board[row][col] = ' ';
}
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Board size
int n = 4;
int ways = 0;
vector > board;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vector tmp;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
tmp.push_back(' ');
}
board.push_back(tmp);
}
int rowmask = 0, ldmask = 0, rdmask = 0;
int row = 0;
// Function Call
result.clear();
solveBoard(board, row, rowmask, ldmask, rdmask, ways);
sort(result.begin(),result.end());
for (auto ar : result) {
cout << "[";
for (auto it : ar)
cout << it << " ";
cout << "]";
}
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Nikhil Vinay
Java
// Java Program for aove approach
import java.util.*;
public class NQueenSolution {
static List > result
= new ArrayList >();
// Program to solve N-Queens Problem
public void solveBoard(char[][] board, int row,
int rowmask, int ldmask,
int rdmask)
{
int n = board.length;
// All_rows_filled is a bit mask
// having all N bits set
int all_rows_filled = (1 << n) - 1;
// If rowmask will have all bits set,
// means queen has been placed successfully
// in all rows and board is diplayed
if (rowmask == all_rows_filled) {
List v = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
v.add(j + 1);
}
}
result.add(v);
return;
}
// We extract a bit mask(safe) by rowmask,
// ldmask and rdmask. all set bits of 'safe'
// indicates the safe column index for queen
// placement of this iteration for row index(row).
int safe = all_rows_filled
& (~(rowmask | ldmask | rdmask));
while (safe > 0) {
// Extracts the right-most set bit
// (safe column index) where queen
// can be placed for this row
int p = safe & (-safe);
int col = (int)(Math.log(p) / Math.log(2));
board[row][col] = 'Q';
// This is very important:
// we need to update rowmask, ldmask and rdmask
// for next row as safe index for queen
// placement will be decided by these three bit
// masks.
// We have all three rowmask, ldmask and
// rdmask as 0 in beginning. Suppose, we are
// placing queen at 1st column index at 0th row.
// rowmask, ldmask and rdmask will change for
// next row as below:
// rowmask's 1st bit will be set by OR operation
// rowmask = 00000000000000000000000000000010
// ldmask will change by setting 1st
// bit by OR operation and left shifting
// by 1 as it has to block the next column
// of next row because that will fall on left
// diagonal. ldmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000100
// rdmask will change by setting 1st bit
// by OR operation and right shifting by 1
// as it has to block the previous column
// of next row because that will fall on right
// diagonal. rdmask =
// 00000000000000000000000000000001
// these bit masks will keep updated in each
// iteration for next row
solveBoard(board, row + 1, rowmask | p,
(ldmask | p) << 1,
(rdmask | p) >> 1);
// Reset right-most set bit to 0 so,
// next iteration will continue by placing the
// queen at another safe column index of this
// row
safe = safe & (safe - 1);
// Backtracking, replace 'Q' by ' '
board[row][col] = ' ';
}
}
// Program to print board
public void printBoard(char[][] board)
{
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
System.out.print("|");
for (int j = 0; j < board[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(board[i][j] + "|");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Board size
int n = 4;
char board[][] = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
int rowmask = 0, ldmask = 0, rdmask = 0;
int row = 0;
NQueenSolution solution = new NQueenSolution();
// Function Call
result.clear();
solution.solveBoard(board, row, rowmask, ldmask,
rdmask);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Nikhil Vinay
Python3
# Python program for above approach
import math
result = []
# Program to solve N-Queens Problem
def solveBoard(board, row, rowmask,
ldmask, rdmask):
n = len(board)
# All_rows_filled is a bit mask
# having all N bits set
all_rows_filled = (1 << n) - 1
# If rowmask will have all bits set, means
# queen has been placed successfully
# in all rows and board is diplayed
if (rowmask == all_rows_filled):
v = []
for i in board:
for j in range(len(i)):
if i[j] == 'Q':
v.append(j+1)
result.append(v)
# We extract a bit mask(safe) by rowmask,
# ldmask and rdmask. all set bits of 'safe'
# indicates the safe column index for queen
# placement of this iteration for row index(row).
safe = all_rows_filled & (~(rowmask |
ldmask | rdmask))
while (safe > 0):
# Extracts the right-most set bit
# (safe column index) where queen
# can be placed for this row
p = safe & (-safe)
col = (int)(math.log(p)/math.log(2))
board[row][col] = 'Q'
# This is very important:
# we need to update rowmask, ldmask and rdmask
# for next row as safe index for queen placement
# will be decided by these three bit masks.
# We have all three rowmask, ldmask and
# rdmask as 0 in beginning. Suppose, we are placing
# queen at 1st column index at 0th row. rowmask, ldmask
# and rdmask will change for next row as below:
# rowmask's 1st bit will be set by OR operation
# rowmask = 00000000000000000000000000000010
# ldmask will change by setting 1st
# bit by OR operation and left shifting
# by 1 as it has to block the next column
# of next row because that will fall on left diagonal.
# ldmask = 00000000000000000000000000000100
# rdmask will change by setting 1st bit
# by OR operation and right shifting by 1
# as it has to block the previous column
# of next row because that will fall on right diagonal.
# rdmask = 00000000000000000000000000000001
# these bit masks will keep updated in each
# iteration for next row
solveBoard(board, row+1, rowmask | p,
(ldmask | p) << 1, (rdmask | p) >> 1)
# Reset right-most set bit to 0 so, next
# iteration will continue by placing the queen
# at another safe column index of this row
safe = safe & (safe-1)
# Backtracking, replace 'Q' by ' '
board[row][col] = ' '
# Program to print board
def printBoard(board):
for row in board:
print("|" + "|".join(row) + "|")
# Driver Code
def main():
n = 4 # board size
board = []
for i in range(n):
row = []
for j in range(n):
row.append(' ')
board.append(row)
rowmask = 0
ldmask = 0
rdmask = 0
row = 0
# Function Call
result.clear()
solveBoard(board, row, rowmask, ldmask, rdmask)
result.sort()
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Vinay
[2 4 1 3 ][3 1 4 2 ]