给定一个M x N矩阵,任意设置几个障碍,计算矩阵中从源到目的地的可能的最长路径的长度。我们只能移动到不是障碍的相邻单元格。该路线不能包含任何对角线移动,并且无法再次访问在特定路径中曾经访问过的位置。
例如,下面的矩阵突出显示了从源到目的地没有障碍的最长路径。路径的长度是24。
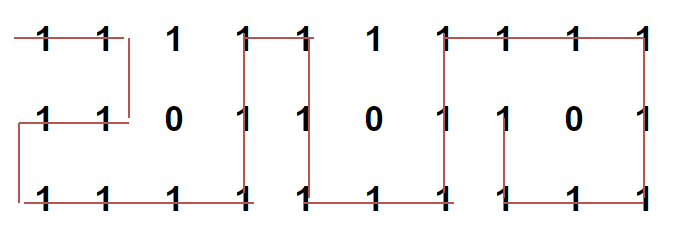
这个想法是使用回溯。我们从矩阵的源单元格开始,在所有允许的四个方向上前进,然后递归检查它们是否导致求解。如果找到了目标,则我们将更新最长路径的值,否则,如果以上解决方案均无效,则我们将从函数返回false。
以下是上述想法的C++实现–
// C++ program to find Longest Possible Route in a
// matrix with hurdles
#include
using namespace std;
#define R 3
#define C 10
// A Pair to store status of a cell. found is set to
// true of destination is reachable and value stores
// distance of longest path
struct Pair
{
// true if destination is found
bool found;
// stores cost of longest path from current cell to
// destination cell
int value;
};
// Function to find Longest Possible Route in the
// matrix with hurdles. If the destination is not reachable
// the function returns false with cost INT_MAX.
// (i, j) is source cell and (x, y) is destination cell.
Pair findLongestPathUtil(int mat[R][C], int i, int j,
int x, int y, bool visited[R][C])
{
// if (i, j) itself is destination, return true
if (i == x && j == y)
{
Pair p = { true, 0 };
return p;
}
// if not a valid cell, return false
if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C ||
mat[i][j] == 0 || visited[i][j])
{
Pair p = { false, INT_MAX };
return p;
}
// include (i, j) in current path i.e.
// set visited(i, j) to true
visited[i][j] = true;
// res stores longest path from current cell (i, j) to
// destination cell (x, y)
int res = INT_MIN;
// go left from current cell
Pair sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i, j - 1, x, y, visited);
// if destination can be reached on going left from current
// cell, update res
if (sol.found)
res = max(res, sol.value);
// go right from current cell
sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i, j + 1, x, y, visited);
// if destination can be reached on going right from current
// cell, update res
if (sol.found)
res = max(res, sol.value);
// go up from current cell
sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i - 1, j, x, y, visited);
// if destination can be reached on going up from current
// cell, update res
if (sol.found)
res = max(res, sol.value);
// go down from current cell
sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i + 1, j, x, y, visited);
// if destination can be reached on going down from current
// cell, update res
if (sol.found)
res = max(res, sol.value);
// Backtrack
visited[i][j] = false;
// if destination can be reached from current cell,
// return true
if (res != INT_MIN)
{
Pair p = { true, 1 + res };
return p;
}
// if destination can't be reached from current cell,
// return false
else
{
Pair p = { false, INT_MAX };
return p;
}
}
// A wrapper function over findLongestPathUtil()
void findLongestPath(int mat[R][C], int i, int j, int x,
int y)
{
// create a boolean matrix to store info about
// cells already visited in current route
bool visited[R][C];
// initailize visited to false
memset(visited, false, sizeof visited);
// find longest route from (i, j) to (x, y) and
// print its maximum cost
Pair p = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i, j, x, y, visited);
if (p.found)
cout << "Length of longest possible route is "
<< p.value;
// If the destination is not reachable
else
cout << "Destination not reachable from given source";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// input matrix with hurdles shown with number 0
int mat[R][C] =
{
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 }
};
// find longest path with source (0, 0) and
// destination (1, 7)
findLongestPath(mat, 0, 0, 1, 7);
return 0;
}
输出:
Length of longest possible route is 24