Linux中Pipe的工作和实现。
先决条件: Linux中的管道
方法: Pipe在Linux中高度使用。管道基本上有两部分,一部分用于书写,另一部分用于读取。因此,采用大小为2的数组。 a [1]用于写入,a [0]用于读取。从管道读取后,程序将在控制台上显示输出。
// C program to implement pipe in Linux
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
// array of 2 size a[0] is for reading
// and a[1] is for writing over a pipe
int a[2];
// opening of pipe using pipe(a)
char buff[10];
if (pipe(a) == -1)
{
perror("pipe"); // error in pipe
exit(1); // exit from the program
}
// writing a string "code" in pipe
write(a[1], "code", 5);
printf("\n");
// reading pipe now buff is equal to "code"
read(a[0], buff, 5);
// it will print "code"
printf("%s", buff);
}
输出 : 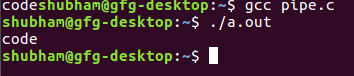
有关pipe()的更多示例
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习和练习问题,请查看《基础知识到高级C的C基础课程》。