队列: 队列是遵循执行操作的先进先出(FIFO)顺序的线性数据结构。这是一种容器适配器,其中元素插入到容器的一端,而从另一端删除。
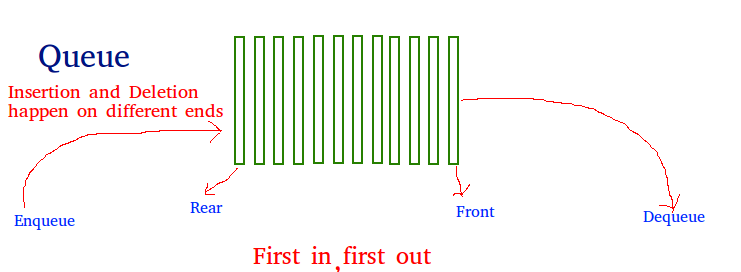
职能:
- empty():测试队列是否为空。
- size():返回队列的无符号int的大小。
- queue :: front()和queue :: back():front()函数返回对队列的第一个元素或最早的元素的引用。 back()函数返回对队列的最后一个或最新元素的引用。
- push(k)和pop():push()函数在队列末尾添加元素“ k”。 pop()函数从队列的开头删除该元素,并将其大小减小1。
- swap():交换两个相同类型但大小相同或不同的队列的元素。
- emplace():用于在队列末尾插入新元素。
句法:
queue q 下面是说明相同内容的程序:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// working of queue
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Declare a queue
queue q;
// Insert elements in the queue
q.push(10);
q.push(5);
q.push(15);
q.push(1);
// Delete elements from the queue
q.pop();
q.pop();
cout << "Elements in Queue are: ";
// Print the element stored
// in queue
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front() << ' ';
// Pop the front element
q.pop();
}
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// working of deque
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Declare a deque
deque dq;
// Insert element in the front
dq.push_front(10);
dq.push_front(5);
dq.push_front(3);
// Delete elements from the the front
dq.pop_front();
dq.pop_front();
// Insert elements in the back
dq.push_back(1);
dq.push_back(50);
dq.push_back(2);
// Delete elements from the the back
dq.pop_back();
dq.pop_back();
cout << "Elements in deque are: ";
// Print the element stored
// in deque
while (!dq.empty()) {
cout << " " << dq.front();
dq.pop_front();
}
return 0;
} 输出:
Elements in Queue are: 15 1
双端队列: Deque是一个序列容器,在两端都有扩展和收缩的能力。它是C++ is中的标准模板库或STL的模板。它与载体相似,但对元素的插入和缺失更有效。不能保证双端队列中的连续存储分配像向量中那样。
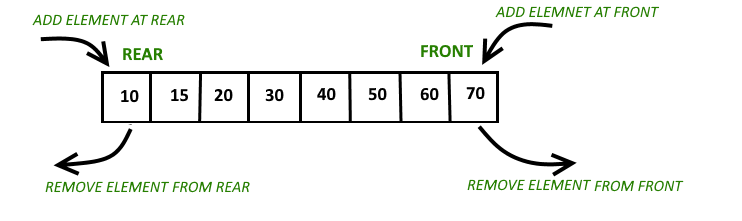
职能:
- max_size():返回双端队列可以包含的最大元素数。
- push_back()和push_front():push_front()从前面将元素推送到双端队列,而push_back()从后面将元素推送到双端队列。
- pop_front()和pop_back():pop_front()函数用于从前面的双端队列弹出元素,而pop_back()函数用于从后面的双端队列弹出元素。
- clear()和delete():clear用于删除双端队列的所有元素,而delete用于删除某些指定的元素。
- insert():通过在指定位置插入元素来增加容器侧。
- resize():根据需要更改元素容器的大小。
- rbegin()和rend():rbegin()指向双端队列的最后一个元素,而rend指向双端队列开始之前的位置。
- at()和swap():at()指向参数中给定元素的位置,swap()用于两个双端队列的交换元素。
- emplace_front()和emplace_back():这两个函数分别用于在双端队列的开始和结尾处在容器中插入新元素。
句法:
deque dq 下面是说明相同内容的程序:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// working of deque
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Declare a deque
deque dq;
// Insert element in the front
dq.push_front(10);
dq.push_front(5);
dq.push_front(3);
// Delete elements from the the front
dq.pop_front();
dq.pop_front();
// Insert elements in the back
dq.push_back(1);
dq.push_back(50);
dq.push_back(2);
// Delete elements from the the back
dq.pop_back();
dq.pop_back();
cout << "Elements in deque are: ";
// Print the element stored
// in deque
while (!dq.empty()) {
cout << " " << dq.front();
dq.pop_front();
}
return 0;
}
输出:
Elements in deque are: 10 1
以下是队列和双端队列之间的表格差异:
| S.No. |
Queue |
Deque |
| 1 | Insertion can be done through the front end only. | Insertion is possible through both ends. |
| 2 | Deletion of elements is possible through the front end only. | Deletion of elements possible through both ends. |
| 3 | Elements can not be accessed through iterators. | Elements can be accessed through iterators. |
| 4 | Implemented as container adaptors. | Implemented generally as some form of a dynamic array. |
| 5 | The stack can not be implemented using a queue. | A stack can be implemented using deque. |
要从最佳影片策划和实践问题去学习,检查了C++基础课程为基础,以先进的C++和C++ STL课程基础加上STL。要完成从学习语言到DS Algo等的更多准备工作,请参阅“完整面试准备课程” 。