r最近邻居是k最近邻居的修改版本。 k最近邻居的问题是k的选择。较小的k,分类器对异常值更敏感。如果k的值很大,则分类器将包括来自其他类别的许多点。正是基于这种逻辑,我们得到了r近邻算法。
直觉:
考虑以下数据作为训练集。 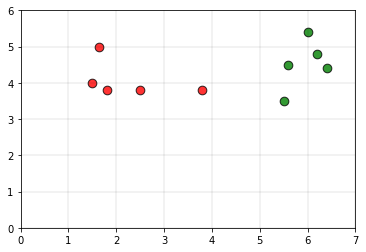
绿色点属于0类,红色点属于1类。
将白点P视为其查询点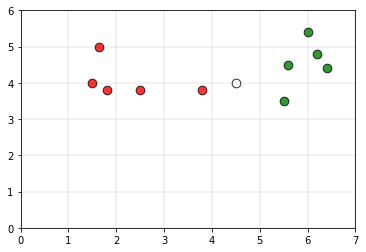
如果我们以圆的半径为2.2单位,并且以点P为圆心绘制一个圆,则绘图如下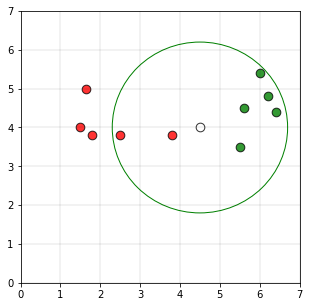
由于圆中属于1类的点数(5个点)大于属于0类的点数(2个点)
算法:
Step 1: Given the point P, determine the sub-set of data that lies in the ball of radius r centered at P,
Br (P) = { Xi ∊ X | dist( P, Xi ) ≤ r }
Step 2: If Br (P) is empty, then output the majority class of the entire data set.
Step 3: If Br (P) is not empty, output the majority class of the data points in it.
r半径邻居算法的实现如下:
C/C++
// C++ program to implement the
// r nearest neighbours algorithm.
#include
using namespace std;
struct Point
{
// Class of point
int val;
// Co-ordinate of point
double x, y;
};
// This function classifies the point p using
// r k neareast neighbour algorithm. It assumes only
// two groups and returns 0 if p belongs to class 0, else
// 1 (belongs to class 1).
int rNN(Point arr[], int n, float r, Point p)
{
// frequency of group 0
int freq1 = 0;
// frequency of group 1
int freq2 = 0;
// Check if the distance is less than r
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if ((sqrt((arr[i].x - p.x) * (arr[i].x - p.x) +
(arr[i].y - p.y) * (arr[i].y - p.y))) <= r)
{
if (arr[i].val == 0)
freq1++;
else if (arr[i].val == 1)
freq2++;
}
}
return (freq1 > freq2 ? 0 : 1);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of data points
int n = 10;
Point arr[n];
arr[0].x = 1.5;
arr[0].y = 4;
arr[0].val = 0;
arr[1].x = 1.8;
arr[1].y = 3.8;
arr[1].val = 0;
arr[2].x = 1.65;
arr[2].y = 5;
arr[2].val = 0;
arr[3].x = 2.5;
arr[3].y = 3.8;
arr[3].val = 0;
arr[4].x = 3.8;
arr[4].y = 3.8;
arr[4].val = 0;
arr[5].x = 5.5;
arr[5].y = 3.5;
arr[5].val = 1;
arr[6].x = 5.6;
arr[6].y = 4.5;
arr[6].val = 1;
arr[7].x = 6;
arr[7].y = 5.4;
arr[7].val = 1;
arr[8].x = 6.2;
arr[8].y = 4.8;
arr[8].val = 1;
arr[9].x = 6.4;
arr[9].y = 4.4;
arr[9].val = 1;
// Query point
Point p;
p.x = 4.5;
p.y = 4;
// Parameter to decide the class of the query point
float r = 2.2;
printf("The value classified to query point"
" is: %d.\n", rNN(arr, n, r, p));
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to implement the
# r nearest neighbours algorithm.
import math
def rNN(points, p, r = 2.2):
'''
This function classifies the point p using
r k neareast neighbour algorithm. It assumes only
two groups and returns 0 if p belongs to class 0, else
1 (belongs to class 1).
Parameters -
points : Dictionary of training points having two
keys - 0 and 1. Each class have a list of
training data points belonging to them
p : A tuple, test data point of form (x, y)
k : radius of the r nearest neighbors
'''
freq1 = 0
freq2 = 0
for group in points:
for feature in points[group]:
if math.sqrt((feature[0]-p[0])**2 +
(feature[1]-p[1])**2) <= r:
if group == 0:
freq1 += 1
elif group == 1:
freq2 += 1
return 0 if freq1>freq2 else 1
# Driver function
def main():
# Dictionary of training points having two keys - 0 and 1
# key 0 have points belong to class 0
# key 1 have points belong to class 1
points = {0:[(1.5, 4), (1.8, 3.8), (1.65, 5), (2.5, 3.8), (3.8, 3.8)],
1:[(5.5, 3.5), (5.6, 4.5), (6, 5.4), (6.2, 4.8), (6.4, 4.4)]}
# query point p(x, y)
p = (4.5, 4)
# Parameter to decide the class of the query point
r = 2.2
print("The value classified to query point is: {}".format(
rNN(points, p, r)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()输出:
The value classified to query point is: 1.
其他技术(例如kd-tree,局部敏感哈希)可用于降低查找邻居的时间复杂度。
应用范围:
该算法可用于识别异常值。如果图案与所选半径内的图案没有任何相似性,则可以将其识别为离群值。