先决条件:数组基础
在C / C++中,简单单词中的多维数组作为数组的数组。多维数组中的数据以表格形式(以行主顺序)存储。以下是声明N维数组的一般形式:
多维数组的语法:
data_type array_name[size1][size2]….[sizeN];
data_type: Type of data to be stored in the array.
Here data_type is valid C/C++ data type
array_name: Name of the array
size1, size2, …, sizeN: Sizes of the dimensions
3-D数组是二维数组的数组:
3D数组的语法:
data_type array_name[x][y][z];
data_type: Type of data to be stored. Valid C/C++ data type.
有关多维和3D数组的更多详细信息,请参阅C++中的多维数组文章。
问题:给定3D数组,任务是使用C++中的new为3D数组动态分配内存。
解决方案:在以下方法中,使用的方法是制作两个2-D数组,每个2-D数组具有3行和4列,并具有以下值。
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24X = No of 2D arrays.
Y = No of rows of each 2D array.
Z = No of columns of each 2D array.
方法1:使用单个指针–在这种方法中,分配了一个大小为x * y * z的存储块,然后使用指针算法访问这些存储块。以下是相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to dynamically allocate
// the memory for 3D array in C++
// using new operator
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Dimensions of the 3D array
int x = 2, y = 3, z = 4;
int count = 0;
// Allocate memory blocks
// of size x*y*z
int* a = new int[x * y * z];
// Traverse the 3D array
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Assign values to the
// memory blocks created
*(a + i * y * z + j * z + k) = ++count;
}
}
}
// Traverse the 3D array again
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Print values of the
// memory blocks created
cout << *(a + i * y * z + j * z + k) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Deallocate memory
delete[] a;
return 0;
} C++
// C++ program to dynamically allocate
// the memory for 3D array in C++
// using new operator
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Dimensions of the 3D array
int x = 2, y = 3, z = 4;
int count = 0;
// Allocate memory blocks of size
// x i.e., no of 2D Arrays
int*** a = new int**[x];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
// Allocate memory blocks for
// rows of each 2D array
a[i] = new int*[y];
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
// Allocate memory blocks for
// columns of each 2D array
a[i][j] = new int[z];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Assign values to the
// memory blocks created
a[i][j][k] = ++count;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Print values of the
// memory blocks created
cout << a[i][j][k] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Deallocate memory
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
delete[] a[i][j];
}
delete[] a[i];
}
delete[] a;
return 0;
} 1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24方法2:使用三重指针–下图说明了该概念:
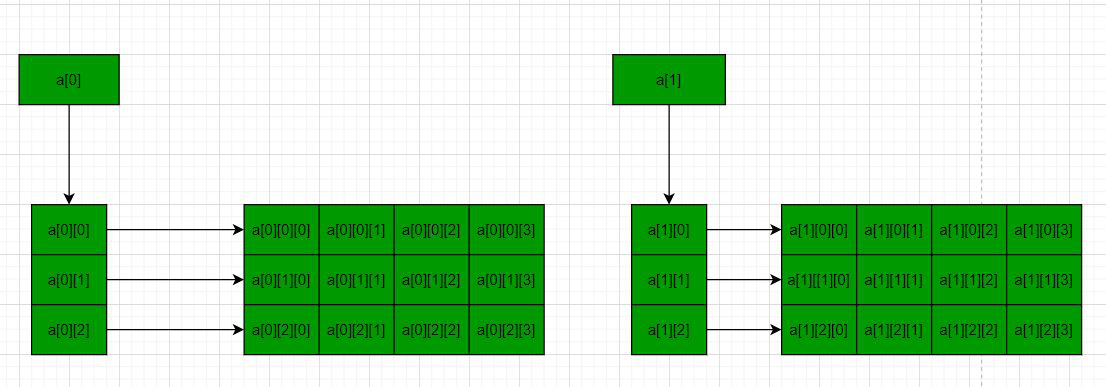
以下是相同的程序:
C++
// C++ program to dynamically allocate
// the memory for 3D array in C++
// using new operator
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Dimensions of the 3D array
int x = 2, y = 3, z = 4;
int count = 0;
// Allocate memory blocks of size
// x i.e., no of 2D Arrays
int*** a = new int**[x];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
// Allocate memory blocks for
// rows of each 2D array
a[i] = new int*[y];
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
// Allocate memory blocks for
// columns of each 2D array
a[i][j] = new int[z];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Assign values to the
// memory blocks created
a[i][j][k] = ++count;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Print values of the
// memory blocks created
cout << a[i][j][k] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Deallocate memory
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
delete[] a[i][j];
}
delete[] a[i];
}
delete[] a;
return 0;
}
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。