C++的传统是每三年以标准形式引入新的改进和功能。随着2017年发布的最新标准C++ 17,C++ 20将成为最新标准。下面是C++ 20中的一些主要功能:
- C++概念库
- 三向比较
- 地图包含
- 基于范围的for循环
- 新标识符(导入,模块)
- 日历和时区库
- std ::字符串函数
- 数组有界/无界
- std :: to_array
- 可能和不太可能的属性
C++概念库:
概念库提供了基本库概念的定义,这些概念可用于执行模板参数的编译时验证并基于类型的属性执行函数分派。这些概念为程序中的教育推理提供了基础。
本节包含大约15个概念,这些概念应该是不言自明的。这些概念表示类型,类型分类和基本类型属性之间的关系。
Defined in header
Defined in namespace std
- 整数:指定类型为整数类型。
- signed_integral :指定类型是已签名的整数类型。
- unsigned_integral :指定类型是无符号的整数类型。
- float_point :指定类型为浮点类型。
- same_as :指定一个类型与另一个类型相同。
- named_from :指定一个类型是从另一个类型派生的。
- convertible_to :指定一种类型可以隐式转换为另一种类型。
- common_with :指定两种类型共享一个公共类型。
句法:
template
concept integral = is_integral_v
template
concept signed_integral = integral
template
concept unsigned_integral = integral
template
concept floating_point = is_floating_point_v
三向比较:
三路比较运算符表达式的形式为:
lhs <=> rhs
飞船运算符的模样<=>和其官方C++的名字是3路比较运算符。之所以这样称呼,是因为它用于比较两个对象,然后将该结果与0进行比较:
(x <=> y) < 0 is true if x < y
(x <=> y) > 0 is true if x > y
(x <=> y) == 0 is true if x and y are equal/equivalent.
三路比较运算符不仅让快递对象,但也关系的特性之间的排序和平等。太空船运算符是C++的一个非常受欢迎的功能。它使我们在如何界定我们的关系更加表现,让我们写更少的代码来定义它们,并避免了在其他方面有手动执行一些比较运算符的一些性能缺陷。
程序1:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int a = 91, b = 110;
auto ans1 = a <= > b;
if (ans1 < 0) {
cout << "a < b\n";
}
else if (ans1 == 0) {
cout << "a == b\n";
}
else if (ans1 > 0) {
cout << "a > b\n";
}
vector v1{ 3, 6, 9 };
vector v2{ 3, 6, 9 };
auto ans2 = v1 <= > v2;
if (ans2 < 0) {
cout << "v1 < v2\n";
}
else if (ans2 == 0) {
cout << "v1 == v2\n";
}
else if (ans2 > 0) {
cout << "v1 > v2\n";
}
cout << endl;
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
#include C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
for (std::vector v{ 1, 2, 3 }; auto& e : v) {
std::cout << e;
}
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
// helloworld.cpp module declaration
export module helloworld;
// Import declaration
import;
// Export declaration
export void hello()
{
std::cout << "Hello world!\n";
} C++
// main.cpp import declaration
import helloworld;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
hello();
}C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
std::string str = "GeeksforGeeks";
// Check string str starts_with Geeks
if (str.starts_with("Geeks")) {
std::cout << "true" << endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "false" << endl;
}
// Check string str ends_with Geeks
if (str.ends_with("for")) {
std::cout << "true" << endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "false" << endl;
}
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
#include
// Class A
class A {
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Returns std::array
std::to_array("Geeks");
std::to_array(
{ 1, 2, 3 });
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
// Returns std::array`
std::to_array(a);
} C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 40;
[[likely]] if (n < 100) { cout << n * 2; }
[[unlikely]] while (n > 100)
{
n = n / 2;
cout << n << endl;
}
n = 500;
[[likely]] if (n < 100) { cout << n * 2; }
[[unlikely]] while (n > 100)
{
n = n / 2;
cout << n << endl;
}
return 0;
} 输出: 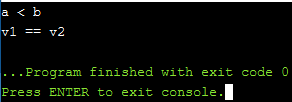
地图/集包含:
句法:
std::map
std::set
它提供了一种更简单的方法来检查C++ 20中的关联容器(集合或映射)中是否存在键。它取代了find内置函数。
程式2:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
#include 输出: 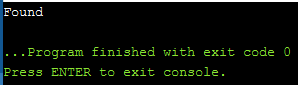
具有初始化的基于范围的for循环:
在C++ 17中更改了基于范围的for循环,以允许begin()和end()表达式具有不同的类型,而在C++ 20中,引入了一个初始化语句来初始化循环作用域中的变量。它允许我们初始化希望在范围声明本身中循环通过的容器。
句法:
for (init-statement(optional) range_declaration : range_expression)
{
/* loop body */}
程序3:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
for (std::vector v{ 1, 2, 3 }; auto& e : v) {
std::cout << e;
}
}
输出: 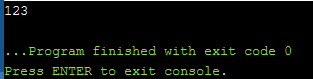
新的标识符(导入,模块) :
- 模块有助于将大量代码分成逻辑部分。模块保证了更快的编译时间,宏的隔离,并使头文件变得多余。
- 它们表达了代码的逻辑结构,并有助于摆脱难看的宏解决方法。模块与名称空间正交。导入模块的顺序没有区别。
- 模块使您能够表达代码的逻辑结构。您可以明确指定不应该导出的名称。此外,您可以将几个模块捆绑成一个更大的模块,并且可以将它们作为逻辑包提供。
- 使用模块,现在无需将源代码分为接口和实现部分。
计划4:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
// helloworld.cpp module declaration
export module helloworld;
// Import declaration
import;
// Export declaration
export void hello()
{
std::cout << "Hello world!\n";
}
C++
// main.cpp import declaration
import helloworld;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
hello();
}
输出: 
日历和时区库:
C++ 11/14的chrono库通过日历和时区功能进行了扩展。日历由各种类型组成,分别代表一年,一个月,一个工作日中的某一天或一个月的第n个工作日。这些基本类型可以与复杂类型组合,例如year_month , year_month_day , year_month_day_last , years_month_weekday和year_month_weekday_last 。为了方便指定时间点,运算符“ /”已重载。另外,我们将获得C++ 20新字面量:d代表一天,y代表一年。
由于扩展了chrono库,因此易于实现以下功能:
- 获取一个月的最后一天。
- 获取两个日期之间的天数。
- 在不同时区打印当前时间。
句法:
Defined in header
Defined in namespace std::chrono
例子:
auto date1 = 2020y/sep/8;
auto date2 = 21d/oct/2018;
auto date3 = jan/27/2019;
std ::字符串函数:
ends_with (“后缀”):检查字符串是否以给定的后缀结尾。
starts_with (“前缀”):检查字符串视图是否以给定的前缀开头。
计划5:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
std::string str = "GeeksforGeeks";
// Check string str starts_with Geeks
if (str.starts_with("Geeks")) {
std::cout << "true" << endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "false" << endl;
}
// Check string str ends_with Geeks
if (str.ends_with("for")) {
std::cout << "true" << endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "false" << endl;
}
}
输出: 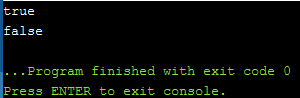
数组有界/无界:
- 如果T是未知范围的数组类型,它将检查T是否为未知范围的数组类型,并提供等于true的成员常量值。否则,值等于false 。
- 如果T是已知界限的数组类型,它将检查T是否为已知界限的数组类型,并提供等于true的成员常量值。否则,值等于false 。
计划6:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
#include
// Class A
class A {
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_unbounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
std::cout << std::is_bounded_array_v << '\n';
}
输出: 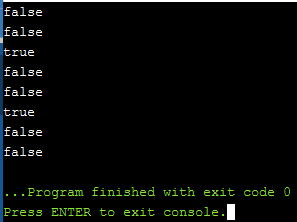
std :: to_array :
它将给定的array /“类似于数组”对象转换为std :: array 。它从一维内置数组a创建一个std :: array 。 std :: array的元素是从a的相应元素进行复制初始化的。不支持复制或移动多维内置数组。
计划7:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Returns std::array
std::to_array("Geeks");
std::to_array(
{ 1, 2, 3 });
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
// Returns std::array`
std::to_array(a);
}
可能和不太可能的属性:
它向优化器提供了一个提示,即标记的语句可能/不太可能执行其主体。这两个属性都可以为优化程序提供提示,无论执行路径是可能的还是不可行的。
计划8:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the
// above concepts
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 40;
[[likely]] if (n < 100) { cout << n * 2; }
[[unlikely]] while (n > 100)
{
n = n / 2;
cout << n << endl;
}
n = 500;
[[likely]] if (n < 100) { cout << n * 2; }
[[unlikely]] while (n > 100)
{
n = n / 2;
cout << n << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出: 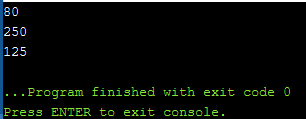
参考: C++ 20,CPP参考。