先决条件: C++中的多维数组, Java的多维数组
多维数组:
多维数组是存储多个元素的数组的表格表示形式。这些维可以是一维数组,二维数组等。多维数组在C++和Java都可用,但是它们的实现和某些属性是不同的。
在C / C++中的实现:
在C++中,多维数组在内部创建为巨型线性数组。 C++语法将该线性内存块抽象为2或3维行为,从而使程序员易于使用。
例子:
尺寸为2行x 3列{{9,45,51},{5,25,6}}的2D数组的实现如下(假设Integer占用4个字节):

因此,特定索引处的内部元素的内部公式为:
arr[rowIndex][colIndex] = arr + (rowIndex * noOfCols * sizeOfDataType) + coLIndex * sizeOfDataType
假设基址为3000 。然后arr [1] [1] = 3000 +(1 * 3 * 4)+ 1 * 4 = 3000 + 12 + 4 = 3016 。
由于这样的实现,每一行的列数必须相等,并且为了正确访问元素,在声明时必须指定列大小。
下面是C++中多维数组的实现:
C++
// C++ program for multidimention array
// implementation
#include
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Create a 2d integer array,
// dimensions: 3rows X 5cols
int arr[3][5] = {
{ 23, 56, 34, 52, 63 },
{ 40, 20, 96, 43, 97 },
{ 75, 51, 10, 82, 43 }
};
// Traversing of 2D array
cout << "Printing entire 2d array: "
<< endl;
// Iterate over the rows
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// Iterate over the cols
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cout << "arr[" << i << "][" << j
<< "]:" << arr[i][j]
<< " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for multidimensional
// array implementation
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a 2D integer array
// dimensions: 3rows X 5cols
int[][] arr = {
{ 23, 56, 34, 52, 63 },
{ 40, 20, 96, 43, 97 },
{ 75, 51, 10, 82, 43 }
};
// Traversing the 2D array
System.out.println("Printing entire 2d array: ");
// Iterate over the rows
for (int i = 0;
i < arr.length; i++) {
// Iterate over the cols
for (int j = 0;
j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(
"arr[" + i + "][" + j
+ "]:" + arr[i][j]
+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
// Reassigning arr[2] to another
// array
// This is not possible in 2D
// arrays in C++, instead of
// there is array of pointers
arr[2] = new int[] { 82, 53, 64,
12, 45, 3 };
// Traversing the array again
System.out.println(
"Printing entire 2d array "
+ "afer modification: ");
// Iterate over the rows
for (int i = 0;
i < arr.length; i++) {
// Iterate over the cols
for (int j = 0;
j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(
"arr[" + i + "][" + j
+ "]:" + arr[i][j]
+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}Printing entire 2d array:
arr[0][0]:23 arr[0][1]:56 arr[0][2]:34 arr[0][3]:52 arr[0][4]:63
arr[1][0]:40 arr[1][1]:20 arr[1][2]:96 arr[1][3]:43 arr[1][4]:97
arr[2][0]:75 arr[2][1]:51 arr[2][2]:10 arr[2][3]:82 arr[2][4]:43
用Java实现:
在Java,多维数组被实现为数组的数组,其中基本数组的每个索引均指的是一个完全不同的数组。因此, arr [rowIndex]返回整个一维数组,而arr [rowIndex] [coLIndex]返回该一维数组中索引为coLIndex的元素。
例子:
A 2D array of dimensions 3 rows x 5 cols is implemented as follows:
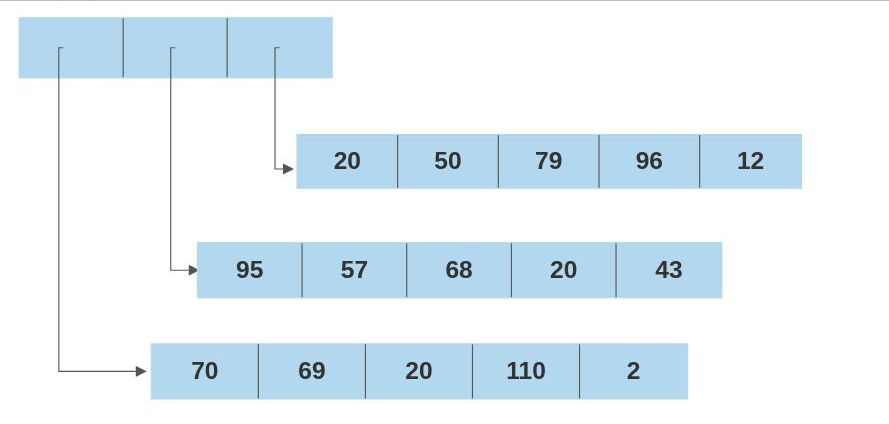
Because of this structure, It is possible to have 2D arrays with different column sizes (even null values) in Java.

以下是Java多维数组的实现:
Java
// Java program for multidimensional
// array implementation
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a 2D integer array
// dimensions: 3rows X 5cols
int[][] arr = {
{ 23, 56, 34, 52, 63 },
{ 40, 20, 96, 43, 97 },
{ 75, 51, 10, 82, 43 }
};
// Traversing the 2D array
System.out.println("Printing entire 2d array: ");
// Iterate over the rows
for (int i = 0;
i < arr.length; i++) {
// Iterate over the cols
for (int j = 0;
j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(
"arr[" + i + "][" + j
+ "]:" + arr[i][j]
+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
// Reassigning arr[2] to another
// array
// This is not possible in 2D
// arrays in C++, instead of
// there is array of pointers
arr[2] = new int[] { 82, 53, 64,
12, 45, 3 };
// Traversing the array again
System.out.println(
"Printing entire 2d array "
+ "afer modification: ");
// Iterate over the rows
for (int i = 0;
i < arr.length; i++) {
// Iterate over the cols
for (int j = 0;
j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(
"arr[" + i + "][" + j
+ "]:" + arr[i][j]
+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Printing entire 2d array:
arr[0][0]:23 arr[0][1]:56 arr[0][2]:34 arr[0][3]:52 arr[0][4]:63
arr[1][0]:40 arr[1][1]:20 arr[1][2]:96 arr[1][3]:43 arr[1][4]:97
arr[2][0]:75 arr[2][1]:51 arr[2][2]:10 arr[2][3]:82 arr[2][4]:43
Printing entire 2d array afer modification:
arr[0][0]:23 arr[0][1]:56 arr[0][2]:34 arr[0][3]:52 arr[0][4]:63
arr[1][0]:40 arr[1][1]:20 arr[1][2]:96 arr[1][3]:43 arr[1][4]:97
arr[2][0]:82 arr[2][1]:53 arr[2][2]:64 arr[2][3]:12 arr[2][4]:45 arr[2][5]:3